Knee joint.doca
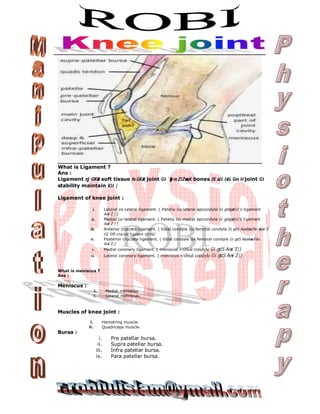
- 1. What is Ligament ? Ans : Ligament nj GKwU soft tissue hv GKwU joint Gi `yyB ev Z‡ZvwaK bones ‡K a‡i iv‡L Ges H joint Gi stability maintain K‡i | Ligament of knee joint : i. Lateral co-lateral ligament. ( Patella Ges lateral epicondyle Gi gvSvgvwS†Z G ligament Aew¯’Z | ) ii. Medial co-lateral ligament. ( Patella Ges medial epicondyle Gi gvSvgvwS†Z G ligament Aew¯’Z | ) iii. Anterior cruciate ligament. ( tibial condyle Ges femoral condyle Gi gv‡S AvovAvwofv‡e &Aew¯’Z e‡j G‡K cruciate ligament ejv nq| iv. Posterior cruciate ligament. ( tibial condyle Ges femoral condyle Gi gv‡S AvovAvwofv‡e Aew¯’Z|) v. Medial coronary ligament. ( meniscus ও tibial condyle Gi gv‡S Aew¯’ Z|) vi. Lateral coronary ligament. ( meniscus ও tibial condyle Gi gv‡S Aew¯’Z|) What is meniscus ? Ans : Meniscus : i. Medial meniscus. ii. Lateral meniscus. Muscles of knee joint : i. Hamstring muscle. ii. Quadriceps muscle. Bursa : i. Pre patellar bursa. ii. Supra patellar bursa. iii. Infra patellar bursa. iv. Para patellar bursa.
- 2. Muscle injury : Muscle injury n‡j H muscle Gi resisted test positive or painful Ges opposite passive movement positive n‡e| Ligament test : Lateral co-lateral ligament test : ( Varus test ) Knee flex n‡e 5- 10º . Medial co-lateral ligament test : ( Valgus test ) Knee flex n‡e 5- 10º. Anterior Cruciate Ligament : ( Anterior Dawer Test ). Posterior Cruciate Ligament: (Posterior Dawer Test ). Miniscus Test : Medial & Lateral Miniscus : ( Mckmarry Test ). Medial Gi ‡ÿ‡Î tibiaÕi lateral rotation Ges Lateral Gi ‡ÿ‡Î medial rotation কের “D” Shape Ki‡Z n‡e. Sign & Symptoms of Injury ( Knee Joint ) Miniscus injury : Sudden traumatic cause. Sign : Immediate loss of function. Swelling. Symptoms : Twings – Sharp pain during knee flexion & extension. Locking –flexion I extension G AvuU‡K hvIqv . Giving way – tibia mvg‡bi w`‡K P‡j hvIqv. Ligament Injury : Main injury nq MCL, M.miniscus & M.coronary ligament G. Pain – started after 1-2 hrs. Healing stage of Soft tissue : 0-5 days – Inflammatory stage. ( Leukocyte,Lymphocyte & macrophage– blood cell for healing soft tissue.) 5-21 days – Repair stage. 3 complication are founds in this stage – Cross linking. Excessive scar. Adhesion.
