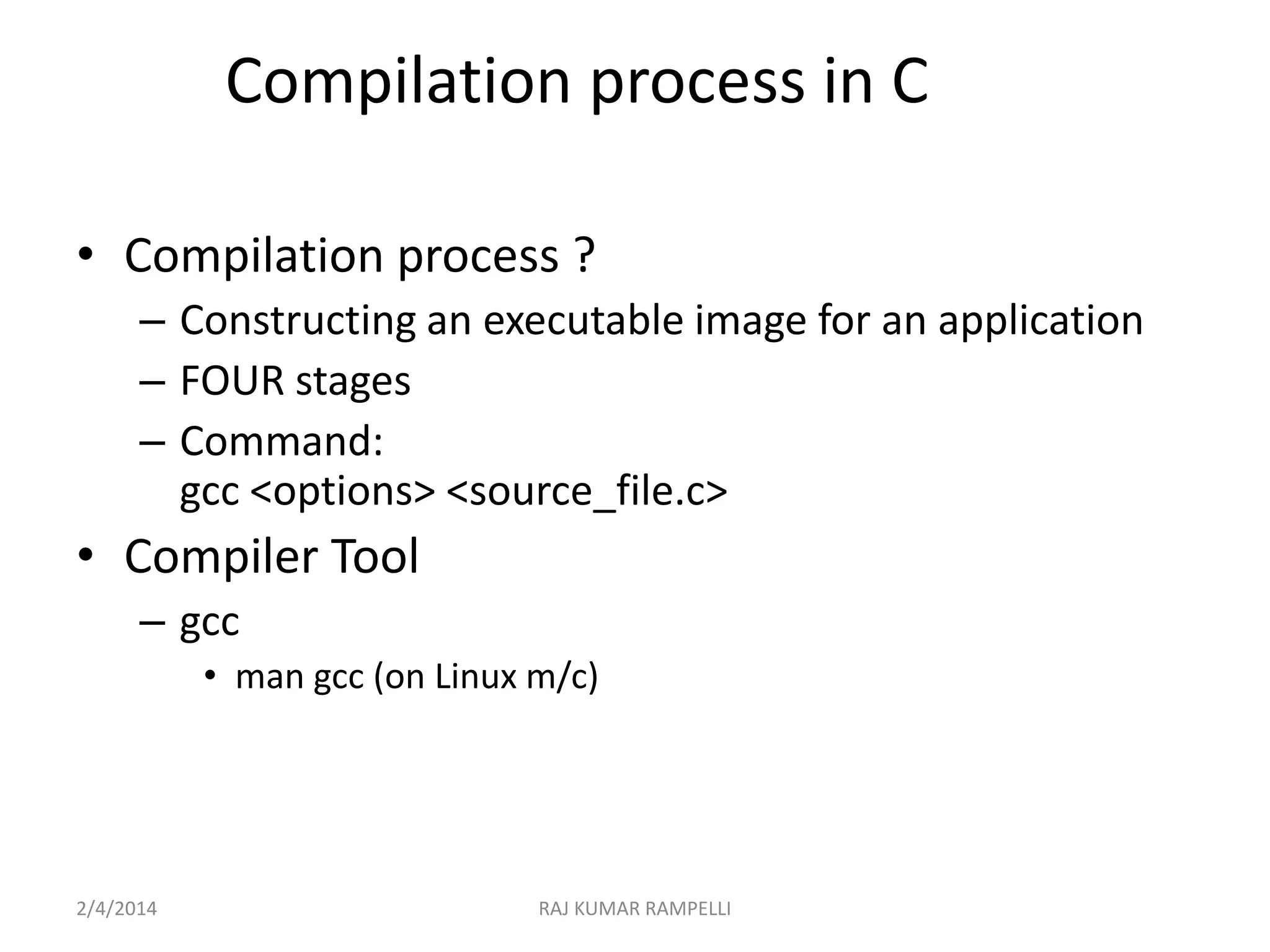
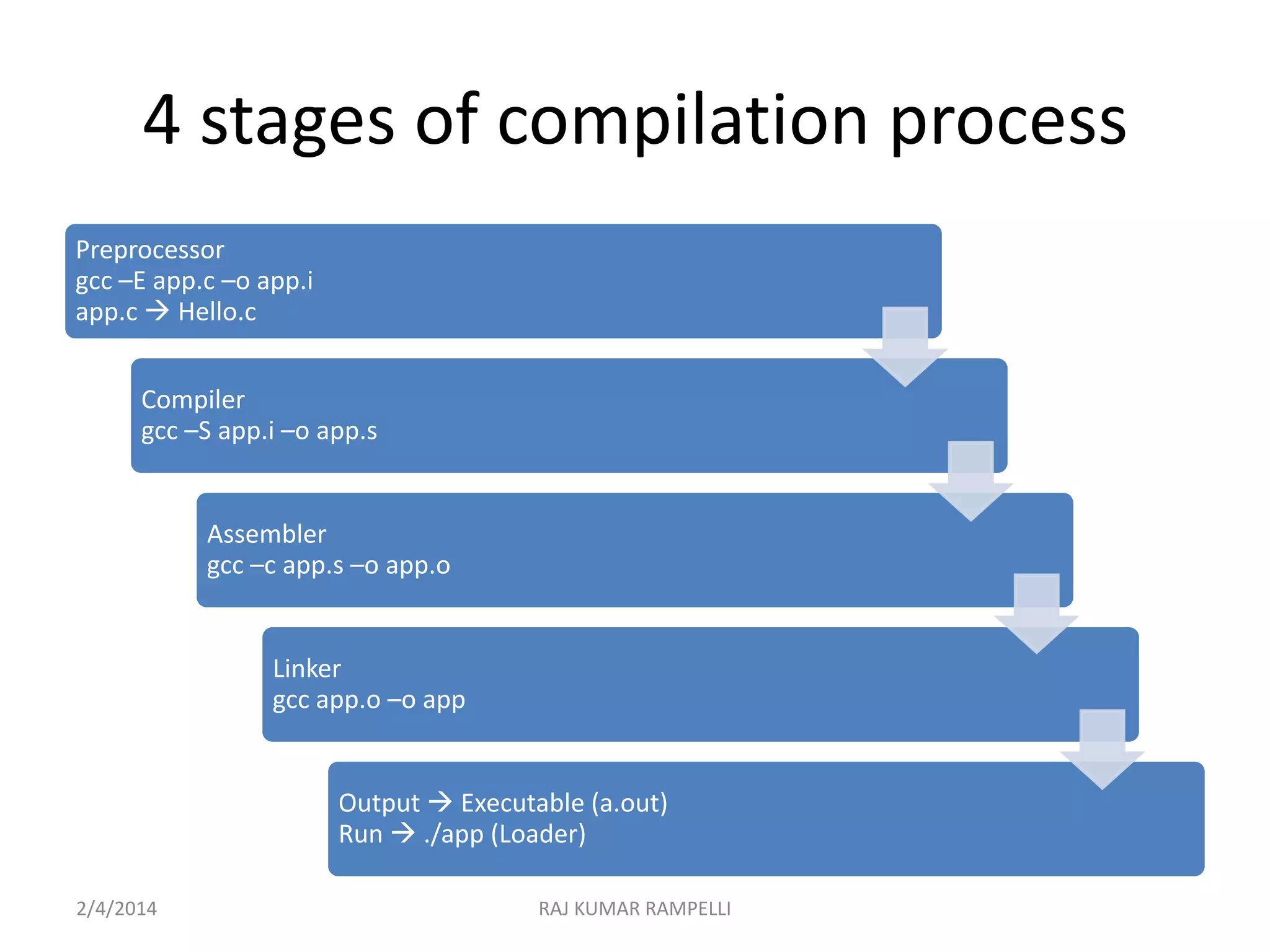
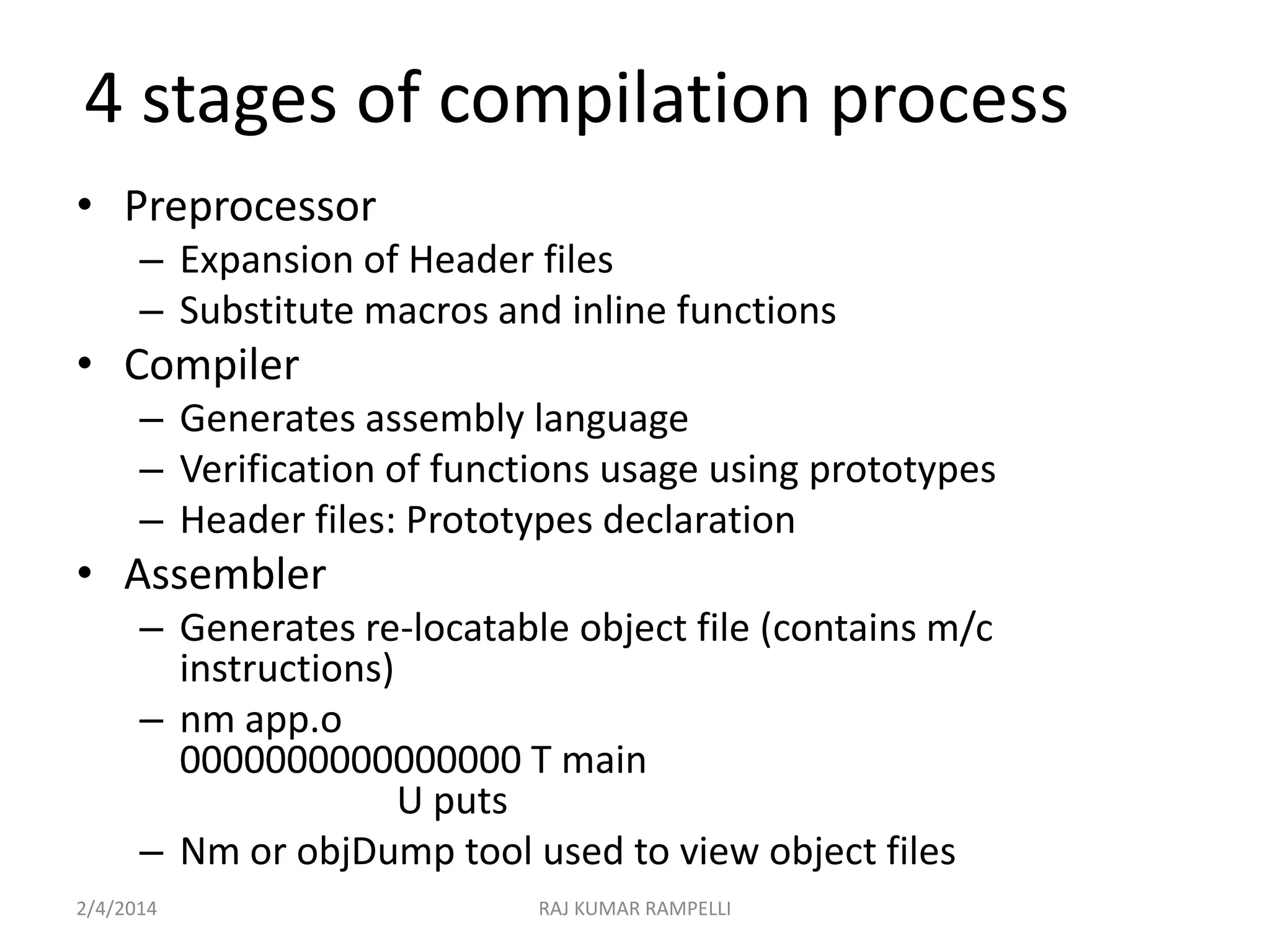
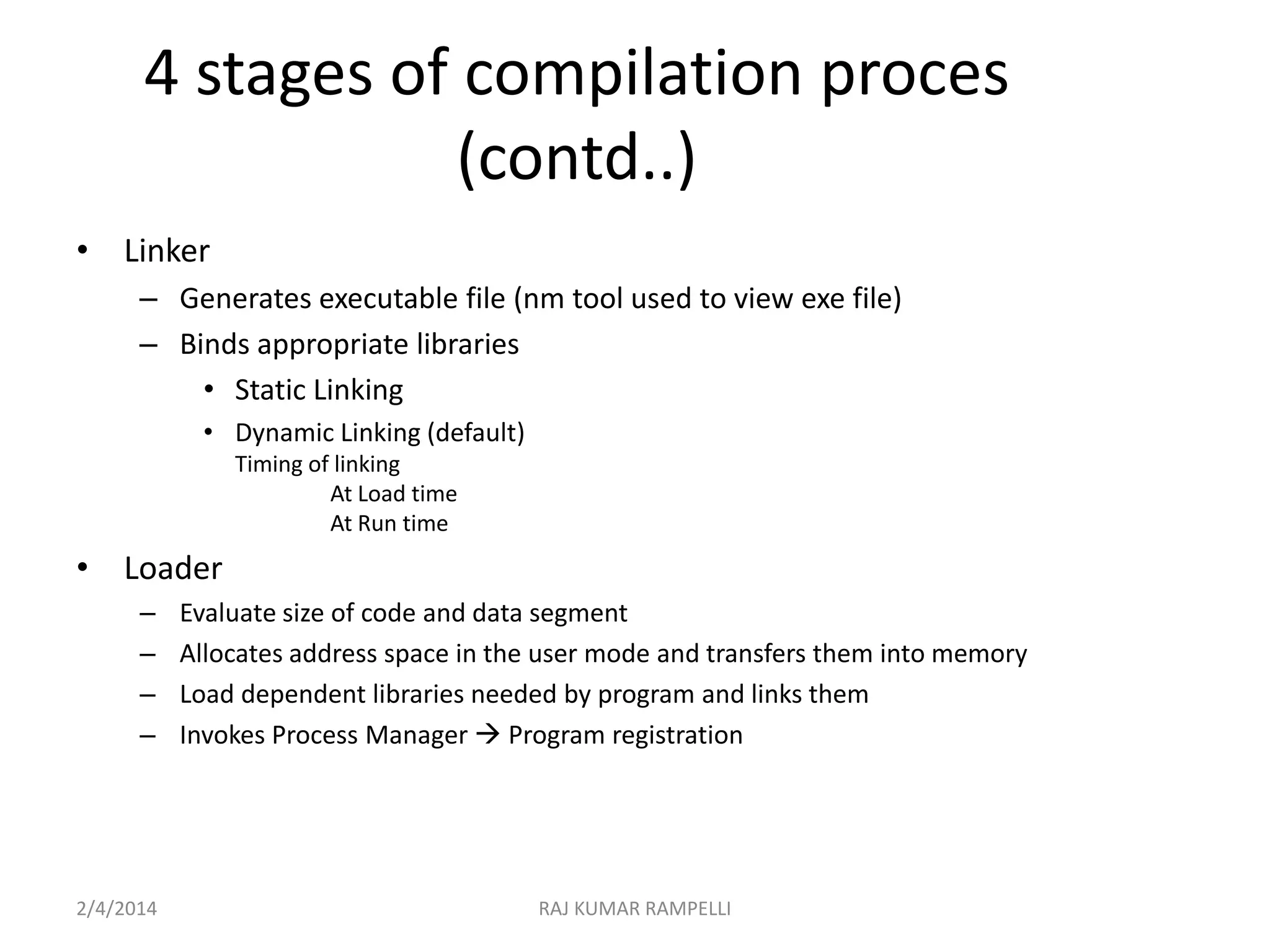
The document outlines the compilation process in C, detailing the four main stages: preprocessing, compiling, assembling, and linking, along with the respective commands using the GCC compiler. It explains the purpose of each stage, such as macro substitution in preprocessing and generating an executable file through linking. Additionally, the document provides instructions for compiling and linking multiple source files and libraries.