More Related Content
PPT
Basic elements of planning and decision making PPT
PPTX
PPT
PPT
Managing decision making and problem solving PPT
Pom unit-ii, Principles of Management notes BBA I Semester OU PDF
Chapter 002 Planning & Decision Making.pdf PDF
Similar to Ch. 2 Basic Planing and Decison making.ppt
PPTX
02. Organizational Goals, Planning & Decision Making (2021).pptx PPT
CHAPTER 9.pptHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH PPT
PPTX
Second chapter of Management PPTX
PPPPlanning-Tools-Decision-Making-1.pptx PPT
PPTX
CHAPTER 3 & 4 PLANNING- DECISION MAKING.pptx PPTX
PPTX
PLANNING, STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT TECHNIQUES& DECISION MAKING.pptx PDF
Management 12th Edition Griffin Solutions Manual PDF
Management 10th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual PPTX
Principles of Management Chapter 3 Planning PPT
Griffin types of decision making PDF
PPT
PPT
PPTX
Planning in Management (Principles of management) PDF
PPT
PPTX
Chapter 07 -- Basics of planning More from aqeelkhankhattak68
PPT
0 Management Fundamentals lec 1 for electrical engineer.ppt PPT
chap 3 Basic element s of organizing.ppt PPT
lec 4 Managing human resources in organizations.ppt PPT
lec 5 Basic element of individual behavior in organization.ppt PPTX
Progress ppt.pptx For iot based anti theft floor mat PDF
lecture1(1).pdf Introduction to measurement and instrumentation PPTX
Lec 1 - Electrical Grid step by step explaiation.pptx PPTX
Lec 4 - Solar Energy explained step by step.pptx Recently uploaded
PDF
EXFUSION - NEW update - english - Forex Copy Trading - DEBIT CARD - Affiliate PPTX
UCM23601J - Management Accounting Unit I DOCX
16 Best Sites To Buy Google Ads Accounts (Aged &.docx PDF
FinSight: An AI-Powered Financial Intelligence Platform for Investors PPTX
Sustainable Alpha Can ESG Portfolios Outperform Conventional Portfolios in Em... DOCX
Top Trusted Marketplaces to Buy Verified Linkedin Accounts.docx PDF
Wise Account Verification for eCommerce & Global Businesses PDF
How to Buy Verified Cash App Accounts for safe and compliant account.pdf DOCX
Sustainable Alpha Can ESG Portfolios Outperform Conventional Portfolios in Em... PDF
Neteller Account Verification: What It Is & How It Works for Online Businesses DOCX
A Study of Instagram Accounts in Digital Media and Communication Systems DOCX
A Study on Gmail Account Structure, Verification, and Usage in Digital Commun... DOCX
Case Studies and Learning Examples in Digital Banking Verification PDF
Payeer Verification Guide for Freelancers & Online Sellers.pdf PDF
Beinsure Media Kit 2026 - advertising in B2B digital media platform focused o... PPTX
WAGES, PRODUCTIVITY AND INNOVATION: BARGAINING OF PERFORMANCE-RELATED-PAY (PR... PDF
Master Your Finances: Ultimate Guide to Achieving Financial Freedom with Rami... PDF
NINTH INTERNATIONAL ASTRIL CONFERENCE - Roma3 PDF
The Service Sectors of Ethiopia_-_Geo-Economy PDF
Labor Shortages and Security Risks Were the Top Obstacles for Business in Dec... Ch. 2 Basic Planing and Decison making.ppt
- 1.
Slide content createdby Joseph B. Mosca, Monmouth University.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
7
Ready Notes
Basic Elements of
Planning and
Decision Making
- 2.
- 3.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 3
Purposes of goals:
• Purposes of goals:
– Provide guidance.
– Promote good
planning.
– Serve as sources of
motivation.
– Mechanism for
evaluation and
control (reward &
punishment).
- 4.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 4
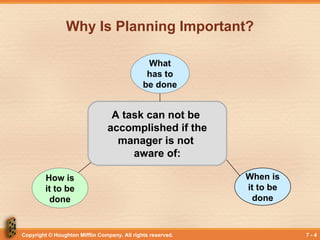
Why Is Planning Important?
A task can not be
accomplished if the
manager is not
aware of:
How is
it to be
done
What
has to
be done
When is
it to be
done
- 5.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 5
Planning steps
• Understanding the environment
• & the organization mission.
• Then set the goals.
- 6.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 6
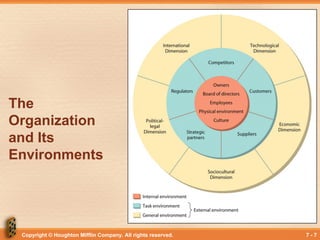
The Organization’s Environments
• External environment:
everything outside an
organization’s
boundaries that might
affect it. The
uncontrollable
environment.