- 3. 21 day -6 month+ – Remodeling stage. Treatment for reduce this complication Inflammatory stage : PRICE – 0-5 days. P = Protection – by Creps bandage, Plaster of parries, Back slab. R = Rest. I = Ice. C = Compression. E = Elevation. Repair stage : 05-21 days. PRICE- continue. GTFM – Gentle Transverse Friction Massage. Pain free mobilization. ( Pain limitation ) Electrical modalities – UST/Wax, & LASER. Tapping. Gentle stretching. Remodeling stage : DTFM – Deep Transverse Friction Massage. Strong stretching. ROM mobilization. Manipulation. UST. Balance, co-ordination & proprioception ex’s. Proprioception : Joint position sense. Stage of Injury : 1. Acute – 2 wk. 2. Sub-acute – 2-5 wk. 3. Chronic – 6+ wk. Treatment of Knee Joint Friction. Mulligan.− Caudal (non weight) & lateral glide-1st wk. Caudal (MWM) after 1st wk. Mobilization. Manipulation. Manipulation of Knee Joint : Miniscus manipulation. Loose body flexion manipulation. Loose body flexion rotation manipulation. Loose body extension varus manipulation. MCL manipulation towards flexion. MCL manipulation towards medial rotation. MCL manipulation towards lateal rotation. Miniscus Injury :
- 4. Loss of function. ( Immediately ) Swelling. Haematoma. Adhesion – MCL (test) : Passive extension + lateral rotation.(Slight pain) Valgus strain – Markedly painful. Flexion – ROM (5˚-10˚) limited. Pain is felt medially. Examination of patient (
- 5. Shoulder Joint Shoulder Capsulitis : 3 question – symptoms : Can you lie on that side at night. Is there any pain at rest. Has the pain spread below elbow. Sign : LAM L = Lateral rotation. A = Abduction. M = Medial rotation.
- 6. Causes of Frozen shoulder : Capsulitis. O.A . Traumatic arthritis. # of humerus. Immobilize – prolong time by POP. Stage : 3 unfavorable ans – stage ІІ 3 favorable ans – stage І 2 favorable+1 unfavorable ans – stage ІІ- 2 unfavorable+1 favorable ans – stage ІІ+ Stage-I – 15 days below ─ no physiotherapy. Only pain killer, heat therapy, SWD, UST/IFT. Management – after 15 days- o Mulligan’s mobilization. (continue) o Home stretching – after 70%-80% Functional Examination : Active abduction/elevation : Diagnosis : Capsular pattern. Shoulder fold. ROM. Tendonitis / Muscle injury. Hard end feel. ( Osteo Arthrosis ). Passive elevation : Diagnosis : Capsular pattern. Shoulder fold. ROM. Tendonitis / Muscle injury. Hard end feel. ( Osteo Arthrosis ). Painful arc : Painful arc is a painful section between two pain free section. Generally 90˚-120˚. Causes of painful arc – Subacromion bursitis. Acromio-clavicular jt. ligament lesion. Supraspinatus tendonitis.
- 7. Passive abduction ( Glenohumoral jt.) : GH(90˚)+ ST(150˚)+ GH(180˚). Diagnosis : Capsular pattern. Shoulder fold. ROM. Tendonitis / Muscle injury. Passive Lateral Rotation : Diagnosis : Anterior capsule shortening. Medial rotator muscle lesion. Capsular pattern. AC joint ligament lesion. Passive Medial Rotation : Diagnosis : posterior capsule shortening. lateral rotator muscle lesion. Capsular pattern. AC joint ligament lesion. Resisted Adduction : Diagnosis : Adductor muscle lesion / tendonitis. Resisted Abduction : Diagnosis : Abductor muscle lesion / tendonitis. Resisted Medial Rotation : Diagnosis : Medial rotator muscle lesion / tendonitis. Resisted Lateral Rotation : Diagnosis : Lateral rotator muscle lesion / tendonitis.
- 8. Resisted Elbow Flexion : Diagnosis : Flexor muscle lesion / tendonitis. Resisted Elbow Extension : Diagnosis : Extensor muscle lesion / tendonitis. Passive Horizontal Adduction : Diagnosis : AC lesion. Subscapularis muscle injury / tendonitis. Sub coracoid bursitis. Muscle – for movt. Of shoulder joint : Adduction : Pectoralis major.(Anterior) Latissimus dorsi.(Posterior) Teris major- Posterior side pain + resisted medial rotation positive/painful. Teris minor- Posterior side pain + resisted lateral rotation positive/painful. Subscapularis muscle : Action – Medial rotation. (Pain on anterior side). - Initial abduction.(0˚-30˚) Abduction : Subscapularis muscle. Deltoid muscle fiber. Elbow flexion : Biceps. Brachialis. Elbow extension : Triceps. Sub deltoid bursitis :