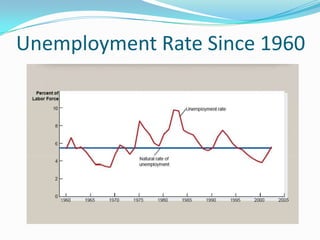
This document defines unemployment and discusses its various types, causes, costs, measurement, and solutions. It defines unemployment as a situation where capable and willing workers cannot find employment. The main types of unemployment discussed are frictional, structural, cyclical, and seasonal unemployment. Causes of unemployment mentioned include population growth, lack of job opportunities, seasonal factors, and slow industry development. Costs of unemployment include individual financial issues and societal underutilization of resources. Unemployment is typically measured by calculating the unemployment rate as a percentage of the unemployed workforce versus the total labor force. Proposed solutions include changing investment patterns, encouraging small businesses, subsidizing employment, and reorienting education.