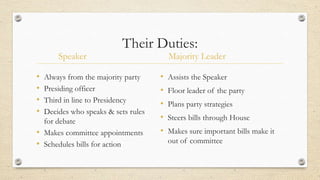
This document provides an overview of Congress and its structure and processes. It defines key terms related to members of Congress and elections. It also outlines the differences between the House and Senate, including that the House has a Speaker and majority leader while the Senate has a President and president pro tempore. Finally, it details the roles and responsibilities of congressional leadership positions in both the House and Senate.