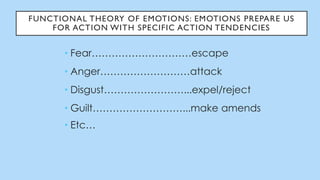
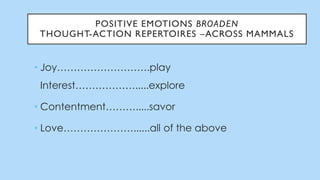
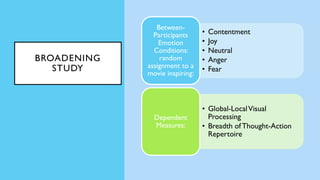
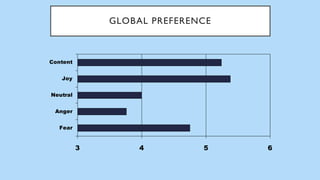
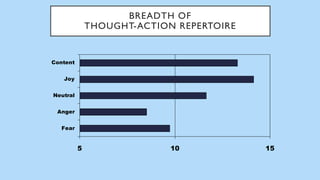
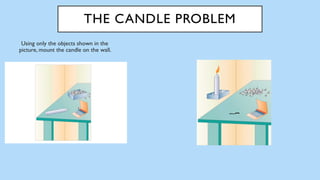
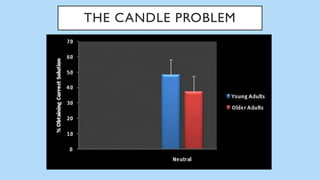
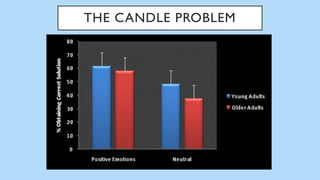
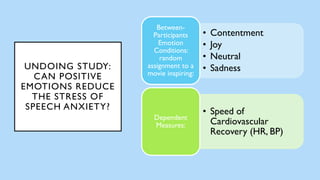
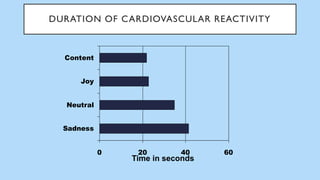
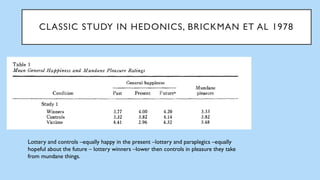
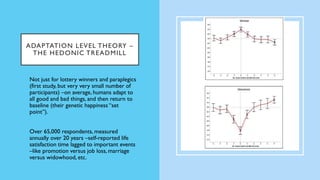
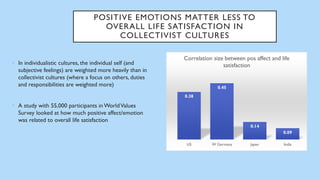
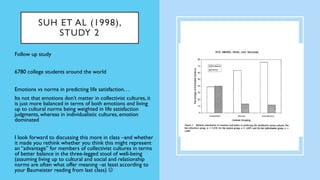
The document discusses hedonic well-being, highlighting its significance in understanding subjective experiences of happiness and their impact on physical health and social engagement. It covers concepts such as positive emotions, the broaden-and-build theory, and cultural differences in perceiving happiness, particularly between individualistic and collectivist societies. Additionally, it addresses the challenges in measuring hedonic experience due to adaptation and memory biases.