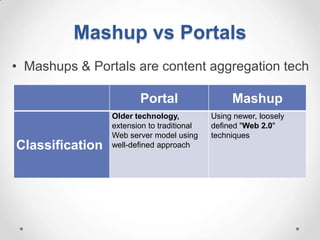
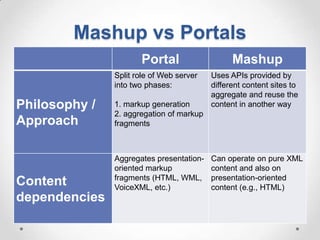
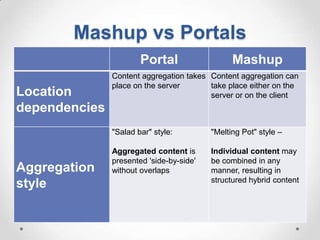
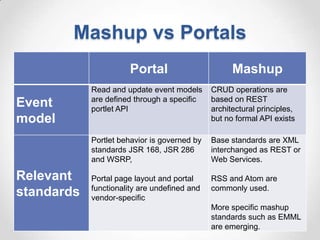
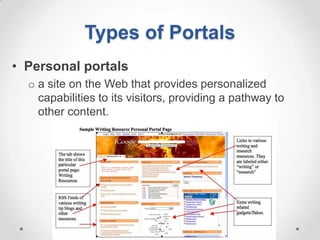
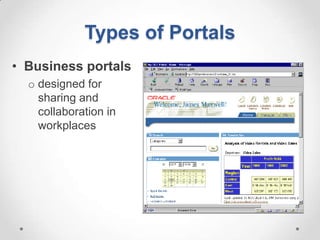
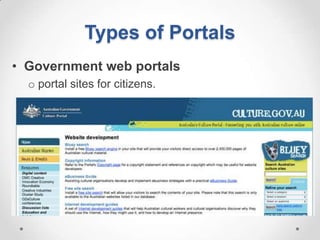
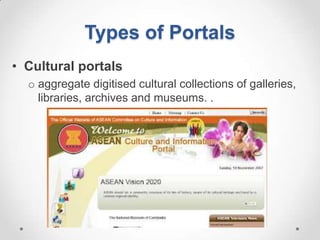
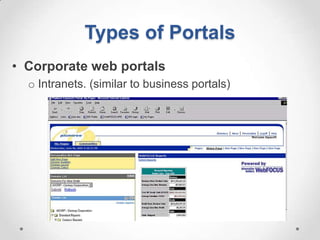
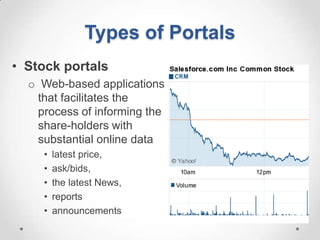
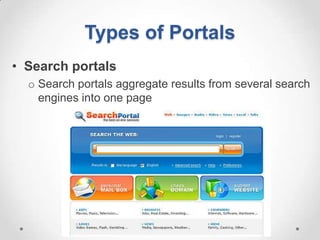
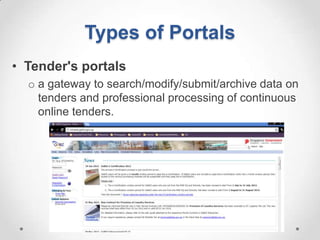
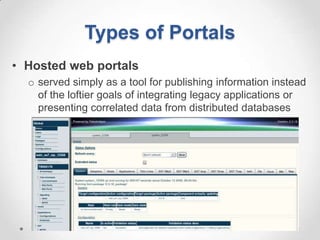
This document defines streaming protocols, compares mashups and portals, and describes different types of portals. It outlines several streaming protocols including RTSP, MMS, PNM, RTMP, and HTTP streaming. It also discusses protocol issues such as using UDP vs TCP and unicast vs multicast delivery. Mashups are described as combining content in new ways using APIs, while portals aggregate pre-existing content on servers. Finally, the document lists various types of portals including personal, business, news, government, and domain-specific portals.