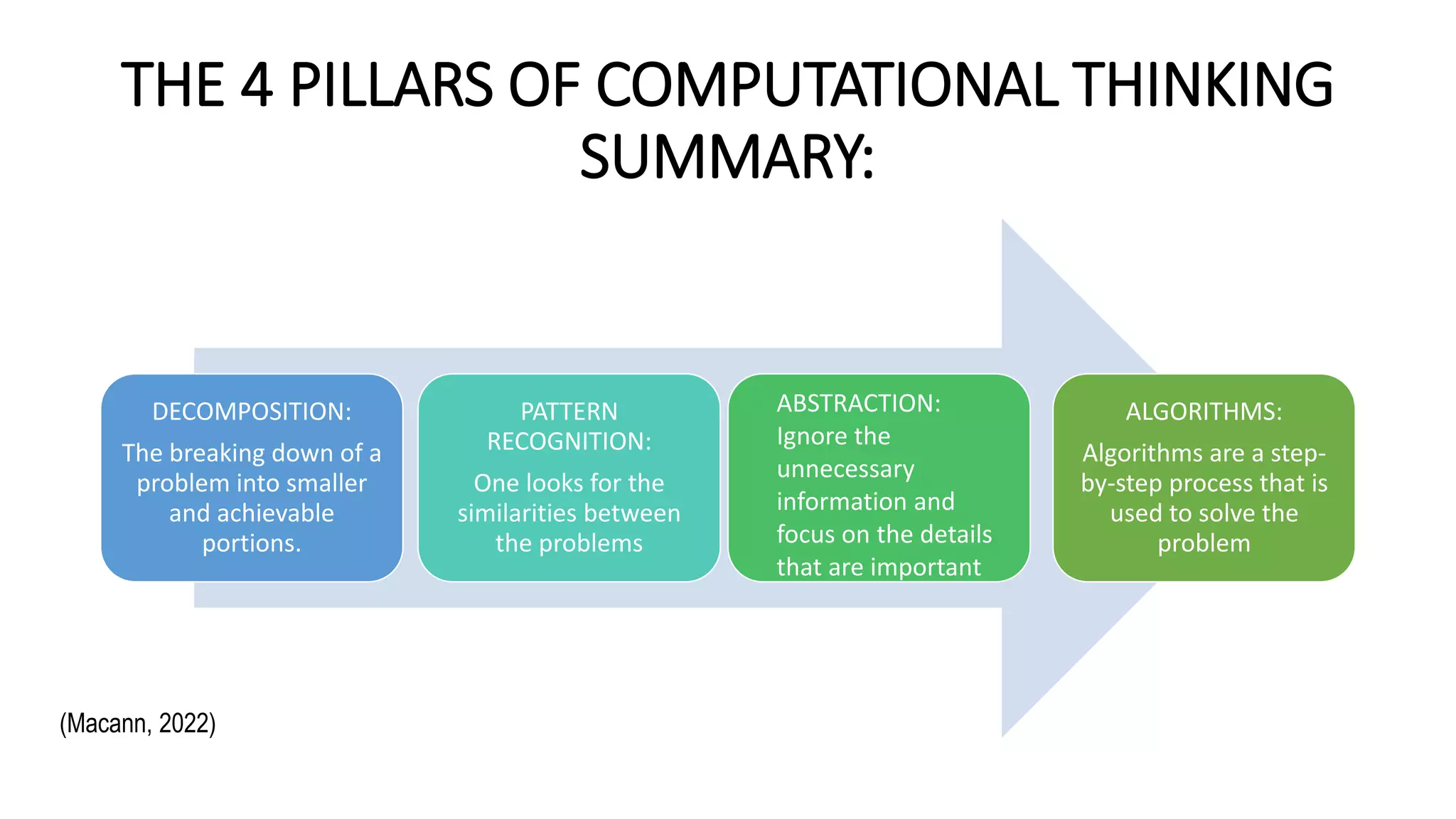
Computational thinking (CT) is the process of breaking complex problems into manageable steps, similar to how computers solve issues. It is based on four pillars: decomposition, abstraction, pattern recognition, and algorithms, each contributing to effective problem solving. Teaching CT in schools fosters innovation, enables learners to produce knowledge, and equips them with skills necessary for navigating a technology-driven world.




![REFERENCES:
• Cummins, K., 2020. Five reasons why computational thinking is an essential tool for teachers and students. — Innovative Teaching Ideas.
[online] Innovative Teaching Ideas. Available at: https://innovativeteachingideas.com/blog/five-reasons-why-computational-thinking-is-an-
essential-tool-for-teachers-and-students [Accessed 10 October 2022].
• Macann, V., 2022. The 4 parts of computational thinking in the digital technologies curriculum > Learning Architects. [online] Learning
Architects. Available at: https://www.learningarchitects.com/the-4-parts-of-computational-thinking-in-the-digital-technologies-curriculum/
[Accessed 10 October 2022].
• McVeigh-Murphy, A., 2019. Computational Thinking, Algorithmic Thinking, & Design Thinking Defined. [online] Equip.learning.com.
Available at: https://equip.learning.com/computational-thinking-algorithmic-thinking-design-thinking [Accessed 10 October 2022].
• Remc.org. 2022. Q2 Decomposition. [online] Available at: https://www.remc.org/21Things4Students/21/21-computational-thinking/q2-
decomposition/ [Accessed 10 October 2022].
• Victoria, K., 2022. Why thinking like a computer builds skills for success. [online] Teach Your Kids Code. Available at:
https://teachyourkidscode.com/what-is-computational-thinking/ [Accessed 10 October 2022].
• 2021. The computational thinkers. [image] Available at: https://blog.playosmo.com/teaching-computational-thinking-to-kids/ [Accessed 10
October 2022].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/addayafsm20b2-230818164102-5aab3e8f/75/Computational-thinking-9-2048.jpg)