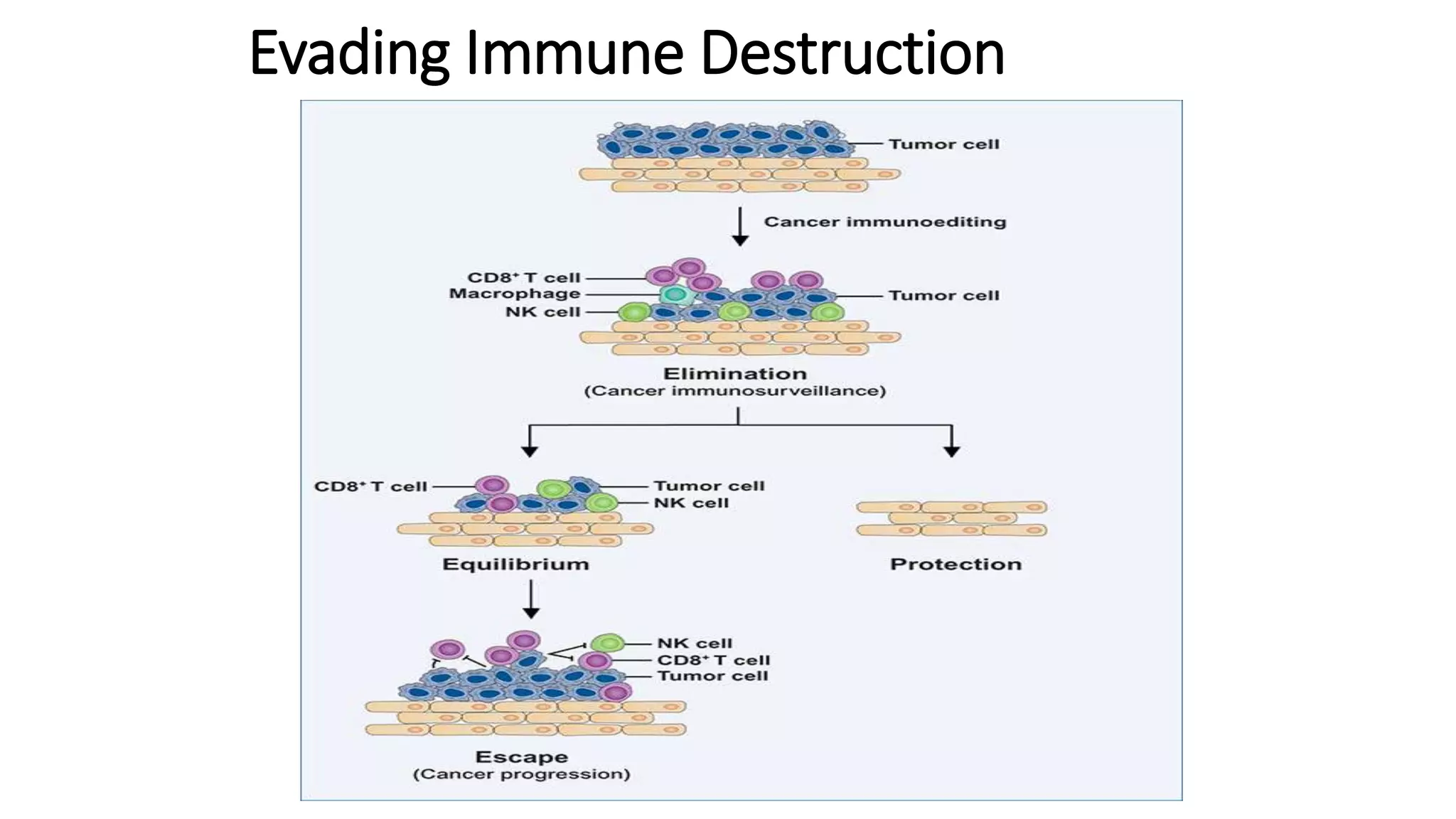
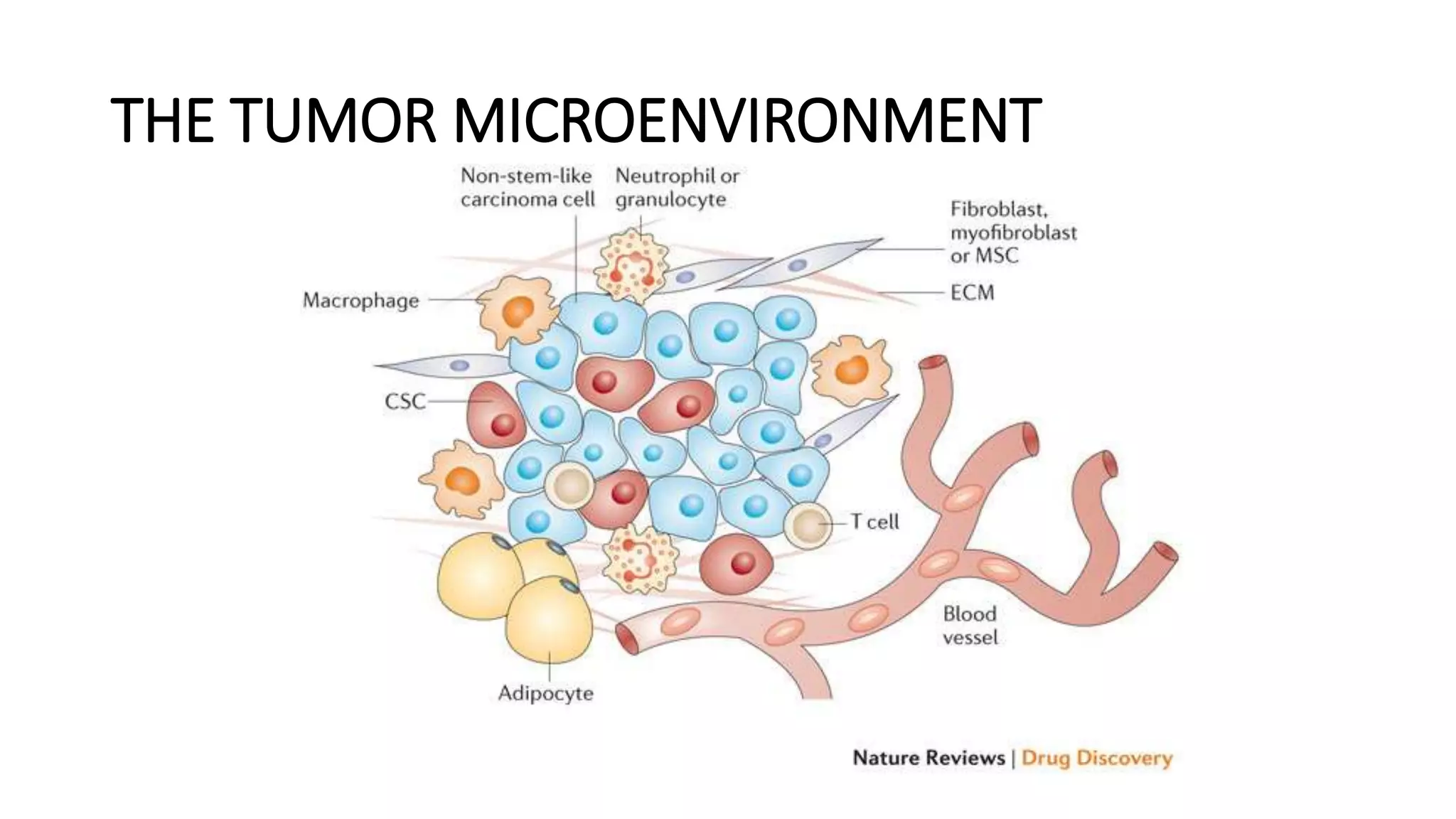
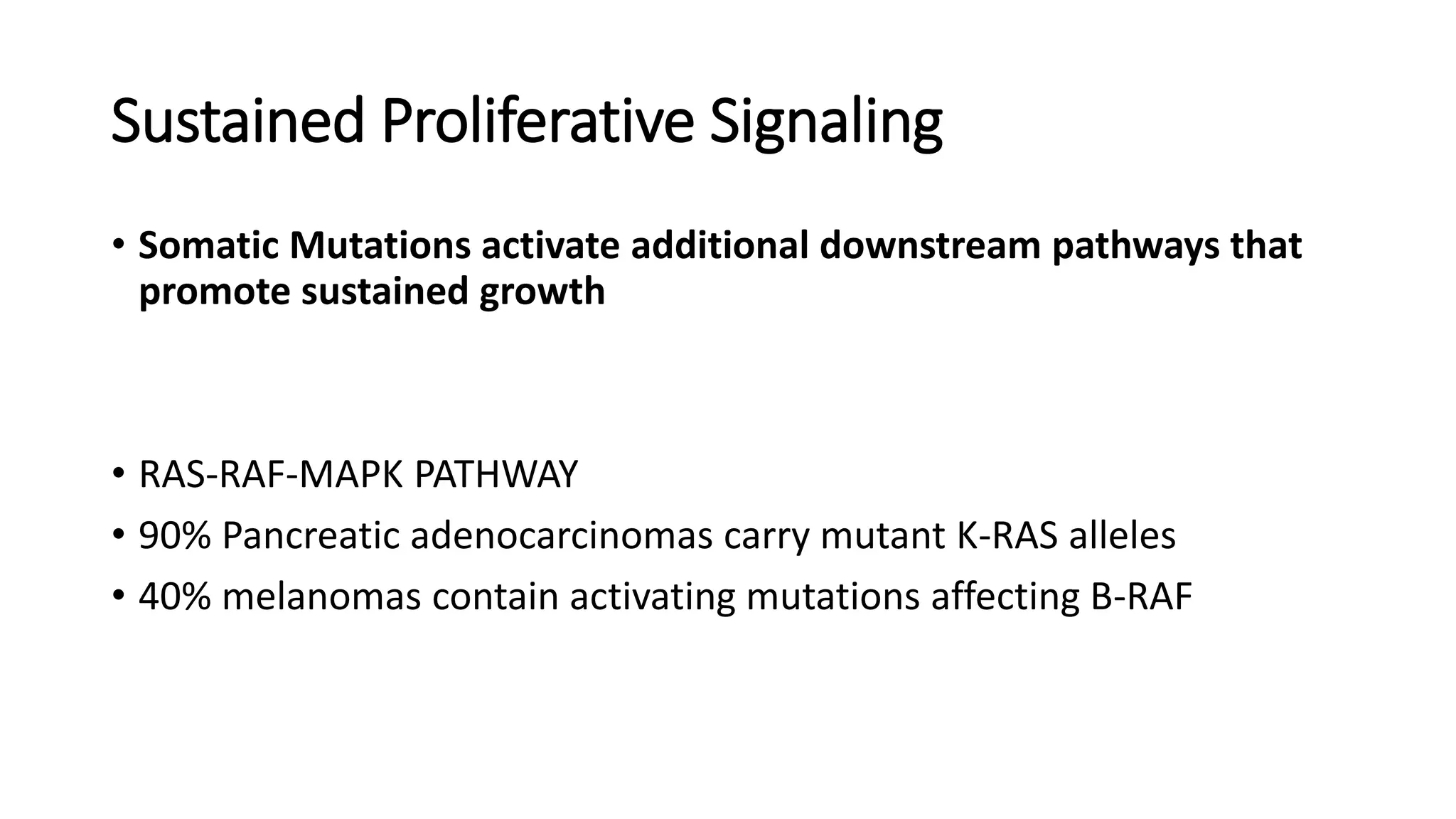
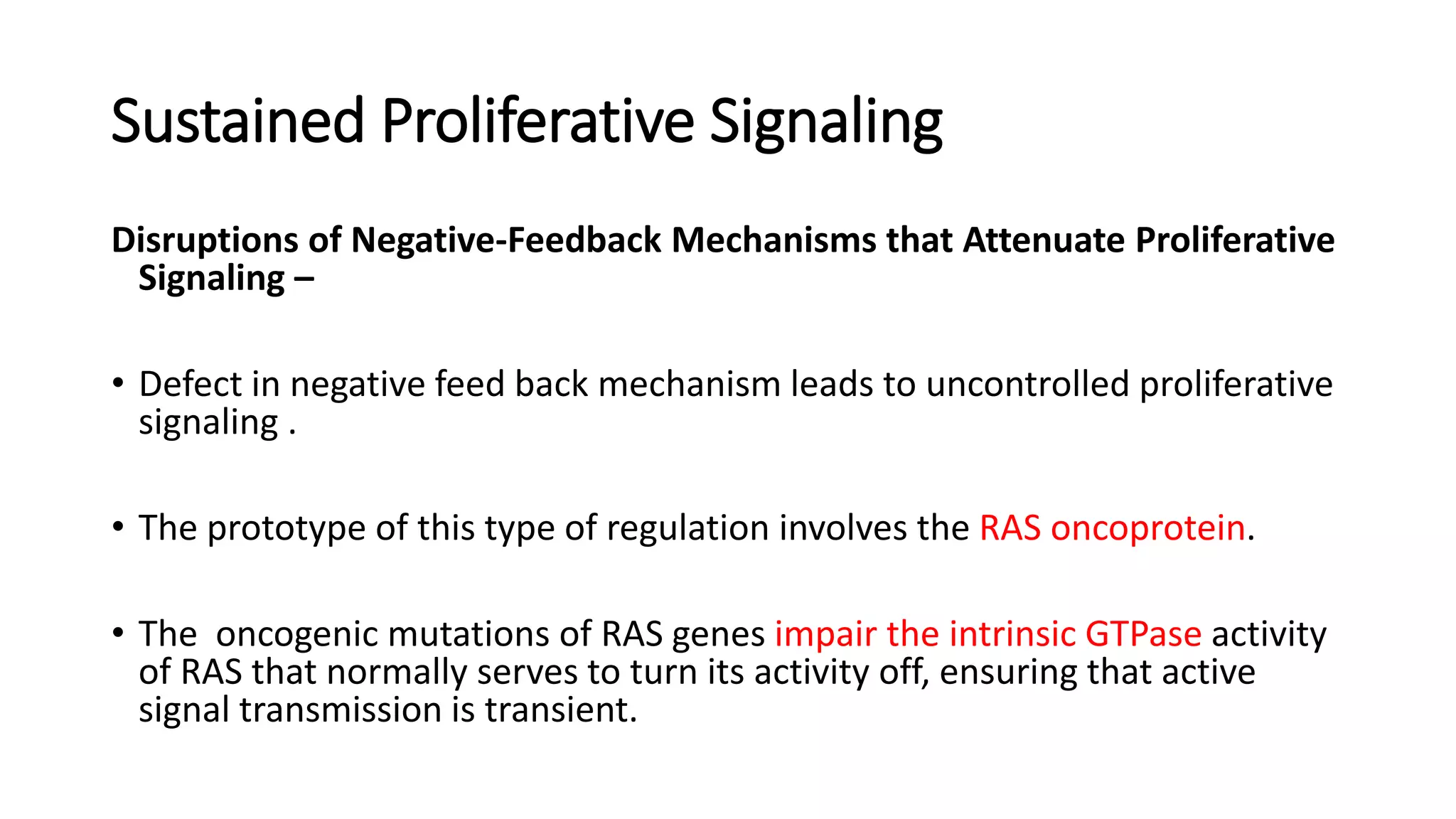
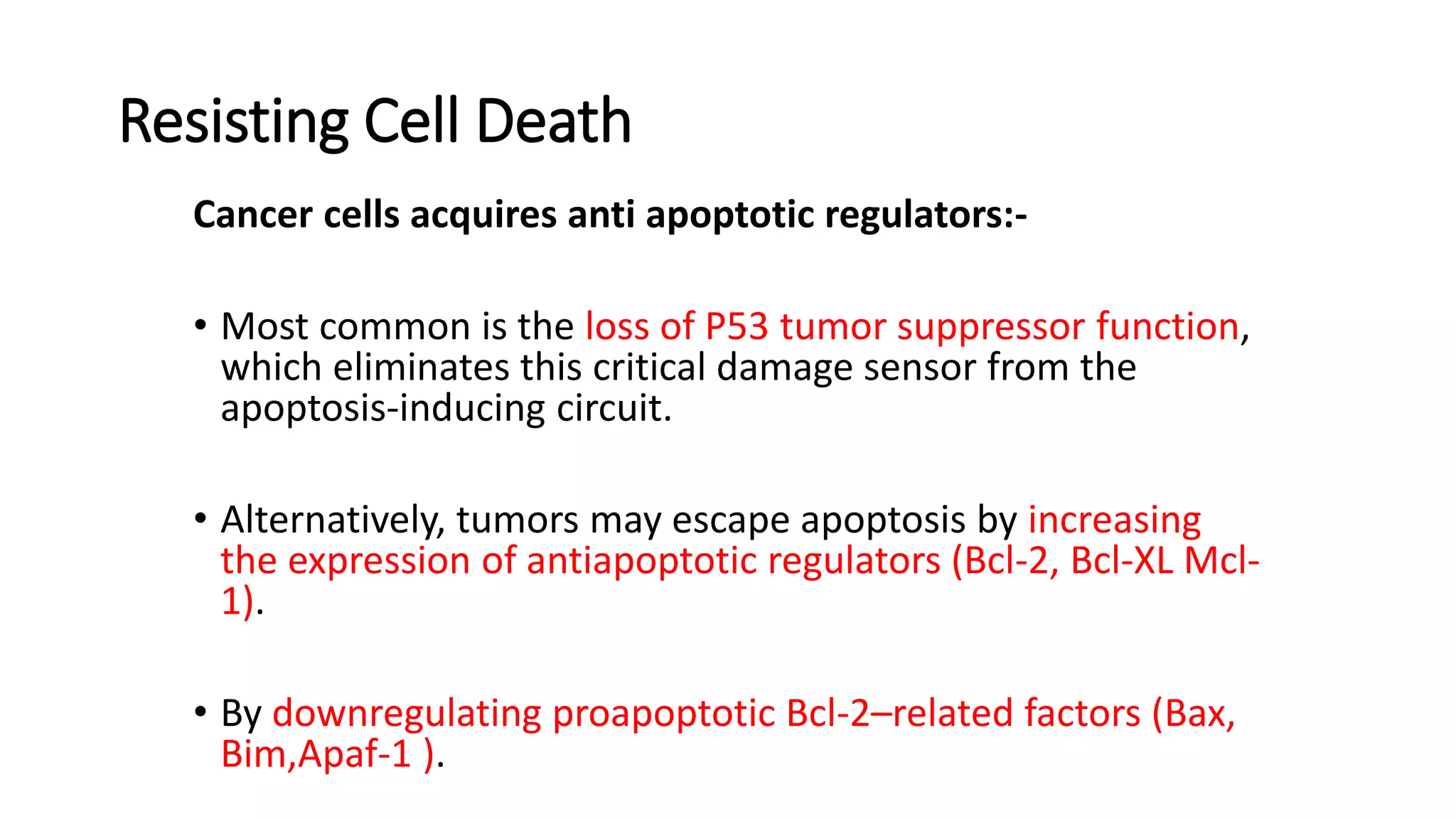
