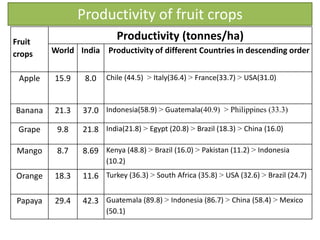
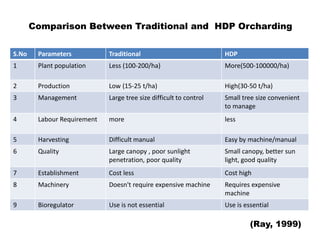
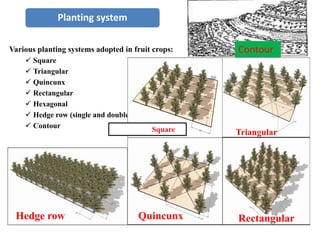
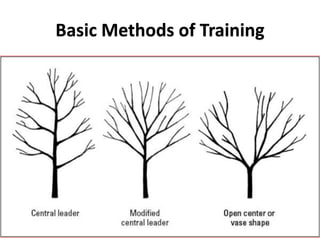
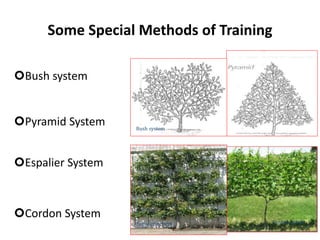
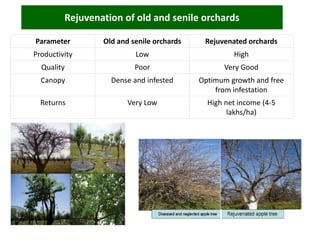
The document discusses strategies to enhance the productivity and quality of fruit crops through advanced agricultural techniques, focusing on various fruit types and their respective yields in different countries. Key strategies include high-density planting, canopy management, micro-irrigation, and the use of appropriate rootstocks and pollinizers. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of rejuvenating old orchards and the benefits of intercropping with compatible crops.