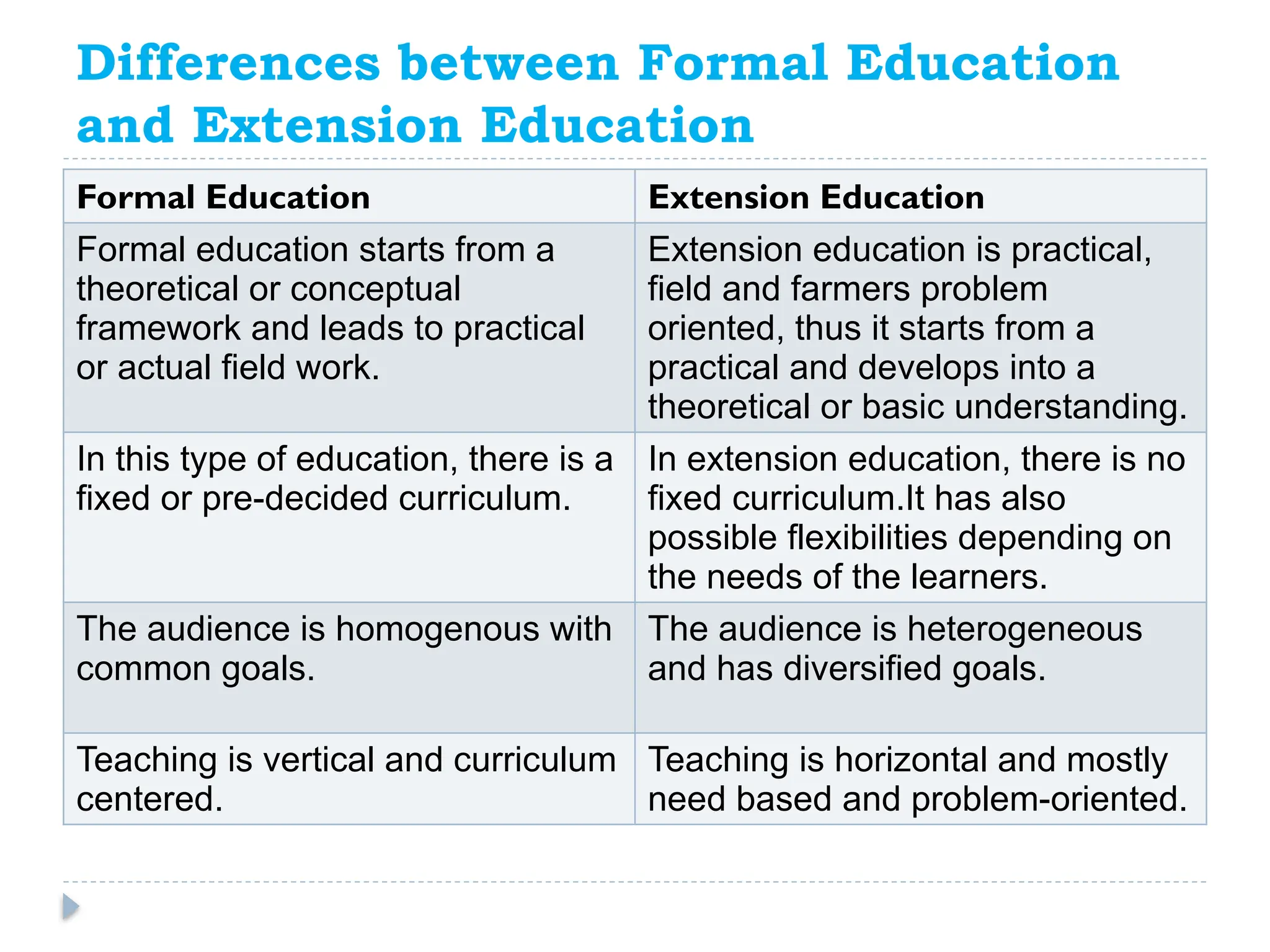
The document provides an introduction to agricultural extension, emphasizing its meaning, philosophy, and objectives. It contrasts extension education with formal education, highlighting its practical, voluntary nature and focus on problem-solving. The philosophy of extension education is rooted in empowering rural individuals and communities through collaborative learning and self-help initiatives.