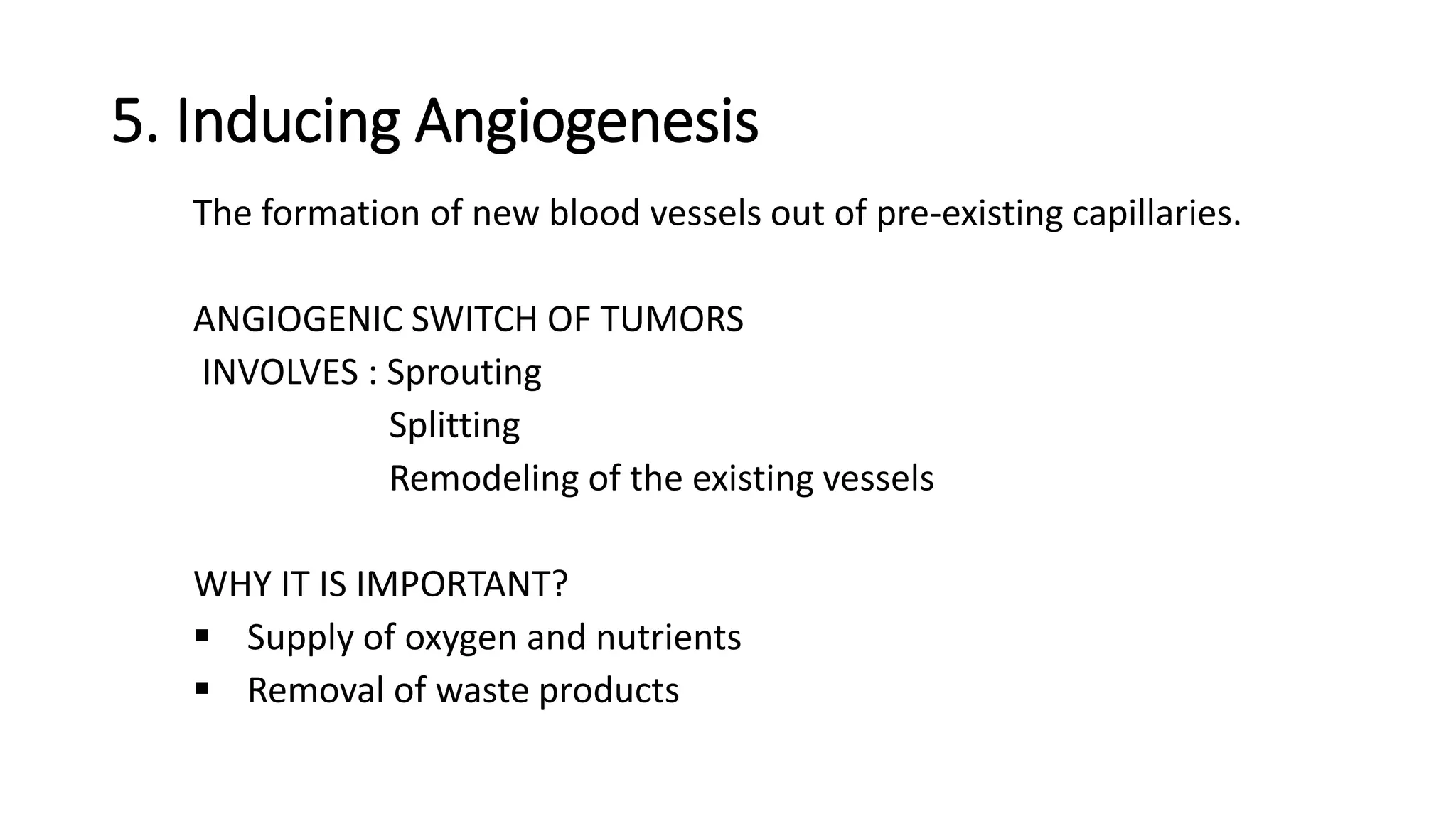
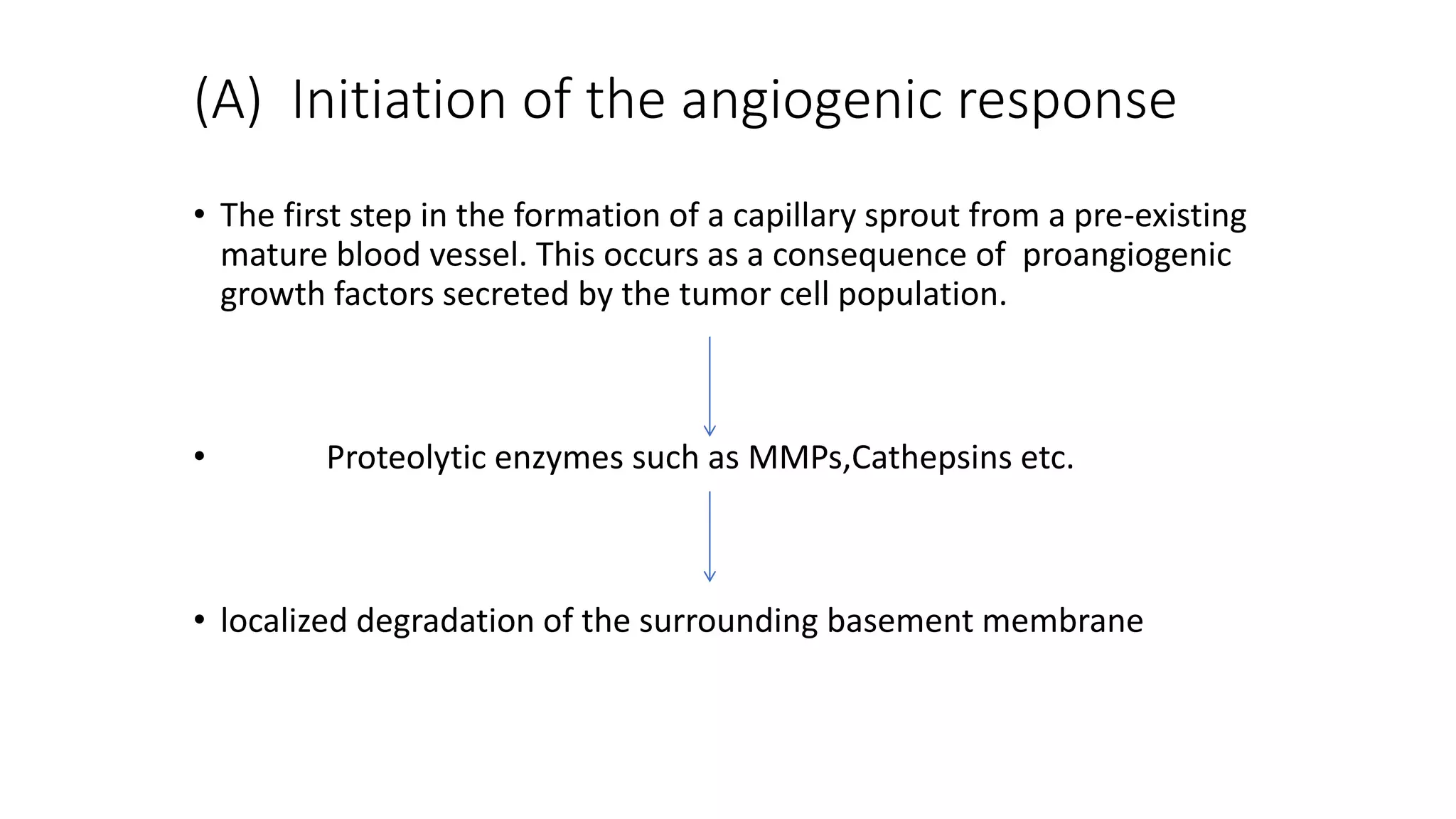
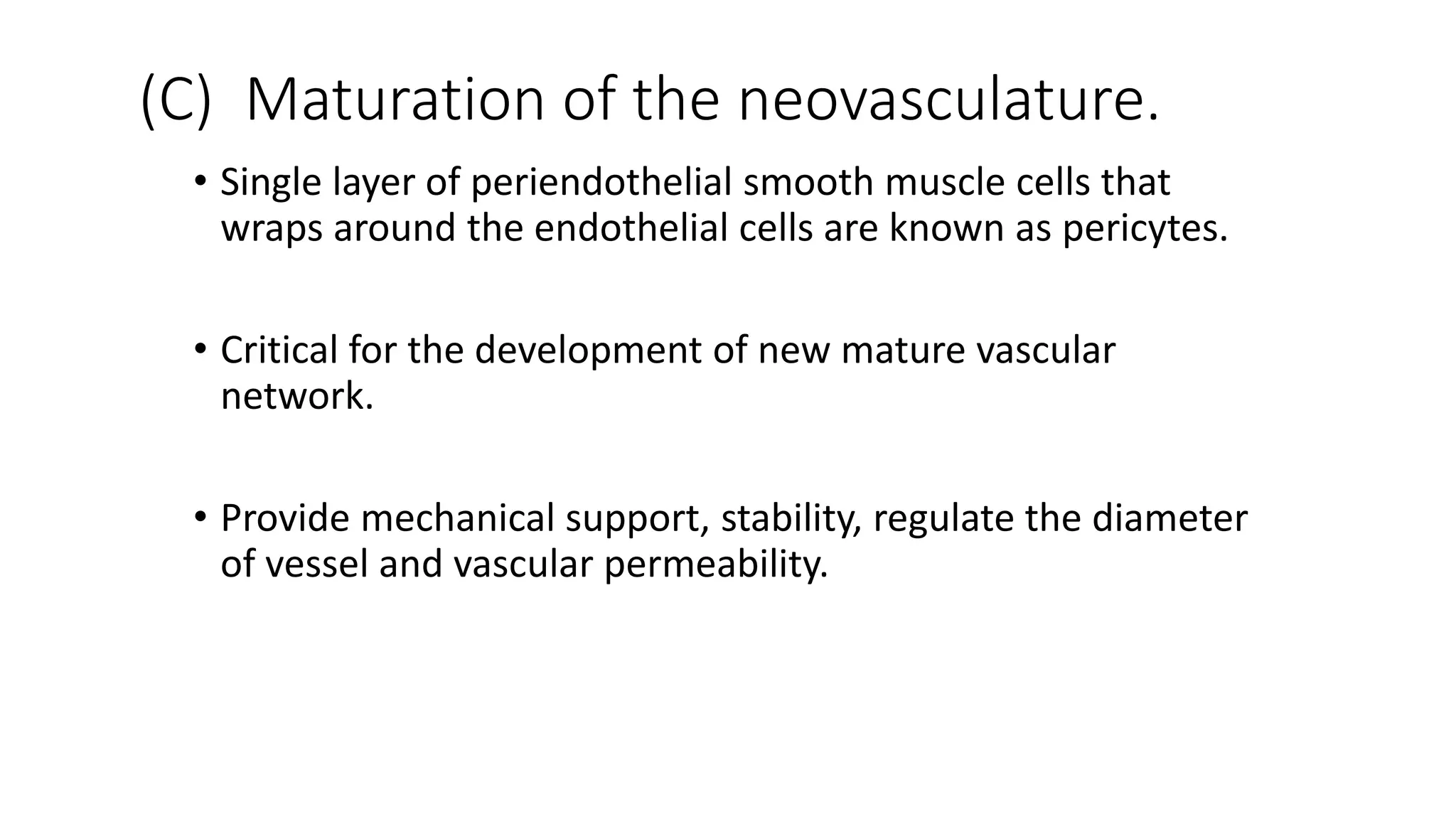
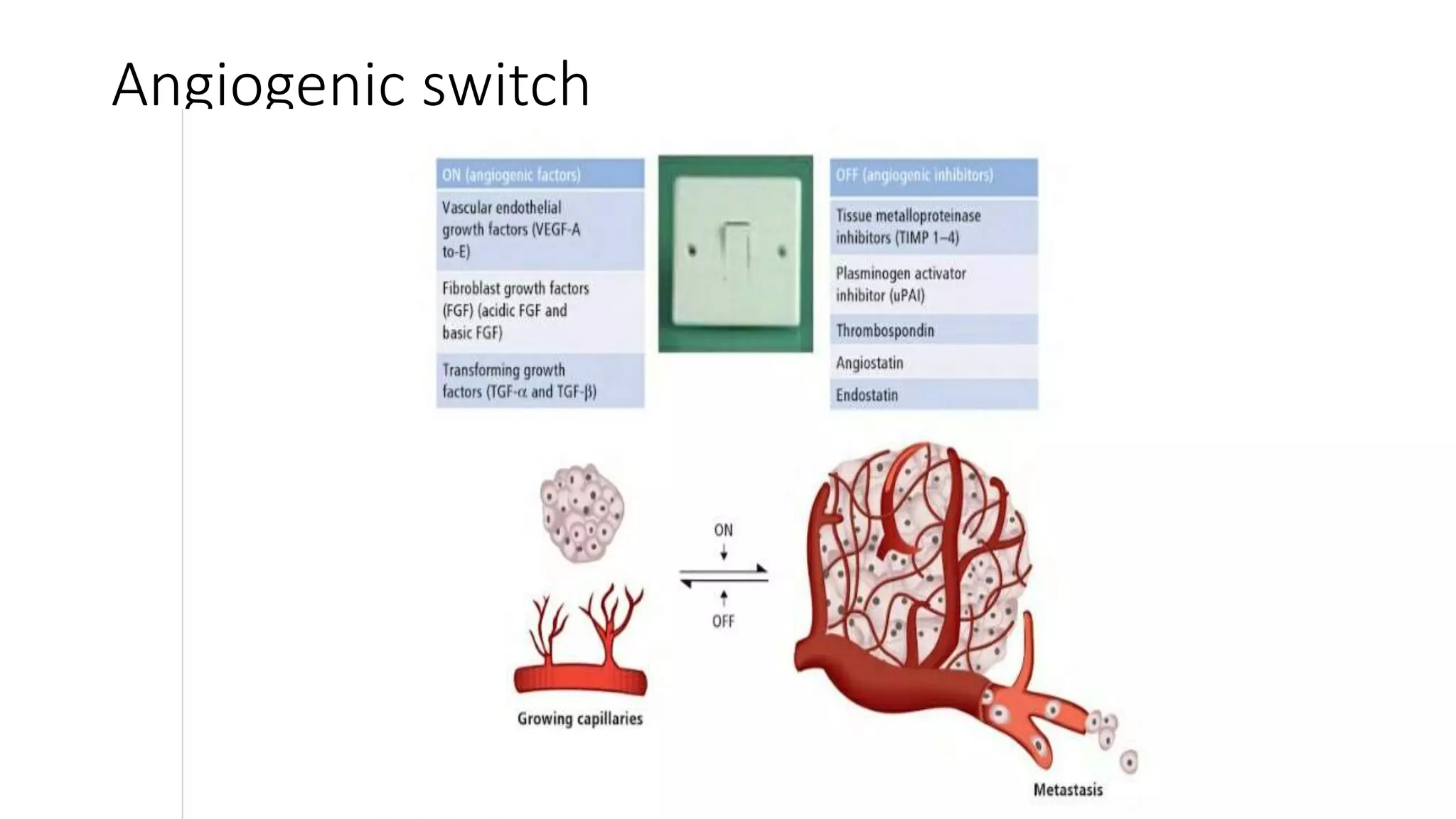
