Embed presentation
Download to read offline




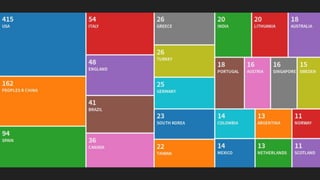
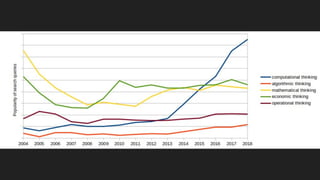


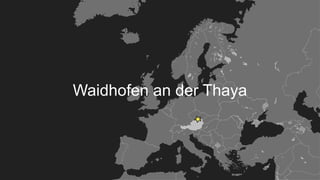


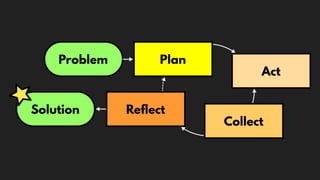

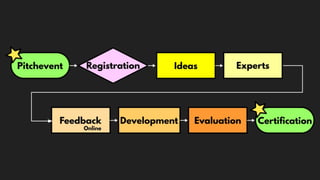



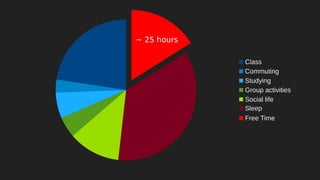






This document discusses integrating practitioner expertise into computational thinking education. It defines computational thinking as recognizing computation in the world and applying computing tools to understand natural, social, and artificial systems. The document then discusses a small-scale experimental setting in Waidhofen an der Thaya, Austria to test lessons learned. It outlines the research design, ideas, outcomes, conclusions and future work to improve computational thinking education through external partnerships.























