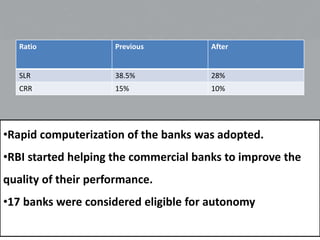
The Narasimham Committee was formed in 1991 and 1998 to reform India's financial system. The 1991 report recommended reducing statutory liquidity and cash reserve ratios, phasing out directed credit programs, deregulating interest rates, restructuring banks, and establishing an asset recovery tribunal. The 1998 report recommended strengthening banks' capital adequacy, narrowing weak banks' scopes, reviewing banking laws, and increasing bank autonomy and privatization. Both reports aimed to modernize and stabilize India's banking system.