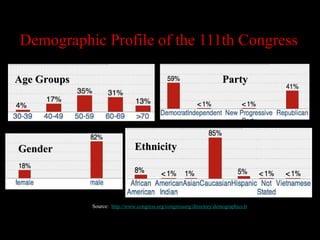
The document provides an overview of the structure and organization of Congress. It describes the two chambers of Congress (House and Senate), including their differences in size, terms of office, and procedural rules. It also outlines the party leadership structure and roles in both chambers, as well as the various types of committees - standing, select, joint - that conduct legislative work.