• Internal environment:
the conditions and
forces within an
organization. The
controllable
environment.
- 7.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 7
The
Organization
and Its
Environments
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 10
Mission
• A statement of an organization’s
fundamental purpose. like humanity
service is Edhi’s mission, Changing life
L.G mission, connecting people is
Nokia’s mission & so on
- 11.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 11
Kinds of Goals
• Goals vary by level, area, and time
frame.
• By Level
1. Strategic goal: a goal set by and for
top management of the organization.
2. Tactical goal: set by and for middle
managers of the organization.
3. Operational goal: set by and for lower
managers of the organization.
- 12.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 12
Kinds of Goals
• By Area:
organizations also
set goals for
different areas.
• By Time frame:
organizations also
set goals across
different time
frames.
- 13.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 13
Responsibilities for Setting Goals
Who sets goals?
– All managers should
be involved in the goal
setting process.
– Each manager has
responsibilities for
setting goals that
correspond to their
level.
- 14.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 14
Managing Multiple Goals
• When setting goals
organizations sometimes
experience conflicts or
contradictions among
goals.
• Conflicts are addressed
through the use of the
Optimizing concept:
– Optimizing: balancing and
reconciling possible conflicts
among goals.
- 15.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 15
Organizational Planning
Kinds of organizational
plans:
1. Strategic plan: a
general plan outlining
decisions to achieve
strategic goals.
- 16.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 16
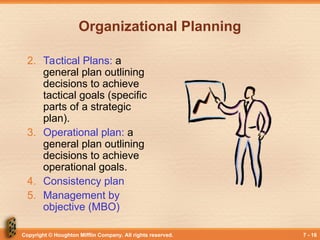
Organizational Planning
2. Tactical Plans: a
general plan outlining
decisions to achieve
tactical goals (specific
parts of a strategic
plan).
3. Operational plan: a
general plan outlining
decisions to achieve
operational goals.
4. Consistency plan
5. Management by
objective (MBO)
- 17.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 17
Using SWOT Analysis for Strategic planning
• SWOT: An abbreviation that stands for
strengths, weaknesses, opportunities,
and threats.
• Organizational strength: a skill or
capability that enables an organization
to set goals for it.
• Organizational weakness: a
shortcoming that hinder in achieving
goal.
- 18.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 18
Using SWOT Analysis for Strategic planning
• Organizational
opportunity: an area in
the environment that, if
exploited, may generate
higher performance.
• Organizational threats:
an area in the
environment that
increases the difficulty
of an organization
performing at a high
level.
- 19.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 19
Types of Operational Planning
Single-use plan:
• Developed to carry out a course of action
not likely to be repeated in the future.
1. Program: a plan for a large set of activities
like introducing new product line, opening a
facility or changing the organization’s
mission. For example the program to
upgrade Mangla dam water & power
capacity.
2. Project: a plan of less scope and complexity
than a program like introducing a new
product within an existing product line. e.g.
the installation of new turbine at Mangla
dam during the up gradation
- 20.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 20
Types of Operational Planning
Standing Plan
• Developed for activities that recur regularly over a
period of time:
1. Policy: a standing plan specifying the organization’s
general response to a designated problem or situation like
admission policy of university.
2. Standard operating procedure: a standing plan outlining
steps to be followed in particular circumstances. e.g Mc
Donald's SOP of Big Mac how they are cooked & how
long must they stay in oven.
3. Rules and regulations: standing plans describing exactly
how specific activities are to be carried out. E.g. telephone
use is prohibited in Mc Donald.
- 21.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 21
Contingency Planning
• The determination of
alternative courses
of action to be taken
if an intended plan
fails.
- 22.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 22
Management by Objective (MBO)
• “A method of management whereby
managers and employees collectively
set the goals”.
• STEPS
1. Set Goals
2. Develop action plans
3. Review progress
4. Appraise overall performance
- 23.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 23
Time Frames for Plans
• Long-range plan: covers many years,
perhaps even decades; common long-
range plans are for five years or more.
• Intermediate plan: usually covers
periods from one to five years.
• Short-range plan: generally covers a
span of one year or less.
- 24.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 24
Responsibilities for Planning
• Planning staff: some large organizations
develop a professional planning staff.
• Planning task force: often comprised of
line managers with special interest in
the relevant area of planning.
• Board of directors: establish the
corporate mission and strategy, and in
some companies take part in the
planning process.
