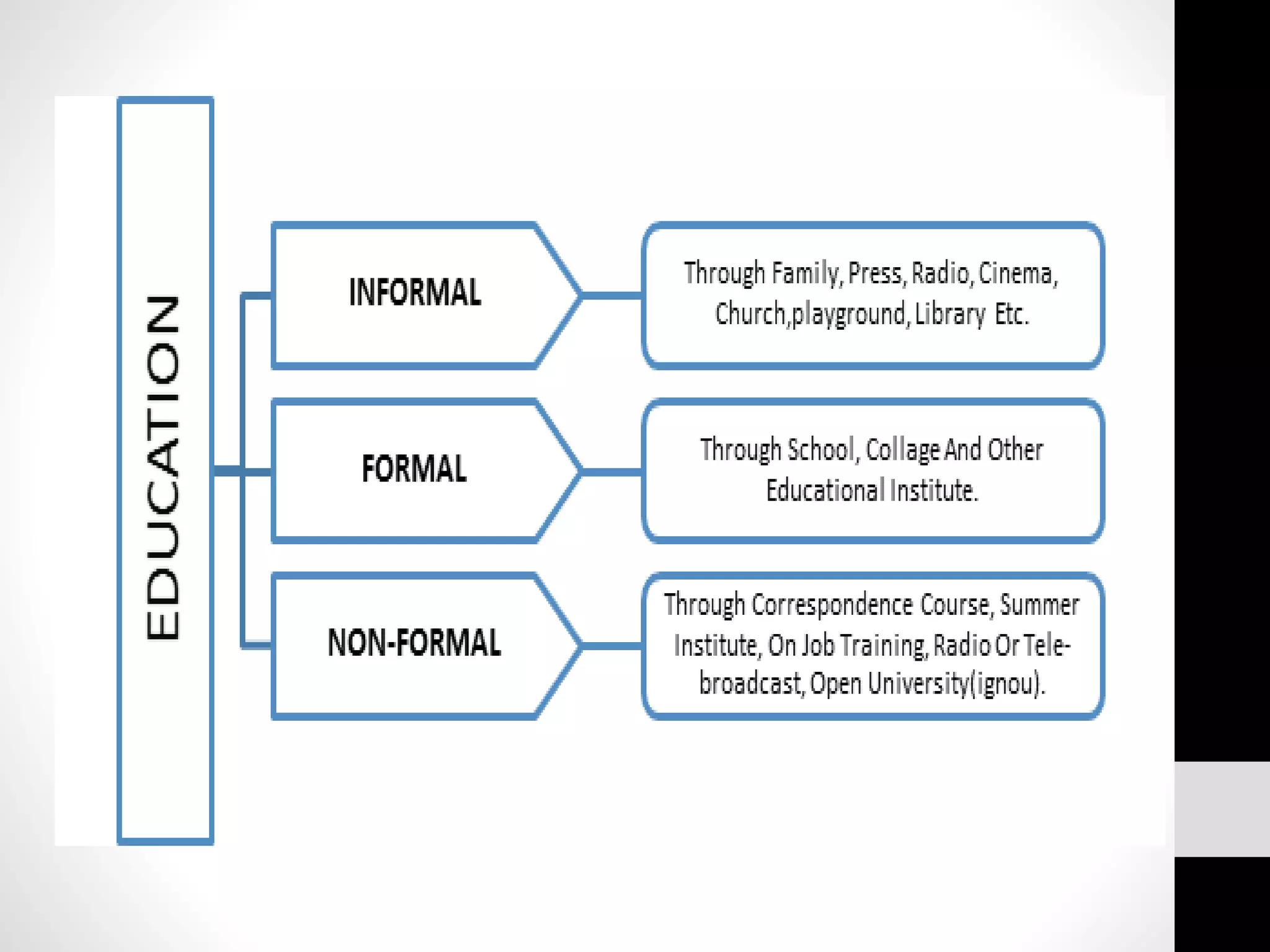
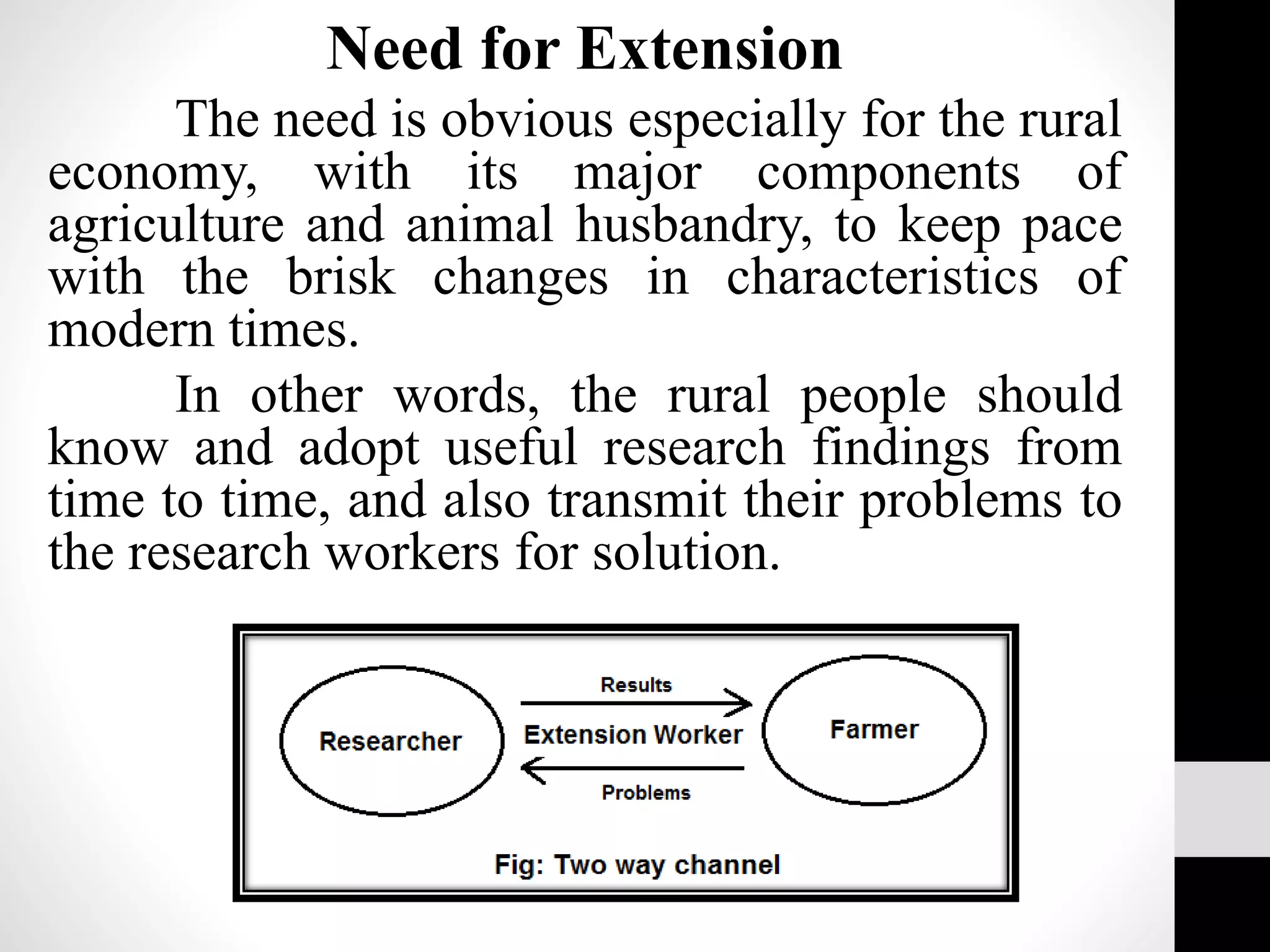
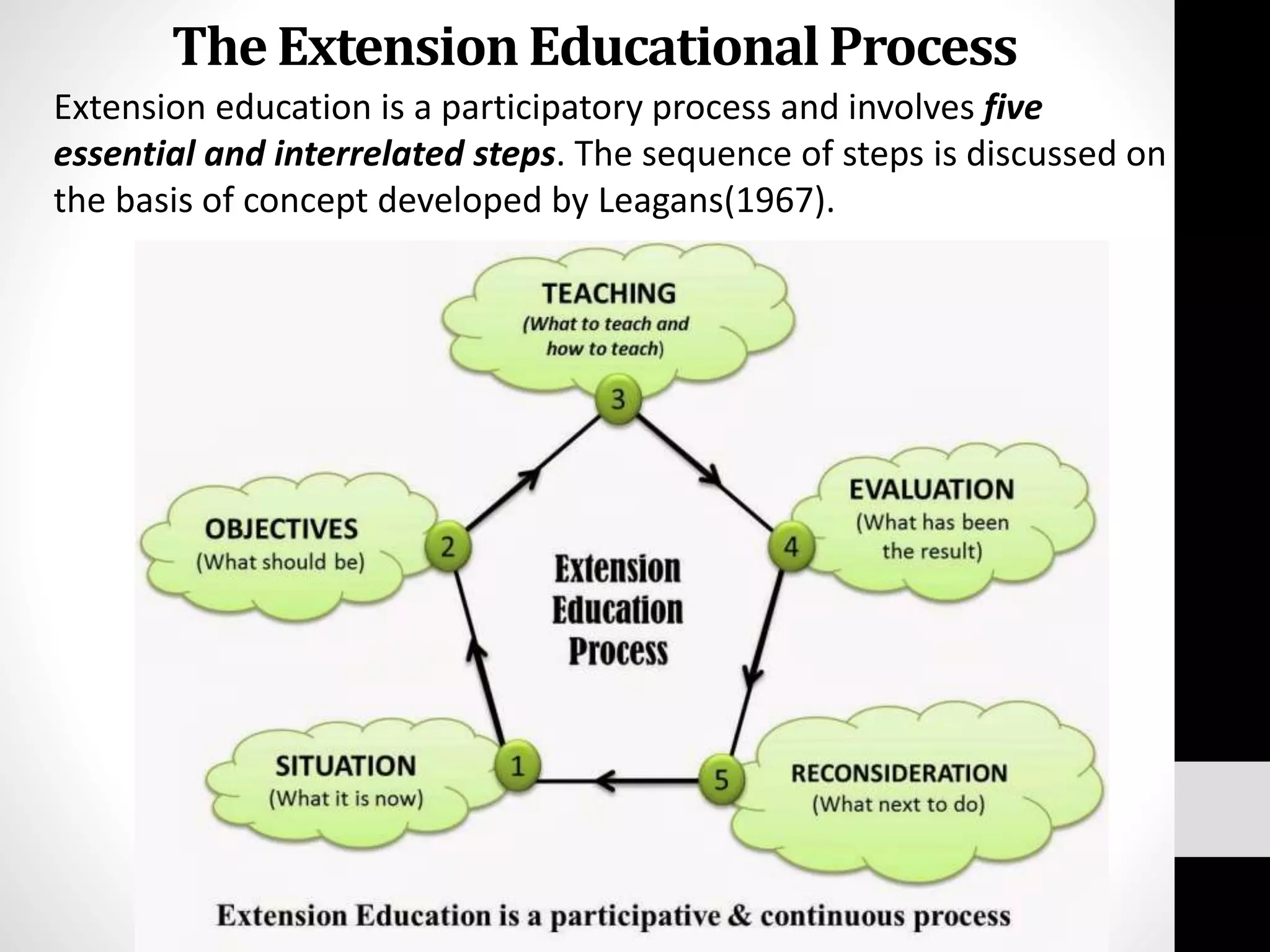
Extension education means stretching education beyond formal schools and colleges into rural areas. It is a type of non-formal education that uses practical, problem-oriented approaches with heterogeneous audiences. The history of extension began in England in 1866 and the terms "extension" and "extension education" were first coined there in the late 1800s. The objectives of extension are to help people discover and analyze problems, develop leadership to solve issues, disseminate research findings, and provide feedback to improve solutions. The extension process involves five interrelated steps of planning, implementation, evaluation and feedback.