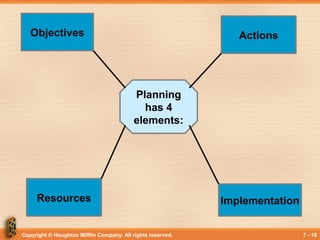
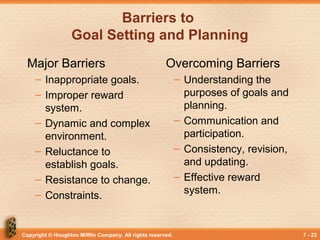
This document discusses organizational goal setting and planning. It covers the purposes of goals in providing guidance, promoting planning, motivating employees, and enabling evaluation. Goals can be set at different levels, such as mission, strategic, tactical, and operational goals. Planning involves determining objectives, actions, resources, and implementation. Effective planning requires identifying what needs to be done, how, and when. Different types of plans include strategic, tactical, operational, contingency, and crisis management plans. Barriers to planning like improper goals, rewards, and resistance must be addressed.