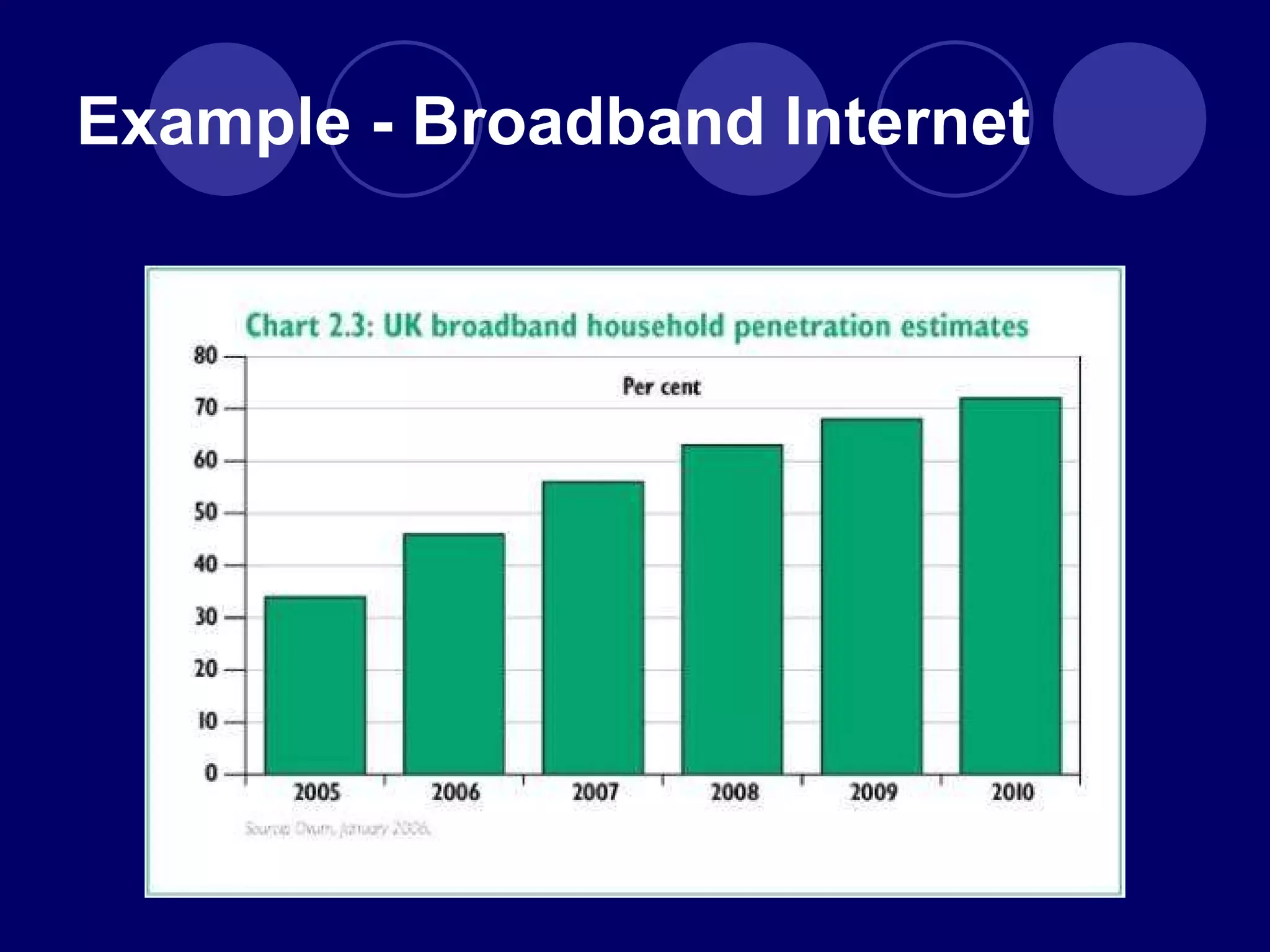
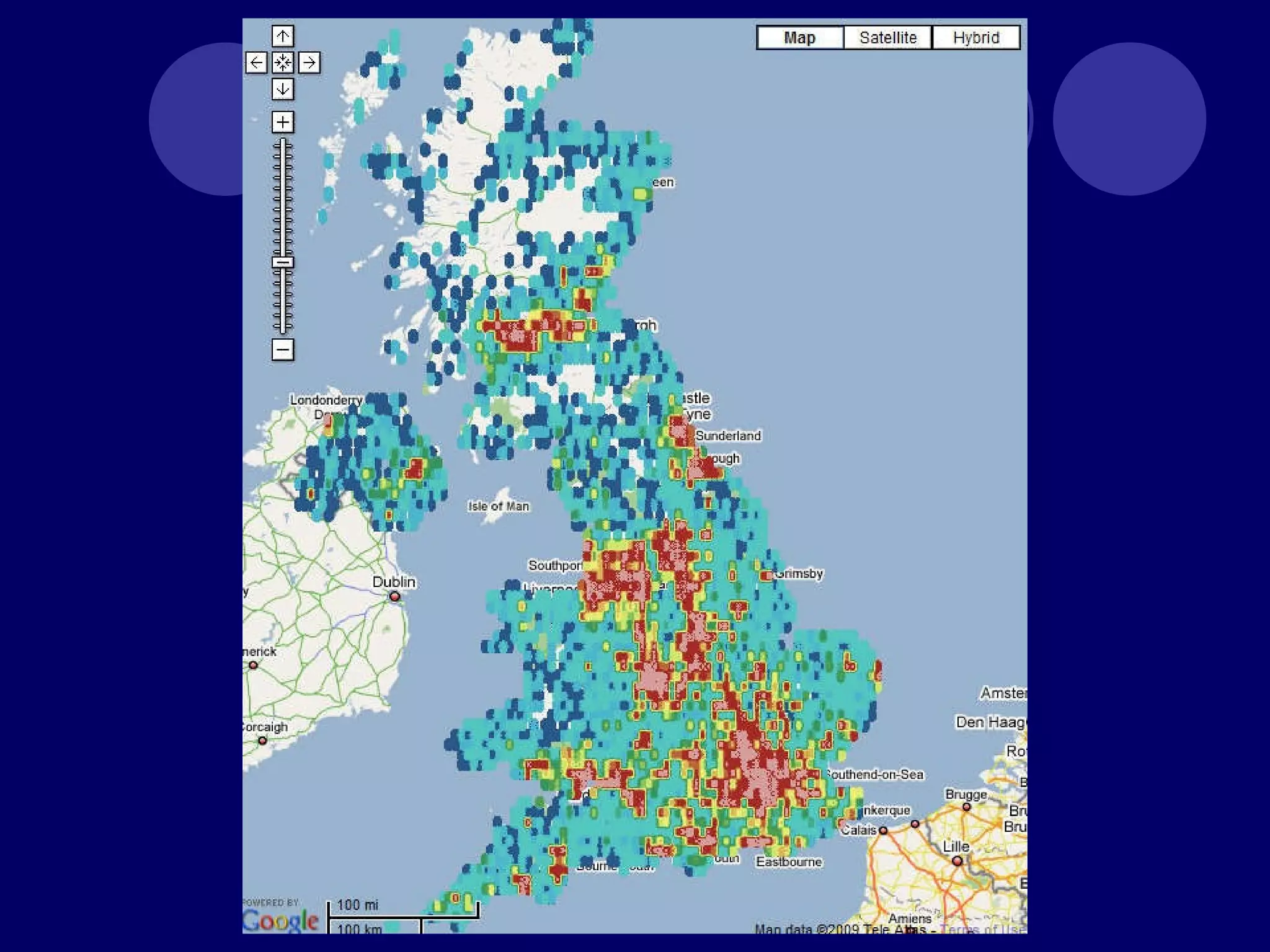
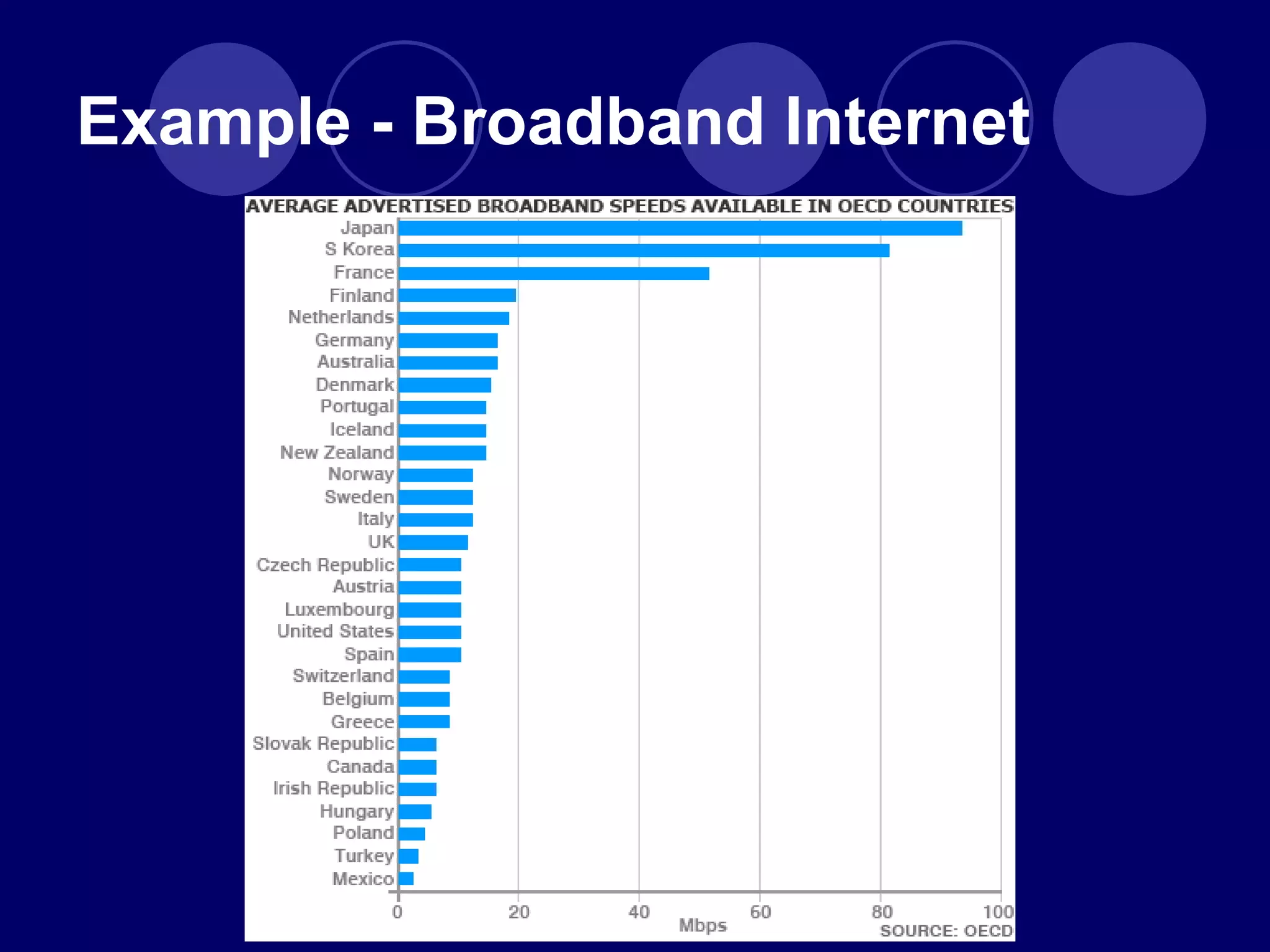
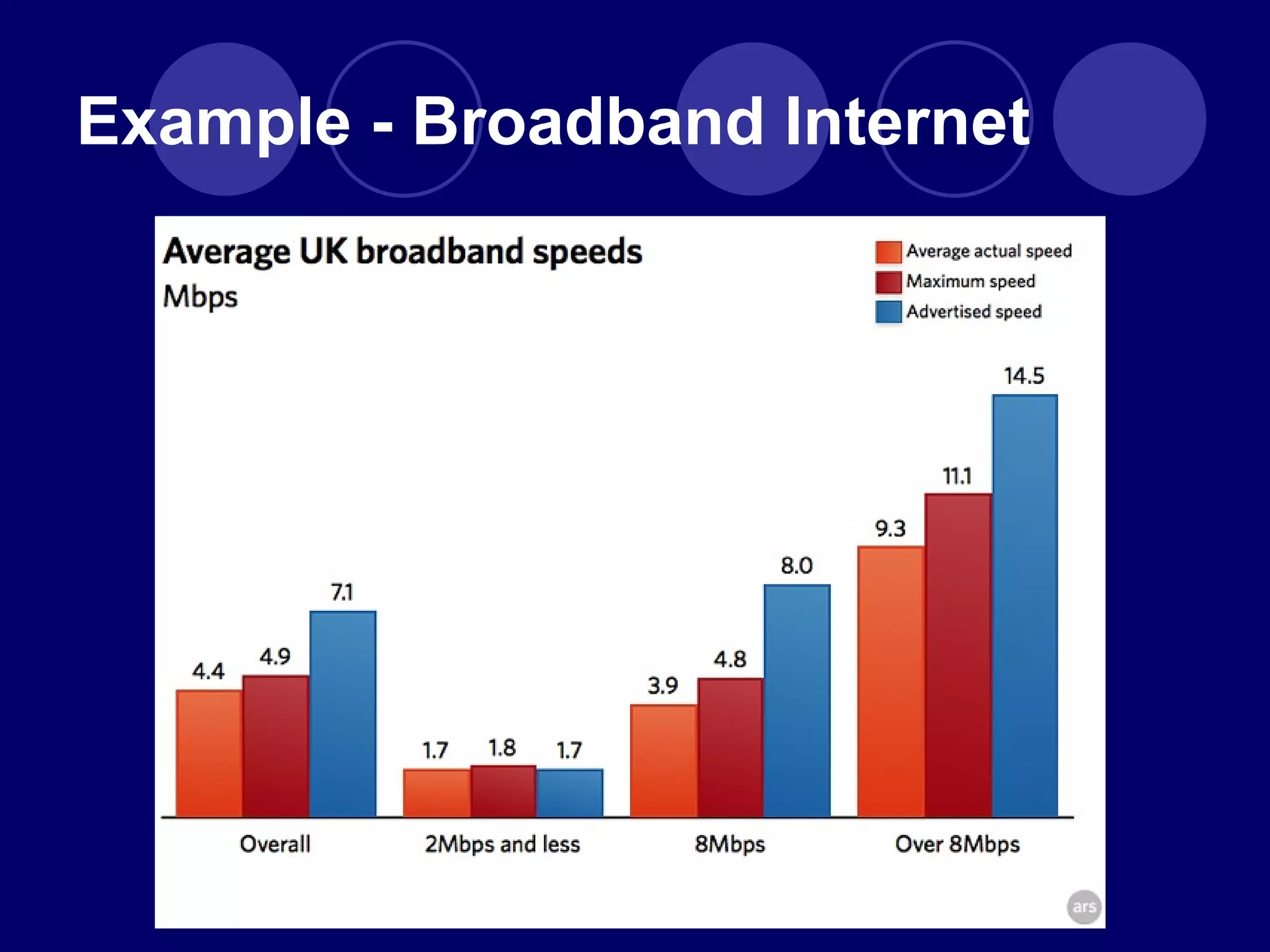
The document discusses how the advent of broadband internet and Web 2.0 has changed media consumption and production by empowering audiences. It explains that Web 2.0 allows ordinary people to participate in citizen journalism by producing and sharing their own accounts of events. Examples are given of how social media platforms like YouTube, Twitter, and BlackBerry Messenger have enabled grassroots reporting of major events and protests. The rise of "we-media" represents a shift from traditional top-down media models to more active audience participation in content creation and circulation.