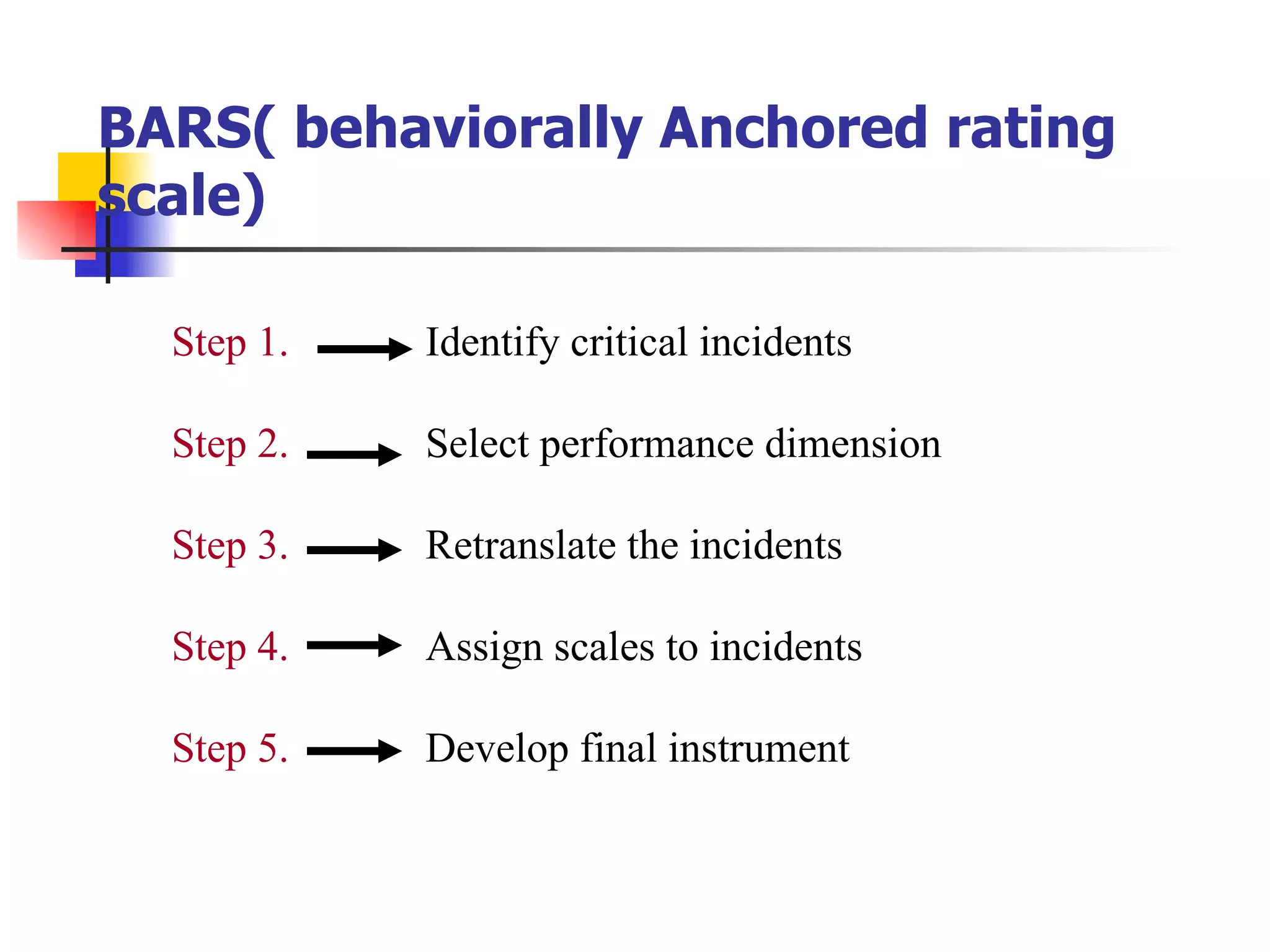
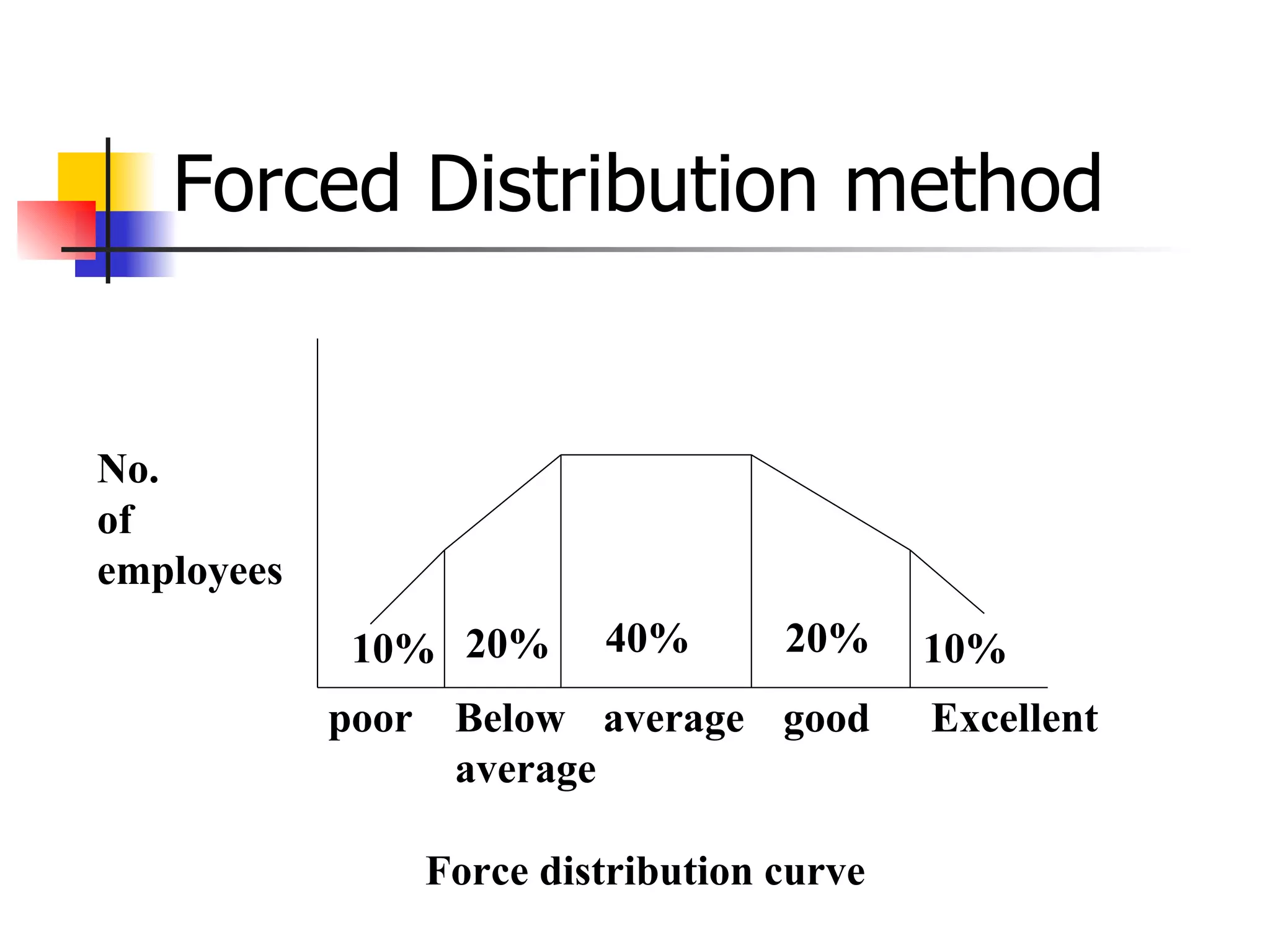
The document discusses traditional and modern approaches to performance appraisal. Traditionally, it focused only on past performance to determine pay increases or decreases. Modern approaches use appraisal for identifying training needs, career paths, and rewards in a more structured way. Several individual evaluation methods are also described like confidential reports, checklists, rating scales, and behavioral incident reports.