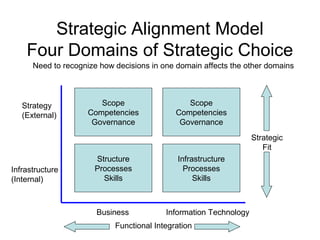
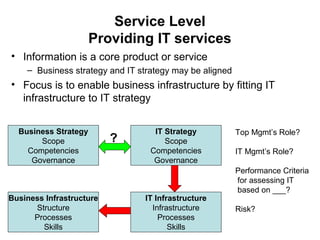
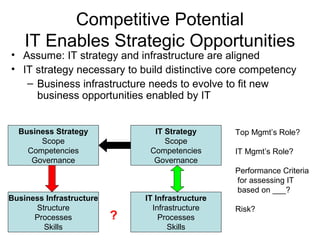
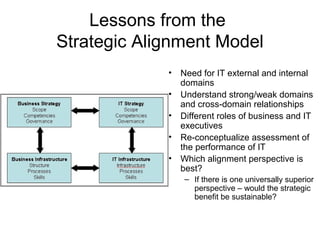
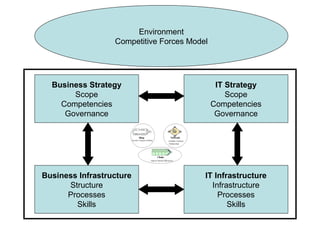
The Strategic Alignment Model is a framework that consists of 4 domains: Business Strategy, IT Strategy, Business Infrastructure, and IT Infrastructure. It is used to align IT with business strategy and leverage IT to achieve competitive advantage. The domains influence each other and decisions in one domain affect the others. The model helps identify strong and weak domains, understand cross-domain relationships, and assess different roles and performance criteria for business and IT executives.