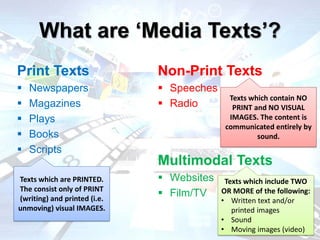
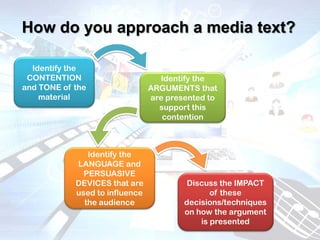
This document defines and categorizes different types of media texts. Print texts include newspapers, magazines, books and scripts which use only written text and printed images. Non-print texts such as speeches and radio use sound without visuals. Multimodal texts like websites and films incorporate two or more modes such as written text, printed images, sound and moving images. The document also discusses analyzing media texts by examining their context, purpose, intended audience, construction and persuasive techniques.