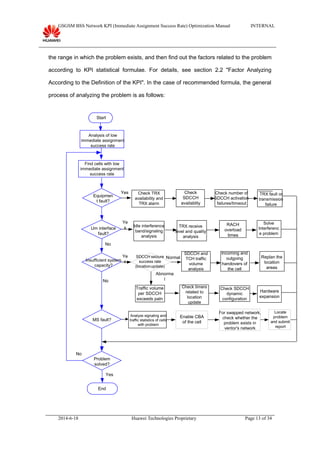
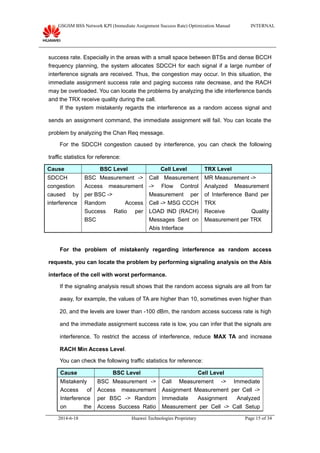
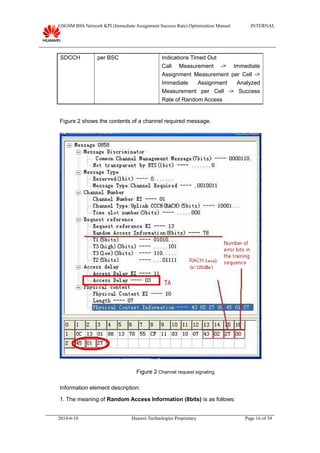
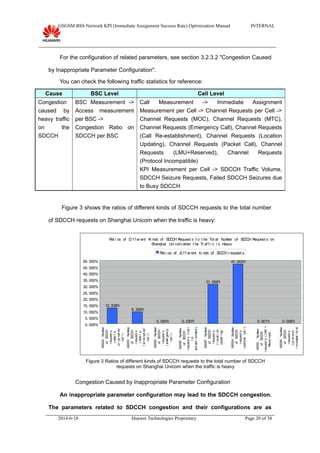
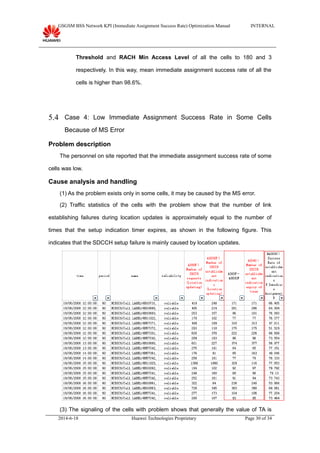
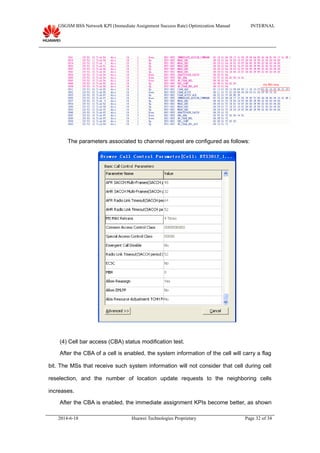
This document provides guidance on optimizing the immediate assignment success rate KPI in GSM networks. It defines immediate assignment success rate, outlines the key factors that influence it such as SDCCH congestion and interface issues. The document also describes methods for analyzing problems, typical cases, and information needed on-site.