Extrinsic and Intrinsic Eye Muscle Functions
- 1. Extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the eye • Learning objectives a. Definition b. Origin and insertion c. Blood supply d. Innervation e. Embryologically f. Some related
- 2. Introduction Orbital muscles Extraocular muscles of the eyeball involved in movement of the eyeball Intraocular muscles Controls shape of lense and size of pupil
- 3. Intraocular muscles Types of intraocular muscles 1. Sphincter pupillae muscle 2. Dilator pupillae muscle. 3. Ciliary muscle
- 4. 1. Sphincter pupillae Sphincter pupillae is a circular muscle, about 1 millimeter wide. It is located at the pupillary margin of iris. The sphincter muscle contracts the pupil in a circular motion while the dilator muscles enlarge the pupil by pulling the iris radially.(diverging from the center) An area called the iris collarette is the thickest portion of the iris where the sphincter muscle and dilator muscle overlap.
- 5. Cont................ Origin and insertion. Pupillary margin of iris. Action Constriction of pupil (miosis) Innervation Parasympathetic fibers of oculomotor nerve (CN III) via short ciliary nerves. Blood supply Long posterior ciliary arteries, anterior ciliary arteries (via minor arterial circle)
- 6. 2=Dilator pupillae muscle The dilator pupillae muscles is a ring of contractile cells within the iris. The pupillary dilator consists of a spokelike arrangement of modified contractile cells called myoepithelial cells. These cells are stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system. When stimulated, the cells contract, widening the pupil and allowing more light to enter the eye.
- 7. Dilator pupillae muscle Origin and insertion outer margins of iris Action Dilates the pupil Innervation Long Ciliary nerves(sympathetic) Blood supply Not found Embryologically Both sphincter and dilator muscles originate from NEUROECTODERM
- 8. 3=Ciliary muscle The ciliary muscle occupies the biggest portion of the ciliary body, which lies between the anterior border of the choroid and iris. The contraction of the ciliary muscle loosens the zonular fibers increasing the convexity of the lens, which induces accommodation for near vision. The ciliary processes are attached to the lens via zonular fibers. Through this indirect attachment, the ciliary muscle acts on the lens facilitating the accommodation.
- 9. Layers of Ciliary muscle The Ciliary muscle consists three main layers :- longitudinal layer is the outermost muscle layer situated adjacent to the loose connective tissue of the ciliary body. The middle layer is the radial layer of muscle. It represents the transition from the longitudinal to the circular muscle layer. The annular or circular layer (Müller’s muscle) is the innermost muscle layer that functions as a sphincter of the eye.
- 10. Cont.............. Origin originates from a protrusion of the sclera (scleral spur) Insertion The llongitudinal part inserts onto the anterior one-third of the choroid The Radial part: inserts connective tissue near the base of the ciliary processe Action Accommodation; and regulation of trabecular meshwork pore size Innervation Parasympathetic component of oculomotor nerve (CN III) Blood supply Long posterior ciliary arteries;(branch of ophthalmic artery) And drained by vorticose veins
- 11. Embrylogical of the ciliary muscle The ciliary muscle developed from the vascular layer of the mesenchyme Surrounding the optic cup.
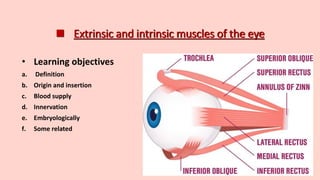
- 12. Extraocular muscles Has two types : Voluntary 1. Levator pulpebrae superioris 2. Superior rectus 3. Inferior rectus 4. Medial rectus 5. Lateral rectus 6. Superior oblique 7. IInferior oblique Involuntary 1. Superior tarsal muscle 2. Inferior tarsal muscle 3. Orbitalis
- 14. 1=Levator pulpebrae superioris 1=The levator pulpebrae superioris, Does not act on eyeball but iit's Responsible for elevating the upper eyelid Length 60mm long Muscle 40mm Tendon 14-20mm
- 15. Cont....... Origin Lesser wing of sphenoid bone Action Elevation of the upper muscle Innervation a) Voluntary part :superior division of oculomotor nerve b) Involuntary part:sympathetic innervation from the carotid plexus whose fibers join the oculomotor nerve Blood supply Receives from ophthalmic artery and it's branch via supraorbital branch
- 16. Insertion (aponeurosis of the muscle splits into 3 lamina) Upper lamina (voluntary) is inserted iinto the skin of upper lid Middle lamina.(involuntary) atached to upper margin of superior Lower lamina (involuntary)is attached to Superior conjunctival fornix Embrylogical At 2.5 months' gestation, the levator palpebrae superioris develops. It separates from the superior rectus muscle at the fourth month of gestation. Clinically, failure of separation of these muscles would result in congenital ptosis.
