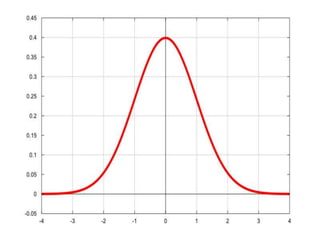
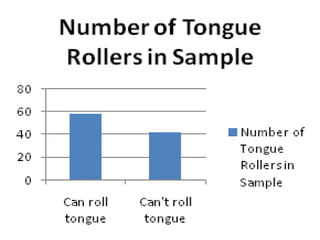
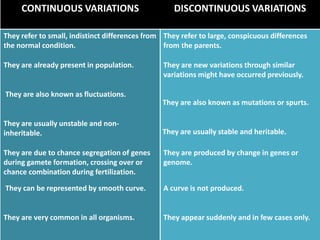
Variation in organisms refers to differences among members of the same species due to genetic and environmental factors. Genetic variation is inheritable and includes traits like height, while environmental variation cannot be passed down and is influenced by external factors such as temperature and nutrients. Continuous variation features slight gradations in traits, measured on a spectrum, whereas discontinuous variation has distinct categories, with examples including blood types and eye color.