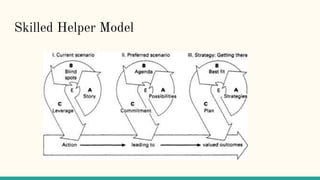
The document outlines the Skilled Helper Model for counseling. It has 3 stages:
1) Reviewing the current problem by clarifying the client's story and identifying blind spots.
2) Developing a preferred scenario by exploring possibilities and setting viable goals.
3) Determining how to achieve goals by brainstorming strategies, choosing the best, and creating an action plan.
The model emphasizes taking action throughout by translating strategies into goal-accomplishing actions. A case example of a woman discovering her husband's pornography addiction is also provided.