- 17. 2=Superior rectus muscle Length=41.8mm long Tendon=5.8mm long Wide=10.6mm Origin Annulus of zinn Insertion Superiorly about 7.7mm from limbus •Action • Elevates, adducts, internally rotates eyeball •Blood supply • muscular branch of ophthalmic artery •Innervation • Superior division of CN III • Expansion of the SR is attached to the LPS. Thus when the SR makes the eye look up the upper lid is also raised.
- 19. 3=inferior rectus muscle • Length=4omm long • Tendon=5.5mm long • Wide=9.8mm •Origin • Annulus of zinn •Insertion • inferiorly about 6.5mm from limbus • Action • Depresses, adducts, externally rotates eyeball • Blood supply • muscular branch of ophthalmic artery and infraorbital artery • Innervatio • InfeInferior division of CN III (oculomotor)
- 20. 4=medial rectus muscle • Length=4o.8mm long Tendon=3.7mm long • Wide=10.3mm Origin • Annulus of zinn • Insertion • Medially about 5.5mm from limbus •Action • Adducts the eyeball •Blood supply • muscular branch of ophthalmic artery Innervation • InfeInferior division of CN III (oculomotor)
- 21. Facial expantion of the sheaths (muscular fascia) of the medial rectus attached to the zygomatic bone.
- 22. 5=lateral rectus muscle Length=4o.6mm long Tendon=8mm long Wide=9.2mm Origin • Annulus of zinn Insertion • laterally about 6.9 mm from limbus from limbus Action • Abducts the eyeball •Blood supply • muscular branch of ophthalmic artery and lacrimal artery •Innervation • CN VI (abducens)
- 23. Facial expantion of the sheaths (muscular fascia) of the lateral rectus attached to the zygomatic bone.
- 24. 6=Superior oblique muscle Length=4omm long Tendon=20mm long Wide=10.8mm Origin • Medial to optic foramen, between annulus of zinn and periorbita Insertion • Through pulley(trochlea) ends superolateral aspect of eyeball. Action Abducts, depresses, internally rotates eyeball •Blood supply muscular branch of ophthalmic artery Innervation • CN IV (trochlear)
- 25. 7=inferior oblique muscle • Length=37mm long • Tendon=1mm long • Wide=9.6mm • Origin • Orbital surface of maxilla. • Insertion • Inferolateral aspect of eyeball (deep to lateral rectus muscle) •Action • Abducts, depresses, internally rotates eyeball •Blood supply • muscular branch of ophthalmic artery •Innervation • CN IV (trochlear)
- 27. Involuntary extraocular muscles(Miller's muscles)
- 28. 1=Superior tarsal muscle Superior tarsal (Muller's muscle) is a small muscle found within the superior eyelid. It is a smooth muscle, but it is considered as a structural component of the larger skeletal muscle of the eyelid; levator palpebrae superioris.
- 29. Cont........ Origin Deep surface of levator palpebrae superioris muscle Insertion Superior tarsal plate of the eyelid Action Elevates and retracts the upper eyelid Innervation Sympathetic nervous system (via internal carotid plexus) Blood supply Ophthalmic artery.
- 30. 2=Inferior tarsal muscle The inferior tarsal muscle :is commonly described as a part of the capsulopalpebral fascia and the smooth muscle fibers under the fornix adjacent to the capsulopalpebral fascia .The inferior tarsal muscle of the lower eyelid is a homologous organ with the Müller muscle of the upper eyelid.
- 32. Cont..... Origin Capsulopalpebral fascia Insertion Inferior tarsal plate Action Lower lid retraction Innervation sympathetic nervous system like the Müller muscle. Blood supply Not found
- 33. 3=orbitalis muscle • The orbitalis muscle is a vestigial or rudimentary nonstriated muscle (smooth muscle) that crosses from the infraorbital groove and sphenomaxillary fissure and is intimately united with the periosteum of the orbit.
- 34. About orbitalis muscle • Vestigial muscle • Crosses inferior orbital fissure and sphenomaxiliary fissure • Unites with periosteum of orbit Action Forward protrusion of orbit Innervation Sympathetic nervous system (via internal carotid plexus)
- 35. • Embreologically of EOM All the extraocular muscles develope from mesodermal mesenchymal tissue