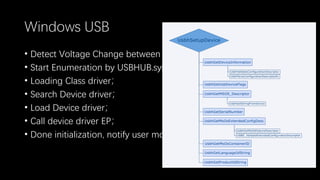
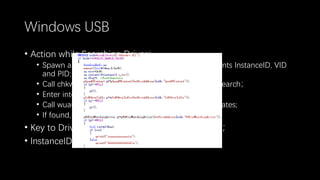
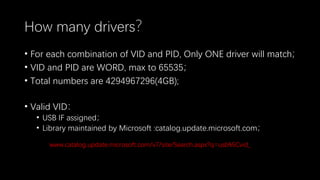
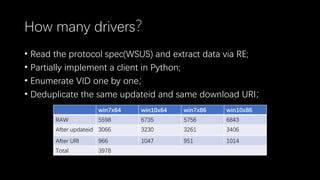
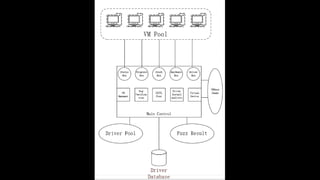
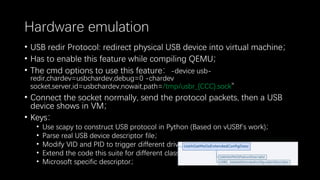
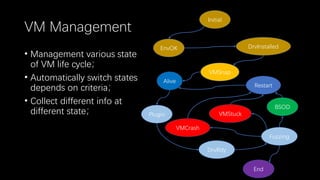
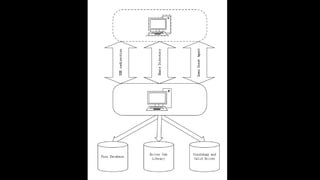
This document discusses a massive fuzzing system for USB device drivers on Windows, addressing the challenges of analyzing closed-source drivers installed via Windows Update. It outlines the architecture of the fuzzing system, including techniques for monitoring and testing without physical hardware, and emphasizes the importance of controlling various system states during the fuzzing process. The goal is to identify vulnerabilities in driver implementations to enhance system security.