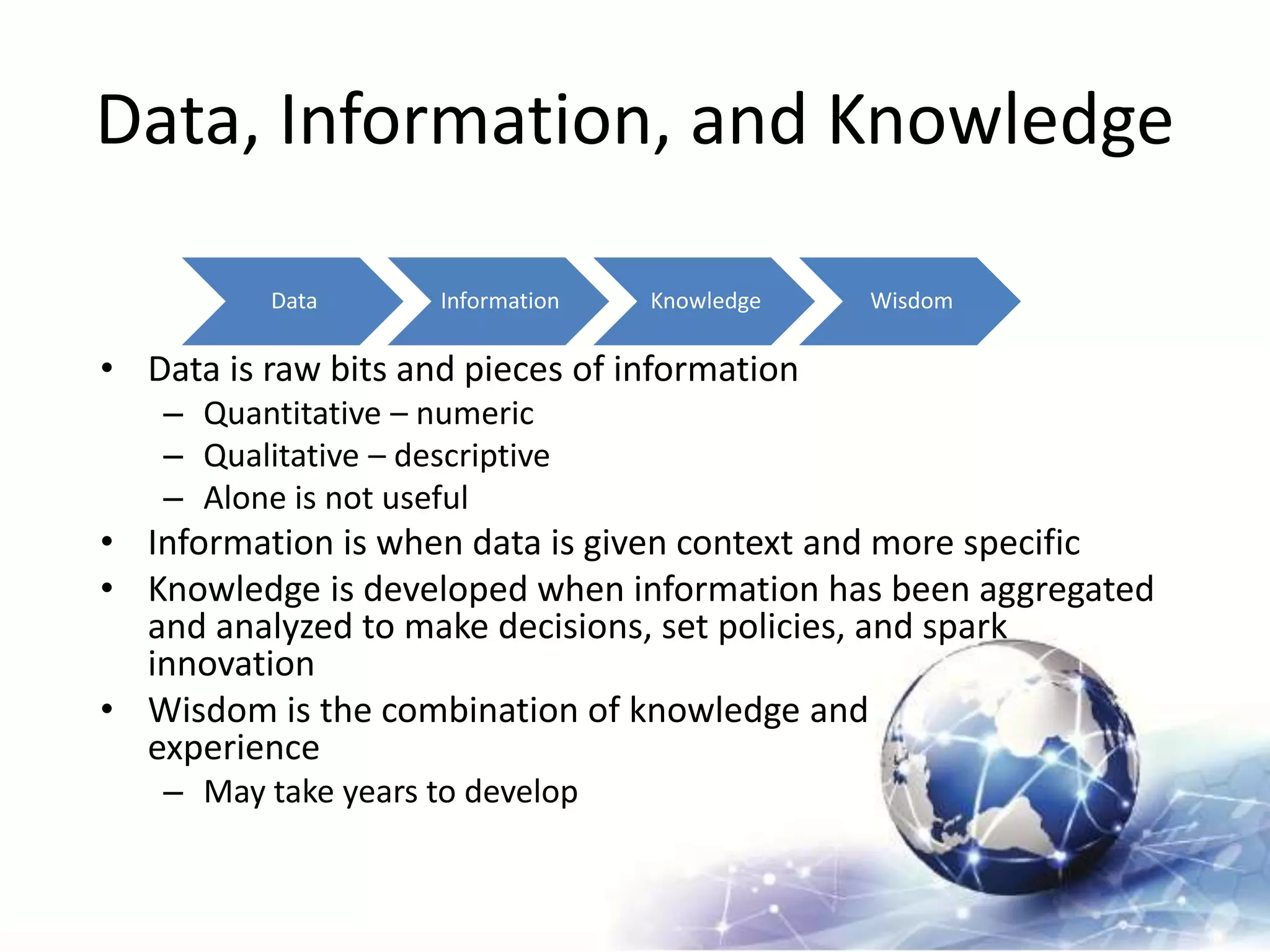
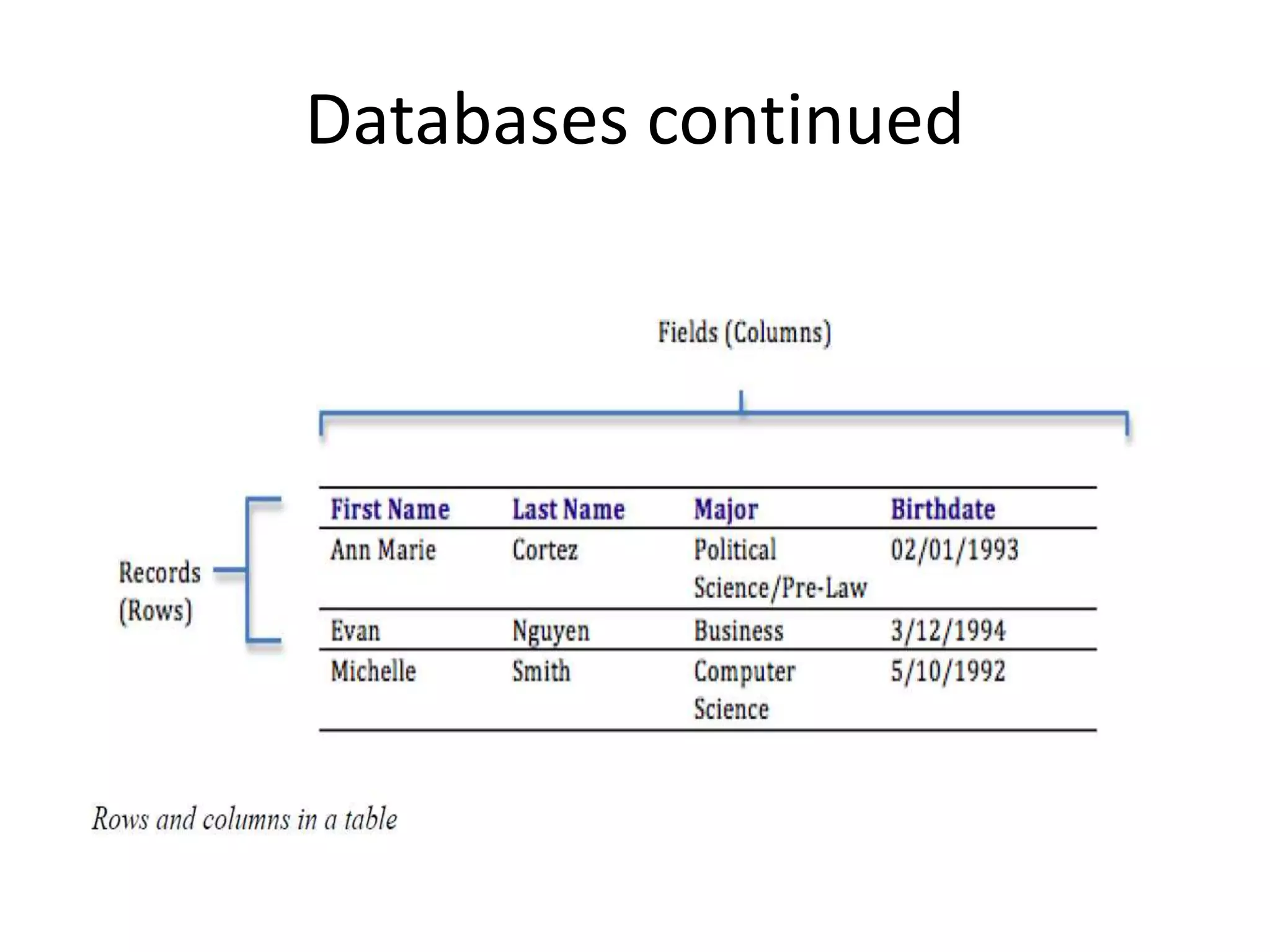
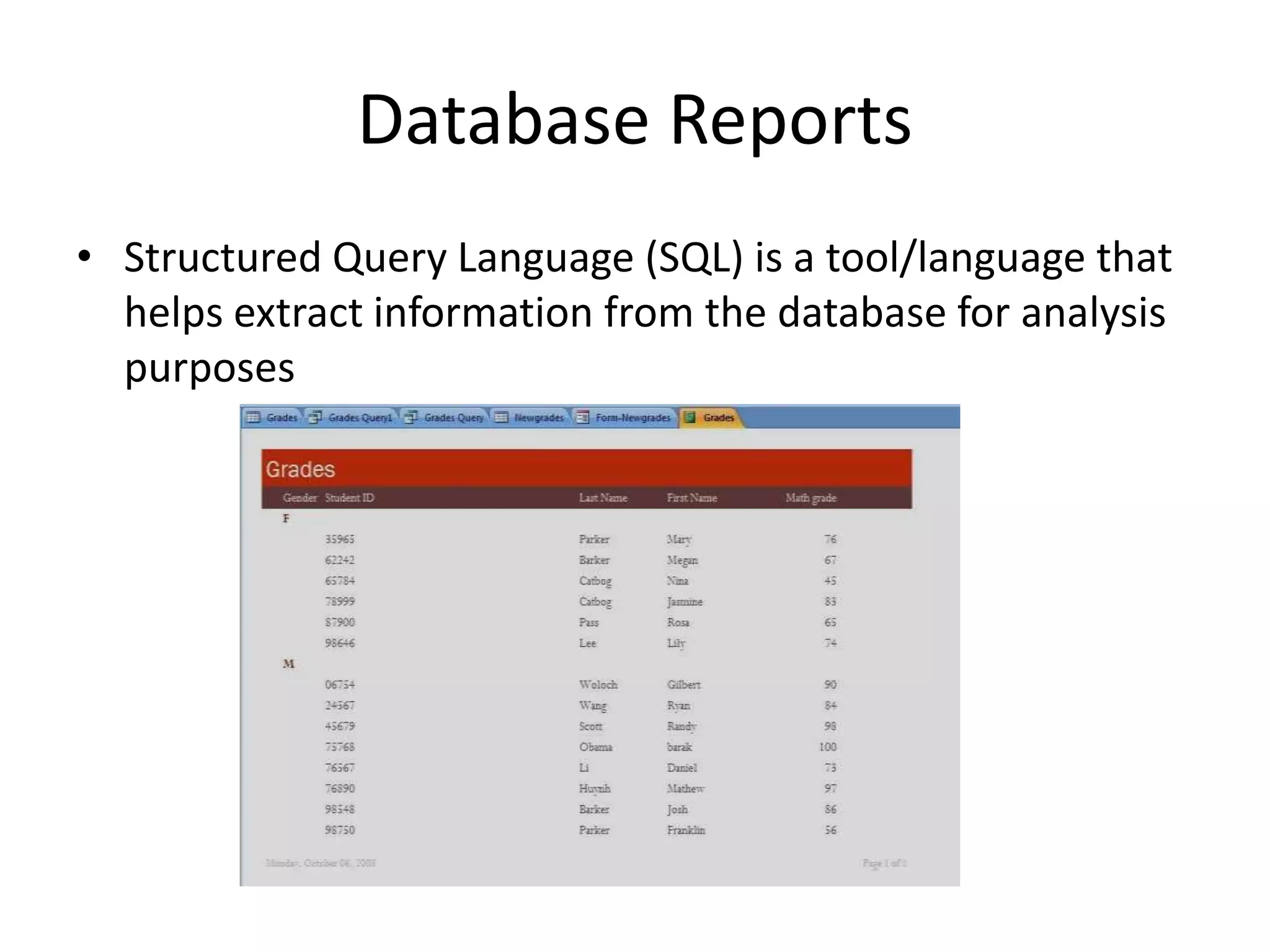
This chapter discusses databases, data warehouses, and data mining. It defines key terms like data, information, and databases. The main points are: Databases organize related information for decision making and knowledge generation. They are designed with tables, fields, and primary keys. Data warehouses store extracted data from multiple databases for analysis over time. Data mining analyzes data to find patterns and trends to improve business decisions.