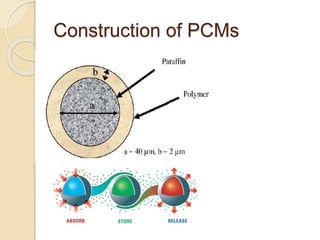
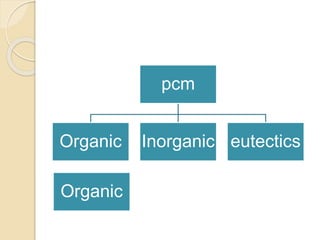
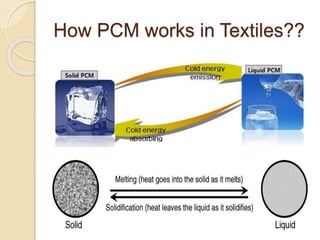
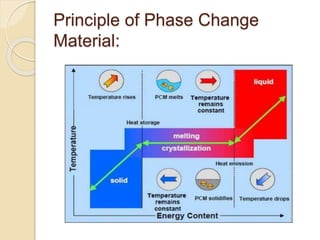
This document discusses phase change materials (PCMs) and their incorporation into textiles. PCMs can absorb, store, and release large amounts of heat as they change phase between solid and liquid. The document defines PCMs and how they work in textiles, describing methods of incorporating PCMs such as filling, impregnating fibers, coatings, and foam dispersion. It also discusses testing of PCM-incorporated textiles and their properties, as well as applications, challenges, opportunities, and limitations.



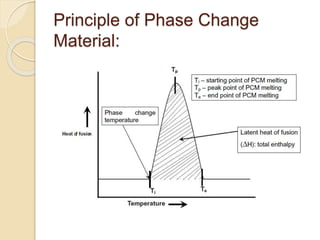

![PCMs Defination
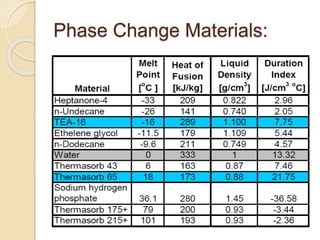
Heat of Fusion [kJ/kg]:
Amount of energy required to melt
one kg.
Duration Index [J/(cm3*oC)]:
Comparison of how long a PCM will
remain at a constant temperature
during the phase change.
Calculated as: D.I. = hf ρ / ΔT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcm-140808084730-phpapp01/85/phase-changing-material-9-320.jpg)