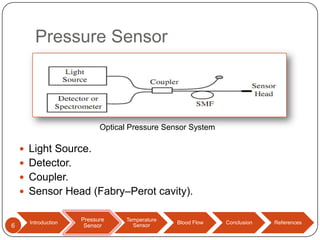
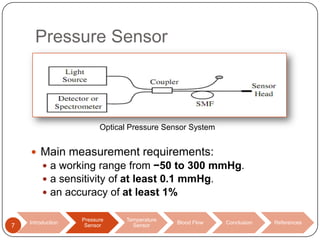
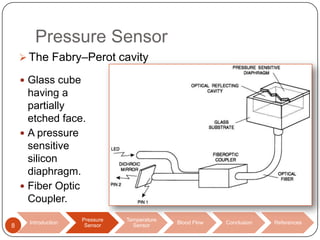
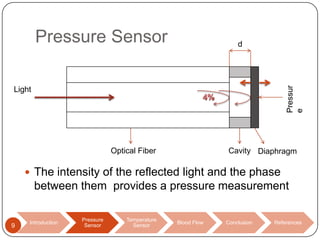
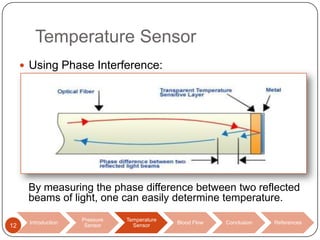
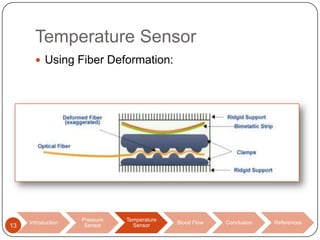
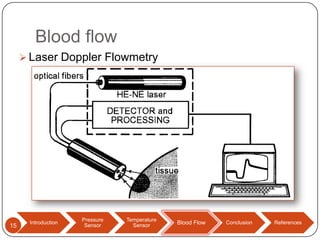
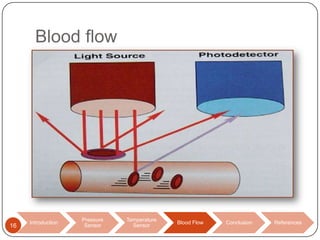
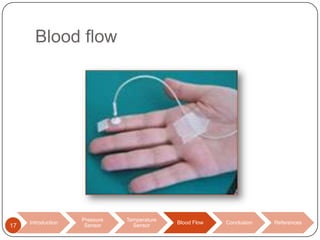
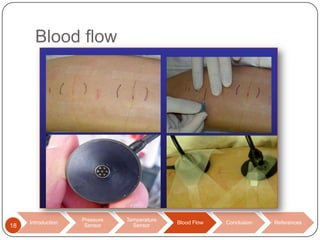
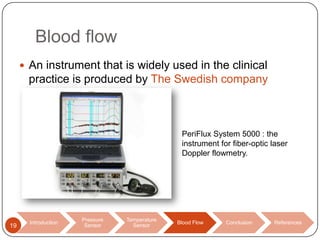
This document discusses biomedical sensors that use optical fibers. It introduces fiber optic sensors and their advantages, such as flexibility, lightness, safety, and immunity to electromagnetic interference. It then describes several specific fiber optic sensors: a pressure sensor that uses a Fabry-Perot cavity, temperature sensors that use phase interference or fiber deformation, and a blood flow sensor that uses laser Doppler flowmetry. Commercially available products are provided as examples for the pressure, temperature, and blood flow sensors. The document concludes that fiber optic sensors are well-suited for a variety of medical measurements due to their low cost, ease of use, and performance comparable to electric sensors.