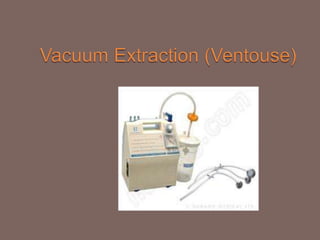
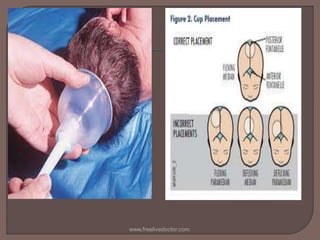
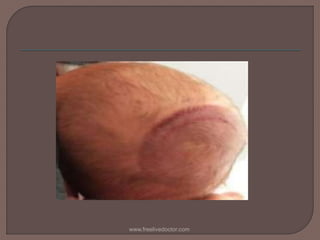
Vacuum extraction is a method to assist in childbirth using suction from a cup placed on the baby's head to help with traction during contractions. The cup is attached by tubing to a bottle that creates negative pressure not exceeding -0.8 kg/cm2. It can be used to assist delivery in cases of delayed descent, twins, or as an alternative to forceps. Risks include cephalhematoma and scalp lacerations for the baby, and vaginal or cervical lacerations for the mother.