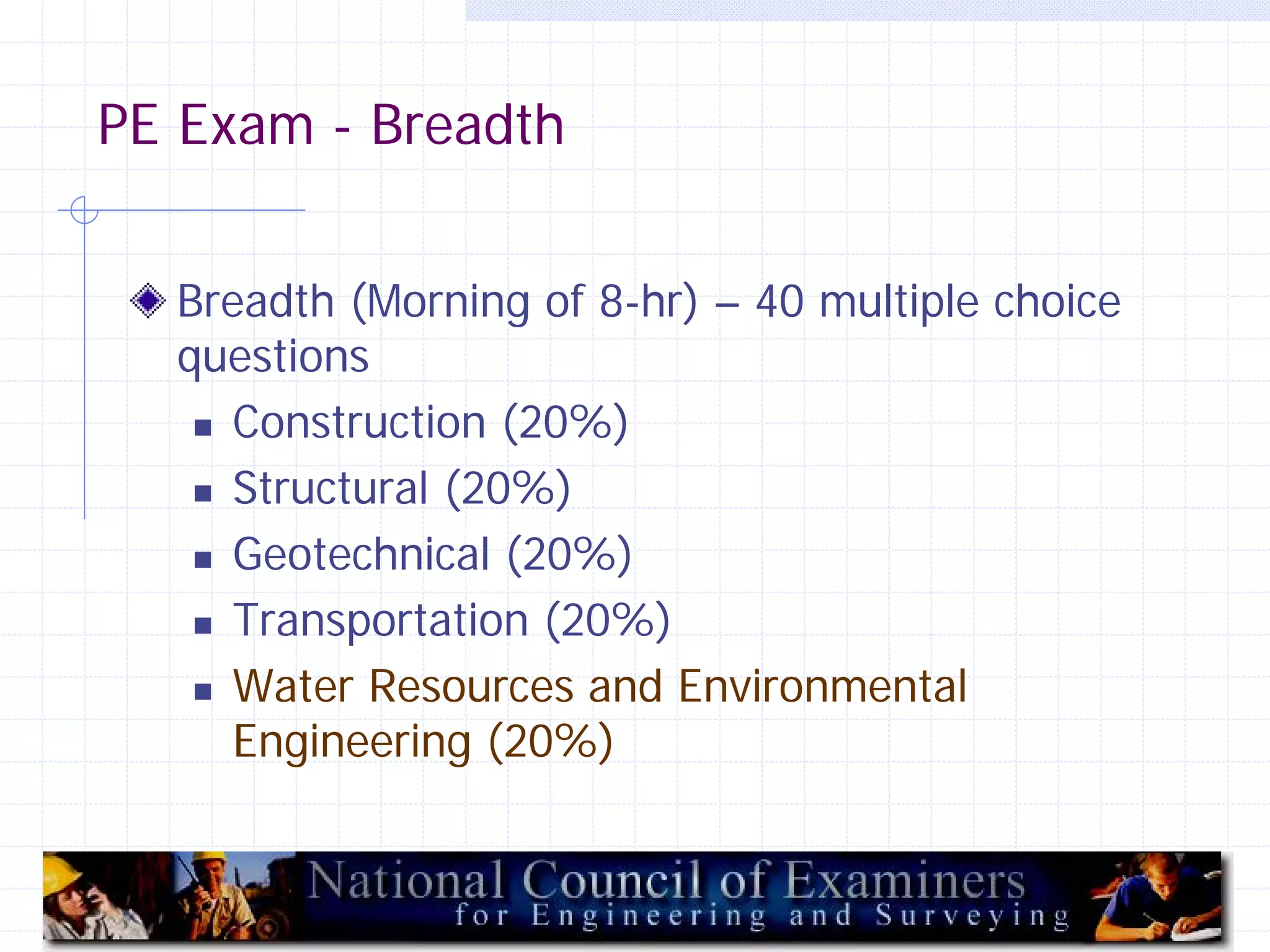
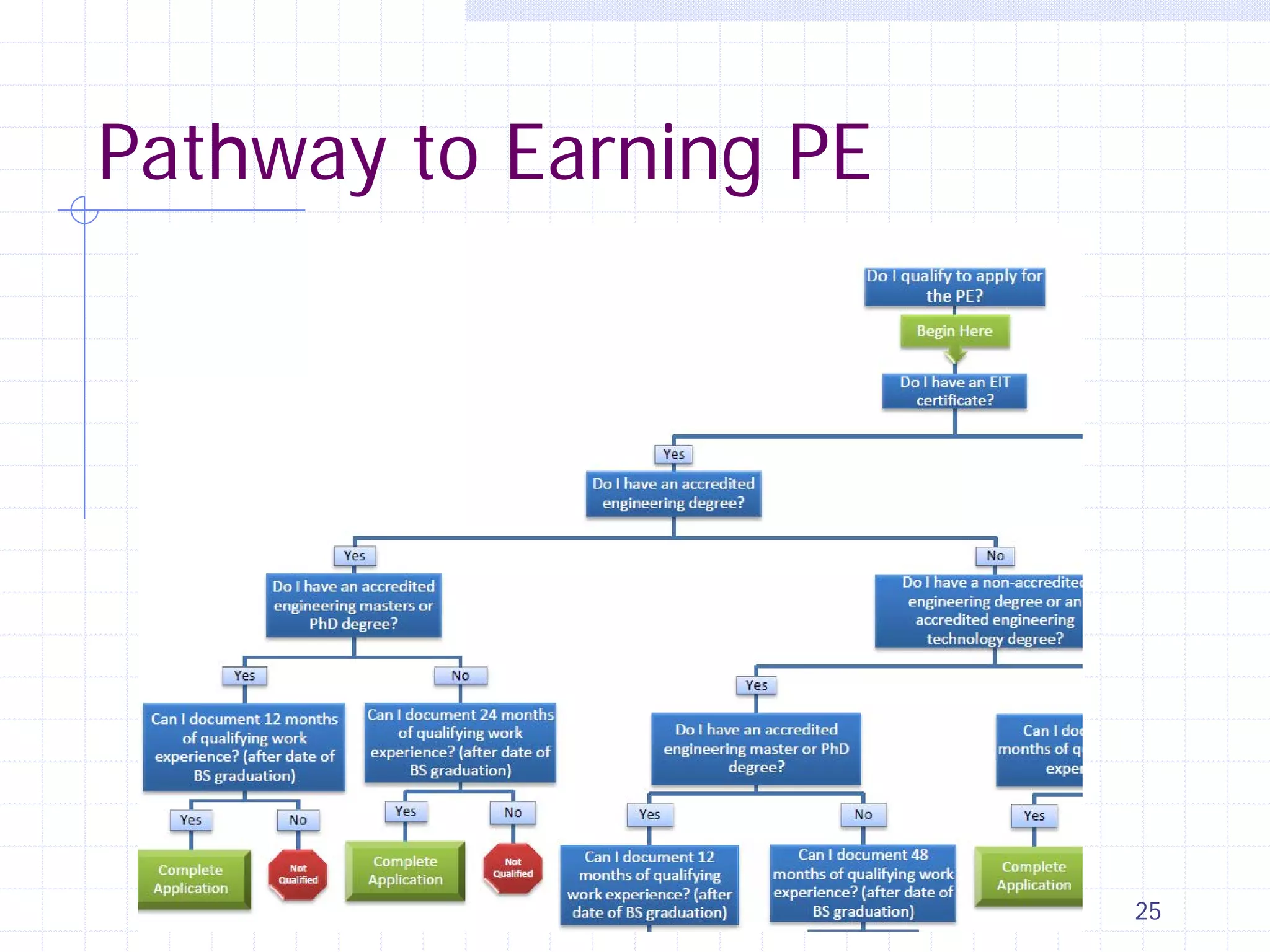
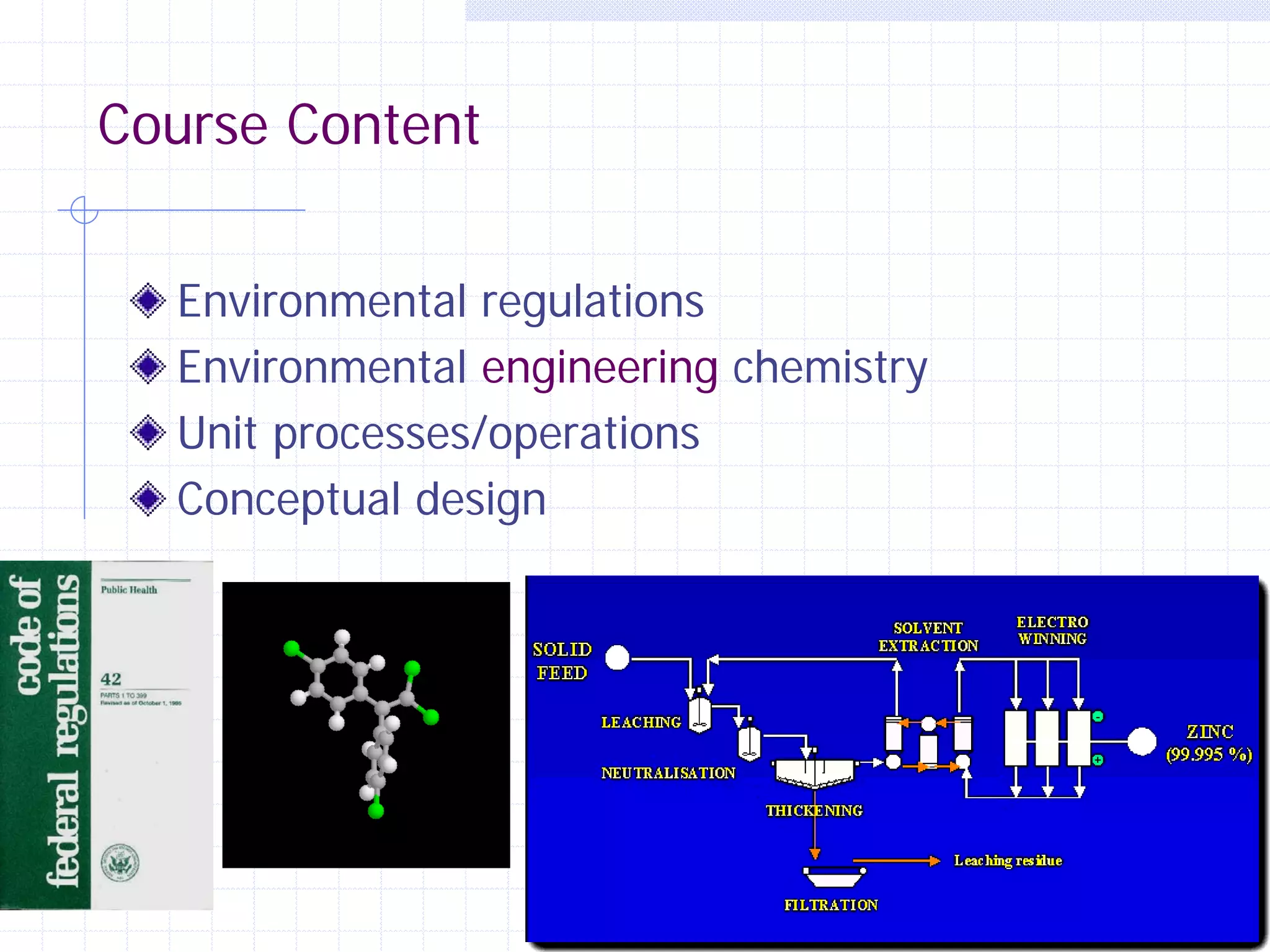
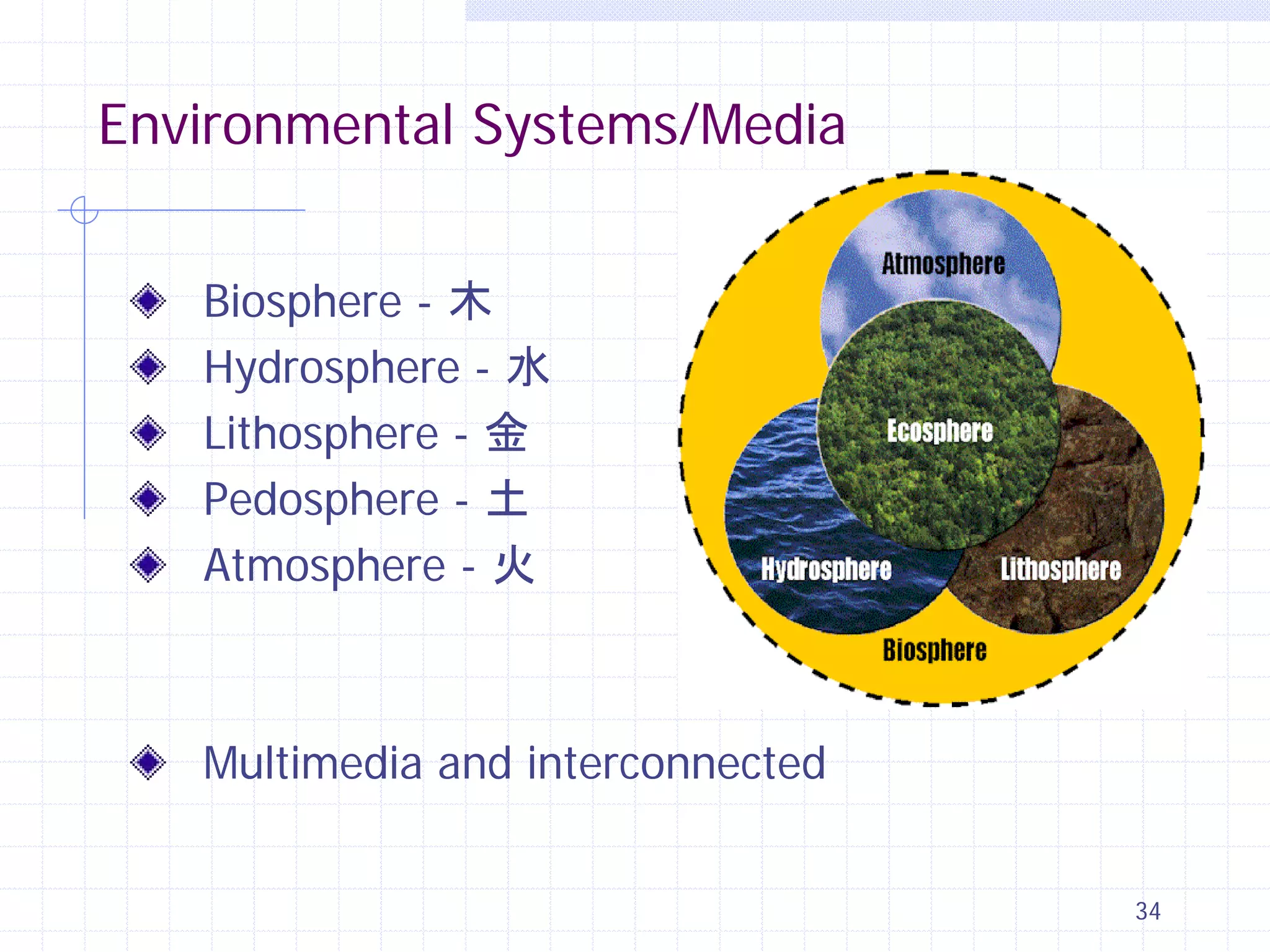
