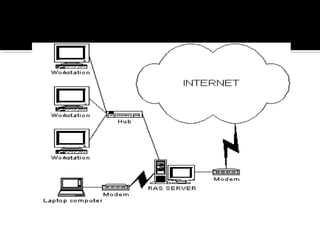
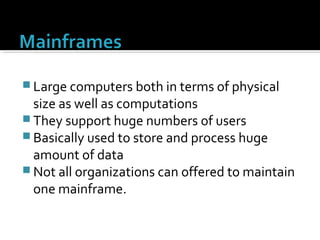
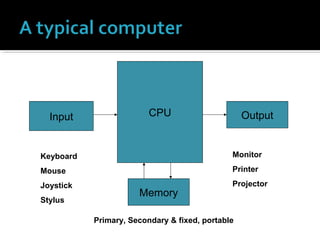
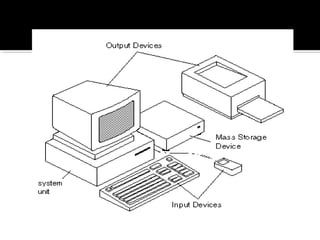
The document discusses different types of computers including personal computers, laptops, network computers, mini and microcomputers, mainframes, and supercomputers. It provides details on their typical uses, key characteristics, and how they compare to each other. For example, it notes that personal computers can be used for a variety of activities at home or work while laptops are more compact and portable but have less storage capacity than desktop PCs.