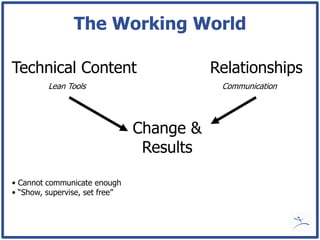
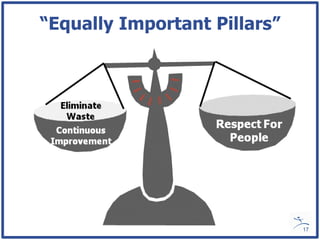
Mark Graban provides an overview of how lean thinking can help hospitals by reducing waste and errors. He discusses the need for lean in healthcare given constraints on resources and high rates of preventable errors. Graban also shares lessons learned from his experience implementing lean as an industrial engineer and consultant, emphasizing the importance of engaging employees and focusing on systems rather than individuals when problems occur.




























![Lack of Lean Leadership
“This [lean] is not the
standard model executive
being produced by U.S
business schools, much
less American medical
schools.”
– Toussaint and Gerard, On the Mend
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/markgraban-utahstatestudents2010-100414200534-phpapp02/85/Mark-Graban-How-Lean-Thinking-Helps-Hospitals-33-320.jpg)