This document provides an overview of basic electrical engineering concepts including:
- An introduction covering India's electrical energy scenario, power system layout, transmission methods, energy sources and electrical safety.
- The importance of electricity including its bulk production capabilities, transportability, ease of control, speed and potential for conversion and storage.
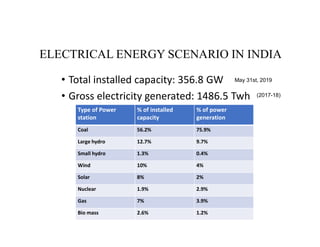
- Key details on India's electrical energy scenario such as total installed capacity, consumption levels in agriculture, and generation sources.
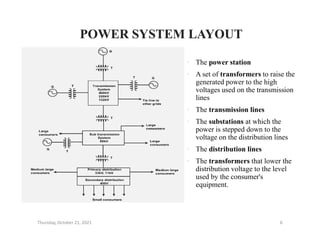
- A breakdown of India's power system layout from generation stations to transmission lines to substations and distribution lines.