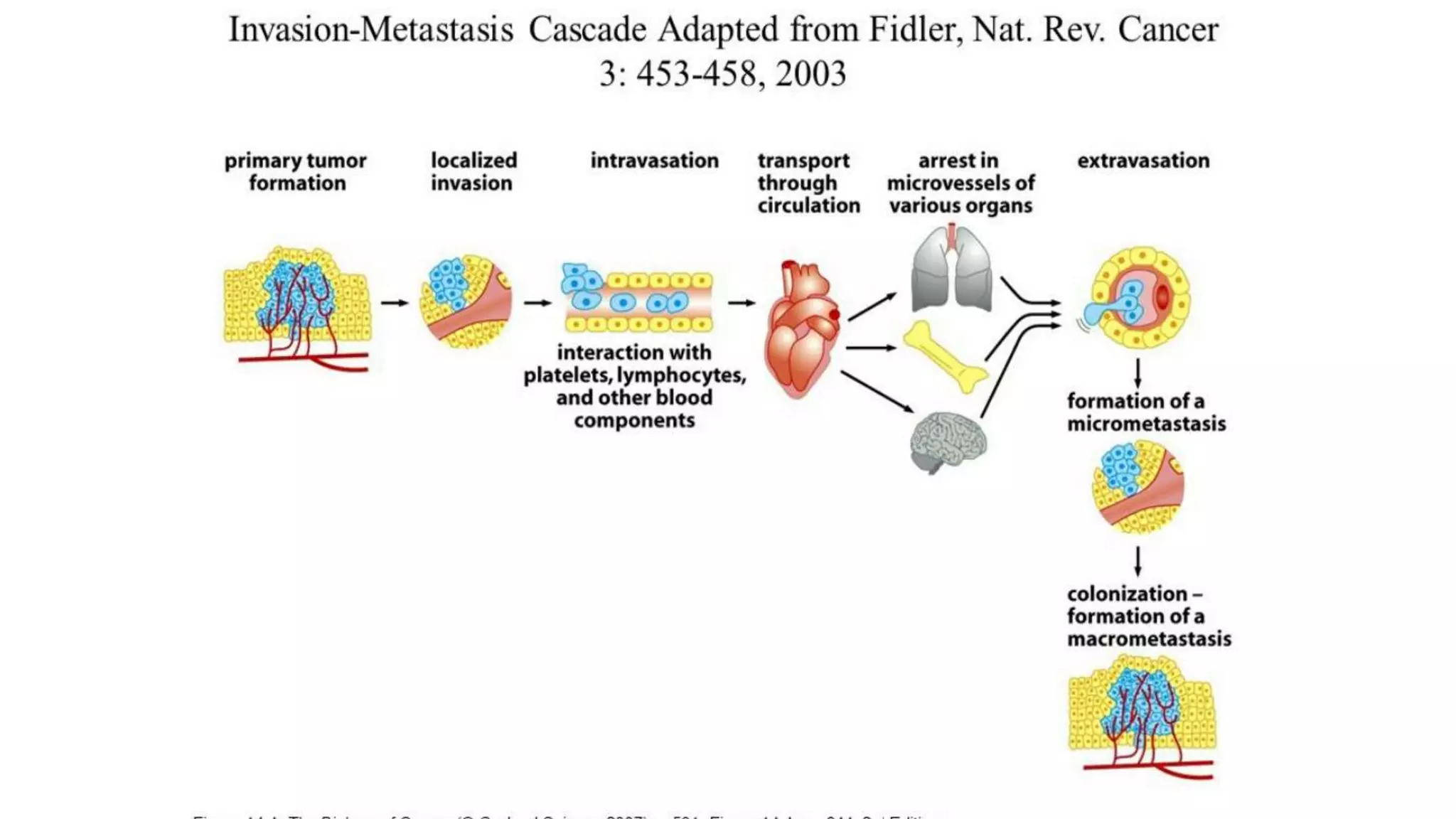
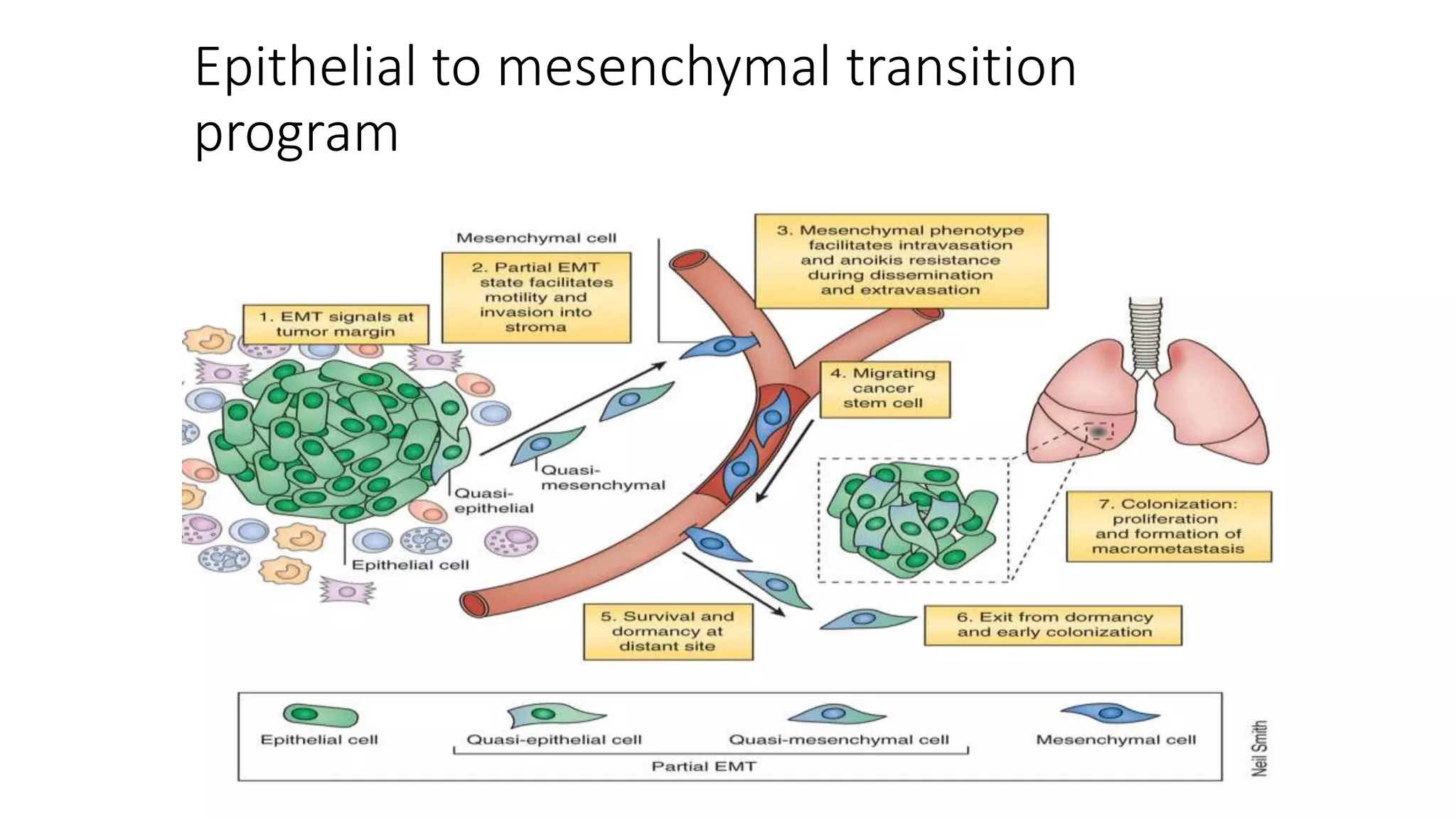
The document discusses the eight hallmarks of cancer identified by Hanahan and Weinberg: 1) sustaining proliferative signaling, 2) evading growth suppressors, 3) resisting cell death, 4) enabling replicative immortality, 5) inducing angiogenesis, 6) activating invasion and metastasis, 7) evading immune destruction, and 8) deregulating cellular metabolism. It provides details on the molecular mechanisms cancer cells use to acquire these hallmark capabilities, such as generating their own growth signals, inactivating tumor suppressors, increasing anti-apoptotic factors, maintaining telomeres, secreting angiogenic factors, enhancing proteases, and adapting metabolism.

































![Mutation in metabolic enzymes
causing cancer
• FH[fumarate hydratase]– metabolizes fumarate in
TCA…mutation leads to RCC ,leiomyomas.
• IDH [ isocitrate dehydrogenase]– in glioma, glioblastoma,
AML, myelodysplastic syndrome,ALL, prostate, colorectal
cancer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3hallmarksofcancer-191105204755/75/Chapter-3-hallmarks-of-cancer-43-2048.jpg)