This document discusses programming in C with questions and answers. It covers topics like the program development cycle, features of a good programming language, algorithms and flowcharts to find the product of first n natural numbers and the largest of three numbers. It also explains the structure of a C program, steps to execute a C program, basic and qualifier data types, formatted and unformatted input/output functions.

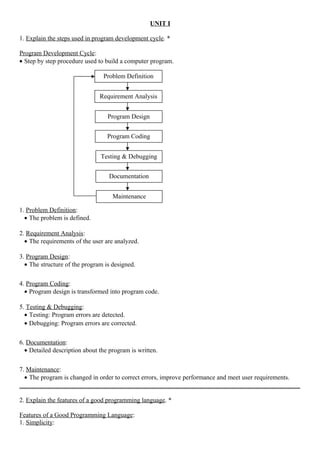

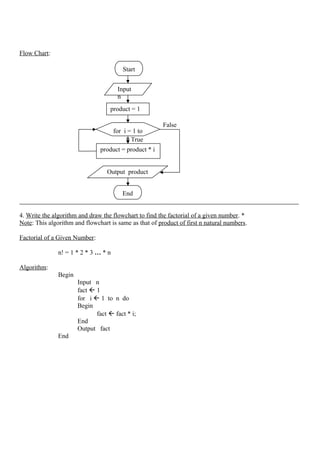
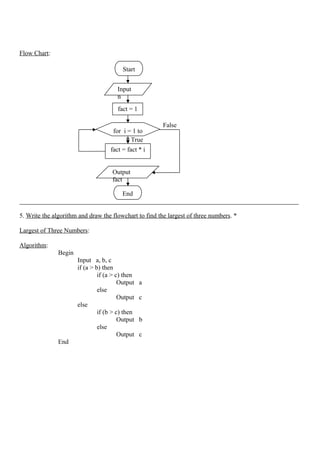
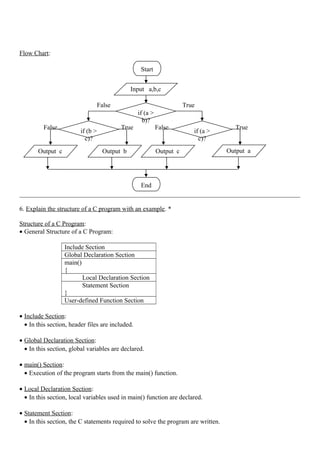

![• Printing Integer:
Example:
int x = 2000; Output:
printf(“%d”, x);
• Printing Float:
Example:
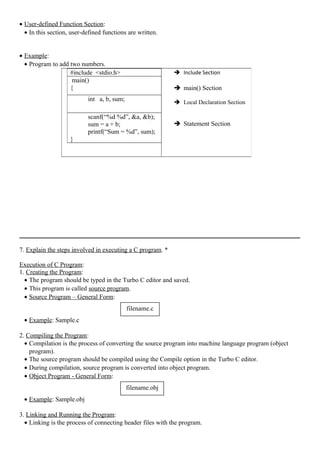
float x = 123.4567 Output:
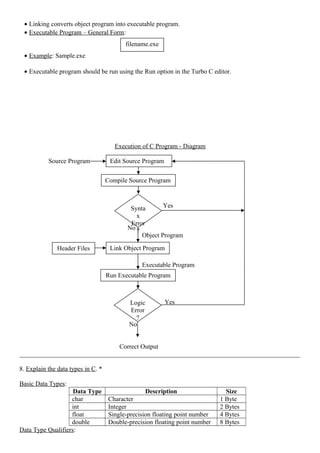
printf(“%8.4f”, x);
• Printing String:
Example:
name = “Kandan”; Output:
printf(“%s”, name);
_______________________________________________________________________________________
10. Explain the unformatted input and output functions in detail. ***
Unformatted Input Functions:
• getchar():
• Used to read a character from the keyboard.
• General Form:
• Example:
char a;
a = getchar();
• gets():
• Used to read a string from the keyboard.
• General Form:
• Example:
char a[10];
gets(a);
Unformatted Output Functions:
• putchar():
• Used to display a character on the monitor.
• General Form:
• Example:
putchar(‘K’);
• puts():
2 0 0 0
1 2 3 . 4 5 6 7
K a n d a n
variablename = getchar();
gets(variablename);
putchar(variablename);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingincnotes-180625124036/85/Programming-in-c-notes-10-320.jpg)
