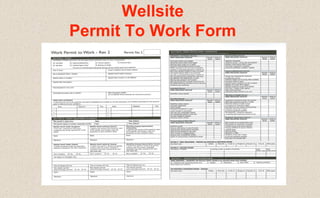
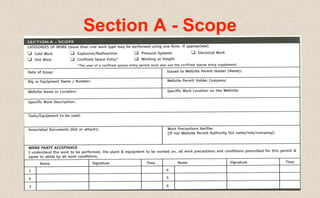
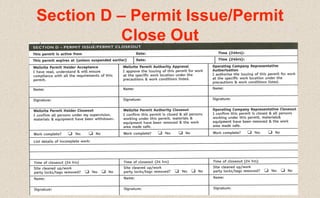
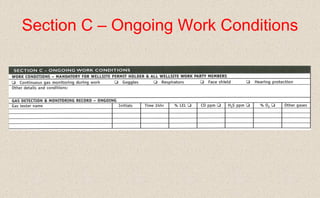
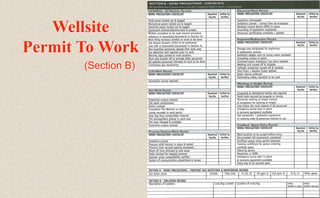
This document provides guidance on permit-to-work procedures for wellsite operations. It outlines the responsibilities of permit authorities, operators, permit holders, and work party members. It also describes the different types of permits that may be required, including for cold work, hot work, pressure systems, electrical work, explosives, confined spaces, and more. Key steps in the permit process are identified such as notifying the permit authority, safety briefings, and filling out permit forms. The document aims to plan and control work safely and ensure all work is properly authorized and carried out according to safe work practices.