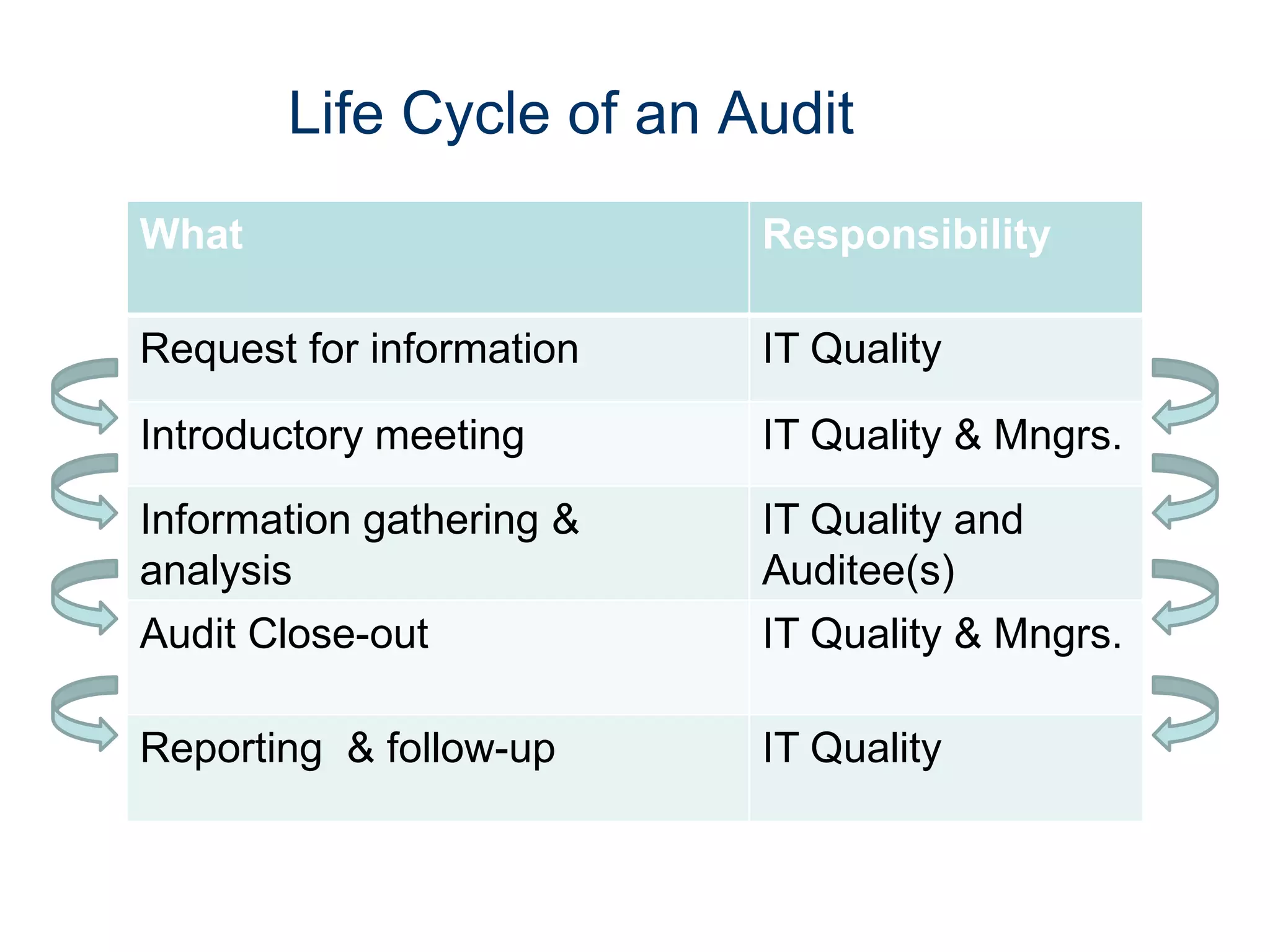
The document outlines best practices for preparing for an IT audit, emphasizing the importance of understanding policies, responsibilities, and procedures. It details the roles of IT quality and managers in facilitating the audit process, including addressing auditor requests and communication etiquette. Additionally, it provides sample questions auditors may ask and stresses the significance of accurate responses and proper document handling.