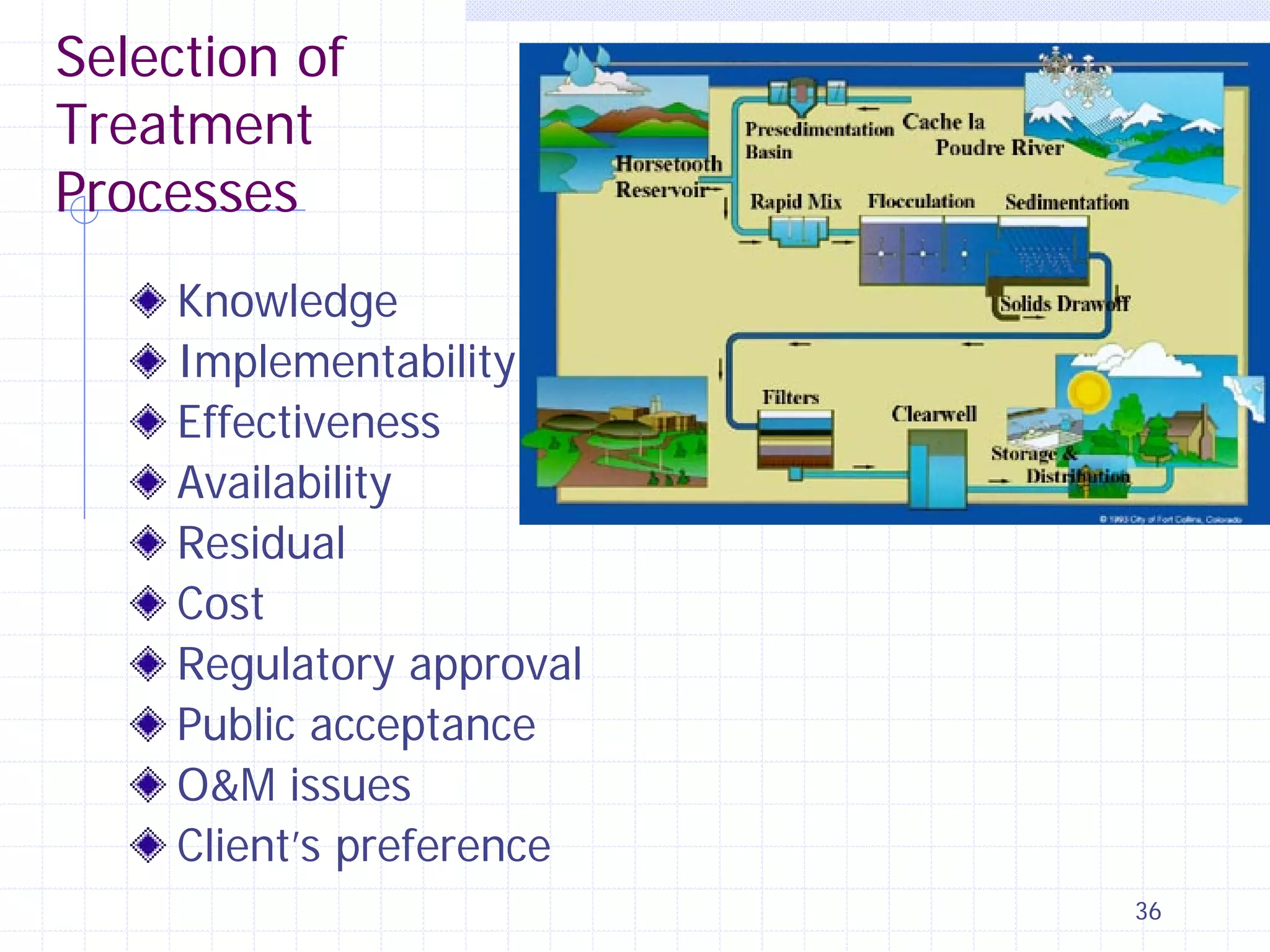
This document provides an overview of CE 441 - Introduction to Environmental Engineering, taught by Dr. Jian Peng at California State University, Fullerton. The course covers fundamental concepts in environmental engineering, including water and wastewater treatment processes, air pollution control, and environmental regulations. It aims to help students understand key environmental topics and prepare for engineering licensing exams. The document outlines the course goals, schedule, assignments, grading policy, and guest speakers.