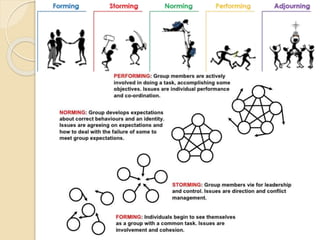
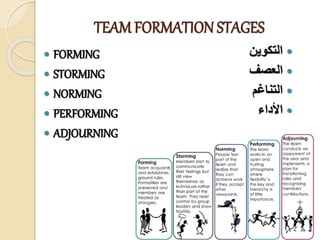
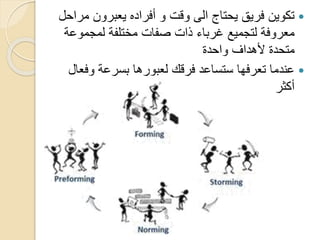
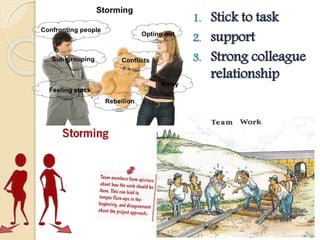
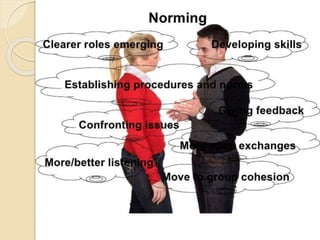
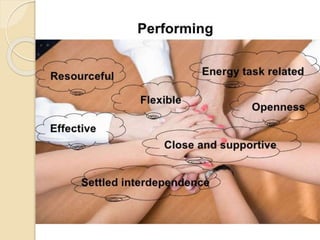
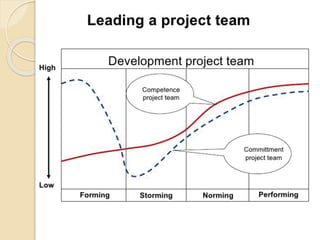
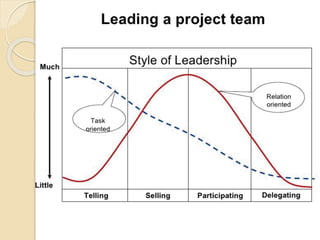
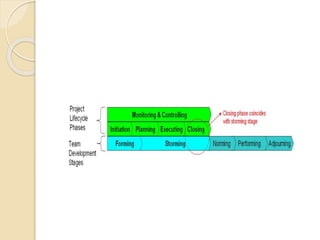
This document discusses Bruce Tuckman's model of team formation, which outlines 5 typical stages of development for teams: forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. It provides descriptions of each stage and advice on leadership strategies to help teams progress through each stage to ultimately become high-performing. The key points are that teams generally follow predictable stages of development, understanding the current stage helps determine the appropriate leadership approach, and focusing on moving the team through each stage leads to optimal performance.