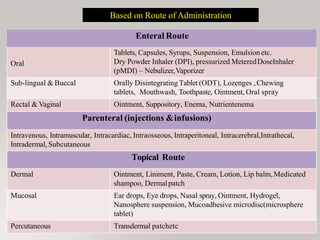
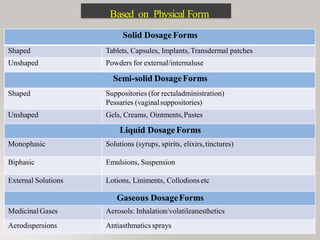
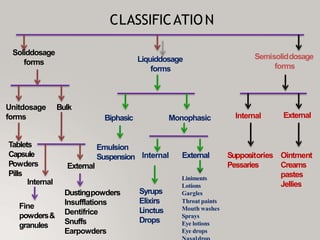
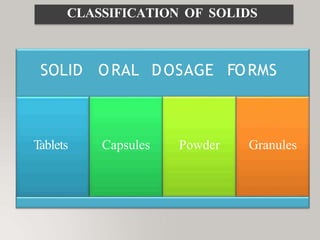
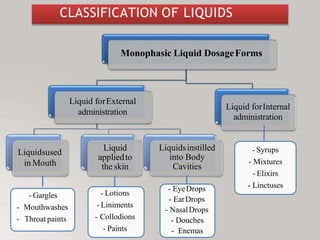
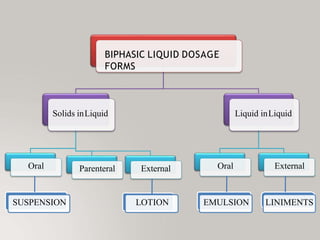
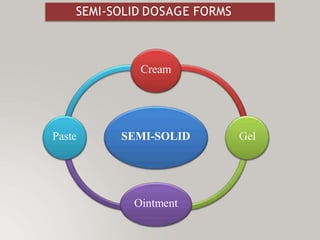
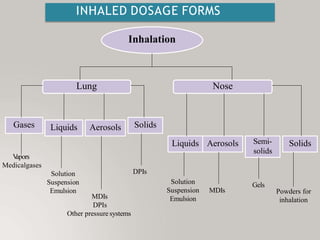
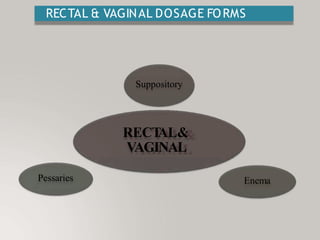
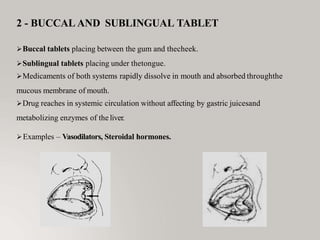
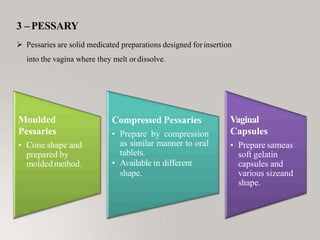
This document discusses different types of dosage forms used to deliver drugs to the body. It begins with an introduction and overview of dosage forms. It then covers the classification and examples of solid, liquid, and semi-solid dosage forms. Solid dosage forms discussed include tablets, capsules, powders, and others. Liquid forms include solutions, emulsions, suspensions and others. Semi-solid forms include creams, ointments, gels and suppositories. The document provides details on the composition, properties and examples of various oral and other administration route dosage forms.