- 25.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 25
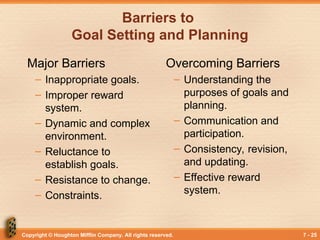
Barriers to
Goal Setting and Planning
Major Barriers
– Inappropriate goals.
– Improper reward
system.
– Dynamic and complex
environment.
– Reluctance to
establish goals.
– Resistance to change.
– Constraints.
Overcoming Barriers
– Understanding the
purposes of goals and
planning.
– Communication and
participation.
– Consistency, revision,
and updating.
– Effective reward
system.
- 26.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 26
“Decision making” the catalyst
• Decision making is the catalyst that
drives the planning process. An
organization goals follow from decisions
made by various managers.
• Likewise deciding on the best plan for
achieving particular goal also reflects a
decision to adopt one course of action
as opposed to others
- 27.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 27
The Nature of Decision Making
Decision making:
– The act of choosing
one alternative from
among a set of
alternatives.
- 28.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 28
Types of Decisions
Programmed decision:
– A decision that is fairly
structured or recurs with some
frequency (or both). E.g. the
cordinator decision to allocate
subjects, class rooms & timings
at the start of semester .
Non-programmed decision:
– A decision that is relatively
unstructured and occurs much
less often than a
PROGRAMMED DECISION.
E.g. if the teacher quits during
semester then the cordinater has
to make decision to whom to
allocate his subject
- 29.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 29
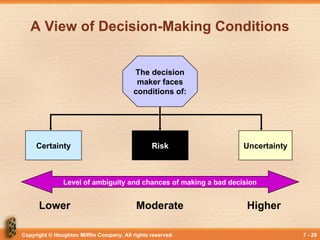
A View of Decision-Making Conditions
Certainty Risk Uncertainty
Level of ambiguity and chances of making a bad decision
Lower Moderate Higher
The decision
maker faces
conditions of:
- 30.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 30
Decision-Making Conditions
State of certainty:
– If, at the time a decisions is
made, only a single outcome
is likely, the decisions is
certain. Certain decisions are
"sure things". for example buying
electronics you know that L.G, Sony &
General will be the best choice.
State of risk:
– If, at the time a decision is
made, the probabilities of
several alternative outcomes
are known, the decision is
risky. For risky decisions,
several different outcomes are
possible and the probability of
each outcome's actually
occurring is known. . e.g. the
decision to buy second hand
electronics has got certain probability
of failure
- 31.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 31
Decision-Making Conditions
• State of Uncertainty: If,
at the time a decision is
made, the range of
possible outcomes is
not known and the
probability of these
different outcomes'
occurring is not known,
the decision is
uncertain. . E.g. deciding
to buy a new electronics
company’s products with no
market
- 32.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 32
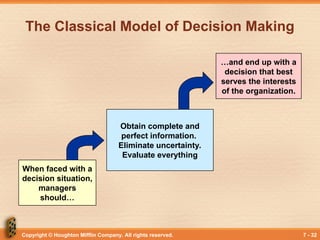
Obtain complete and
perfect information.
Eliminate uncertainty.
Evaluate everything
The Classical Model of Decision Making
When faced with a
decision situation,
managers
should…
…and end up with a
decision that best
serves the interests
of the organization.
- 33.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 33
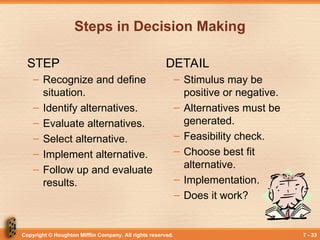
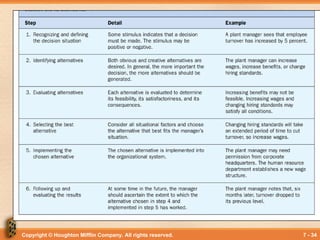
Steps in Decision Making
STEP
– Recognize and define
situation.
– Identify alternatives.
– Evaluate alternatives.
– Select alternative.
– Implement alternative.
– Follow up and evaluate
results.
DETAIL
– Stimulus may be
positive or negative.
– Alternatives must be
generated.
– Feasibility check.
– Choose best fit
alternative.
– Implementation.
– Does it work?
- 34.
- 35.
Copyright © HoughtonMifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7 - 35
Advantages and Disadvantages of Group and
Team Decision Making
ADVANTAGES
– More information
and knowledge
available.
– More alternatives
generated.
– More acceptance.
– Enhanced
communication.
– Better discussions.
DISADVANTAGES
– The process takes
longer.
– Compromised
decisions result from
indecisiveness.
– One person may
dominate.