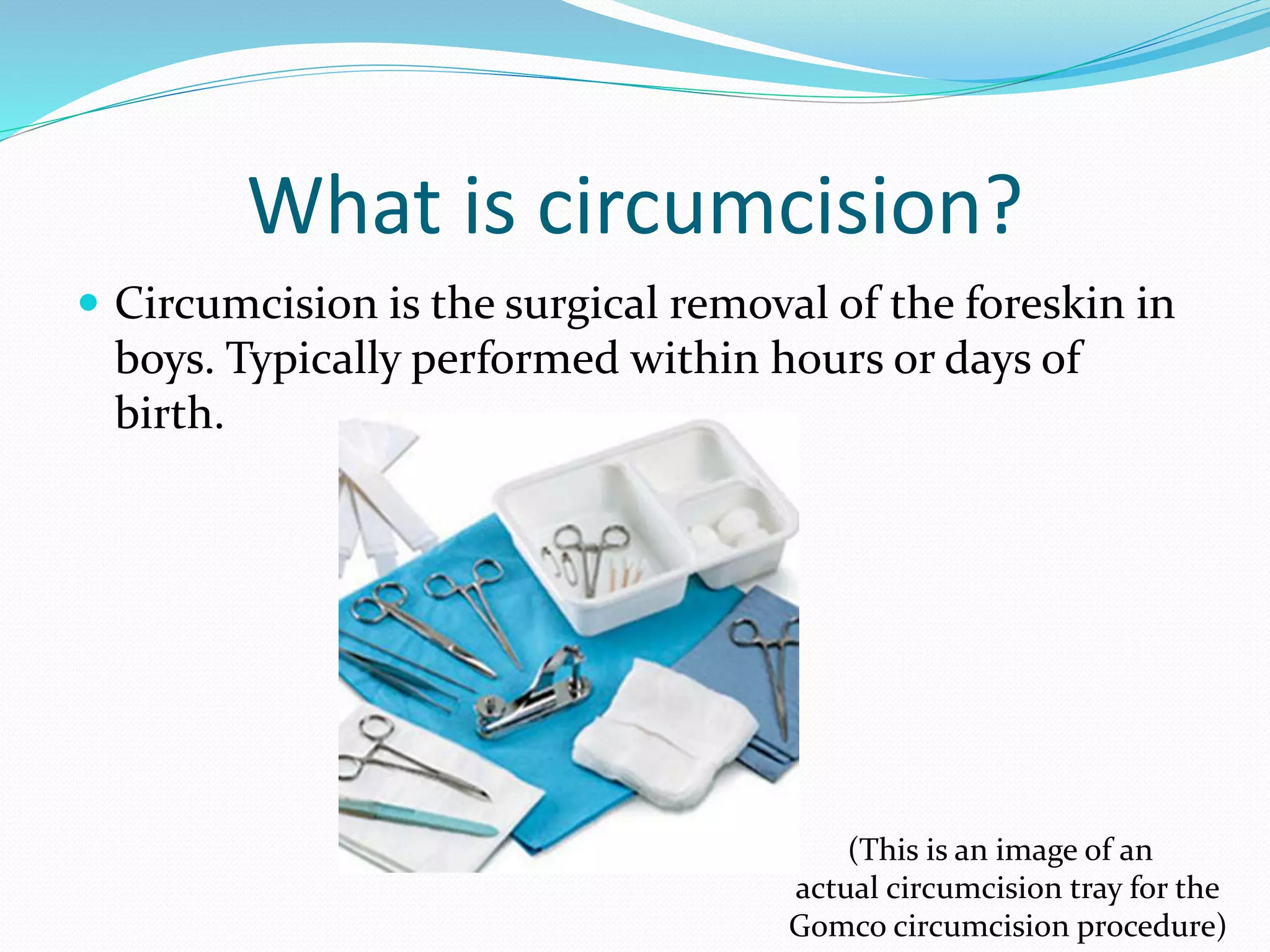
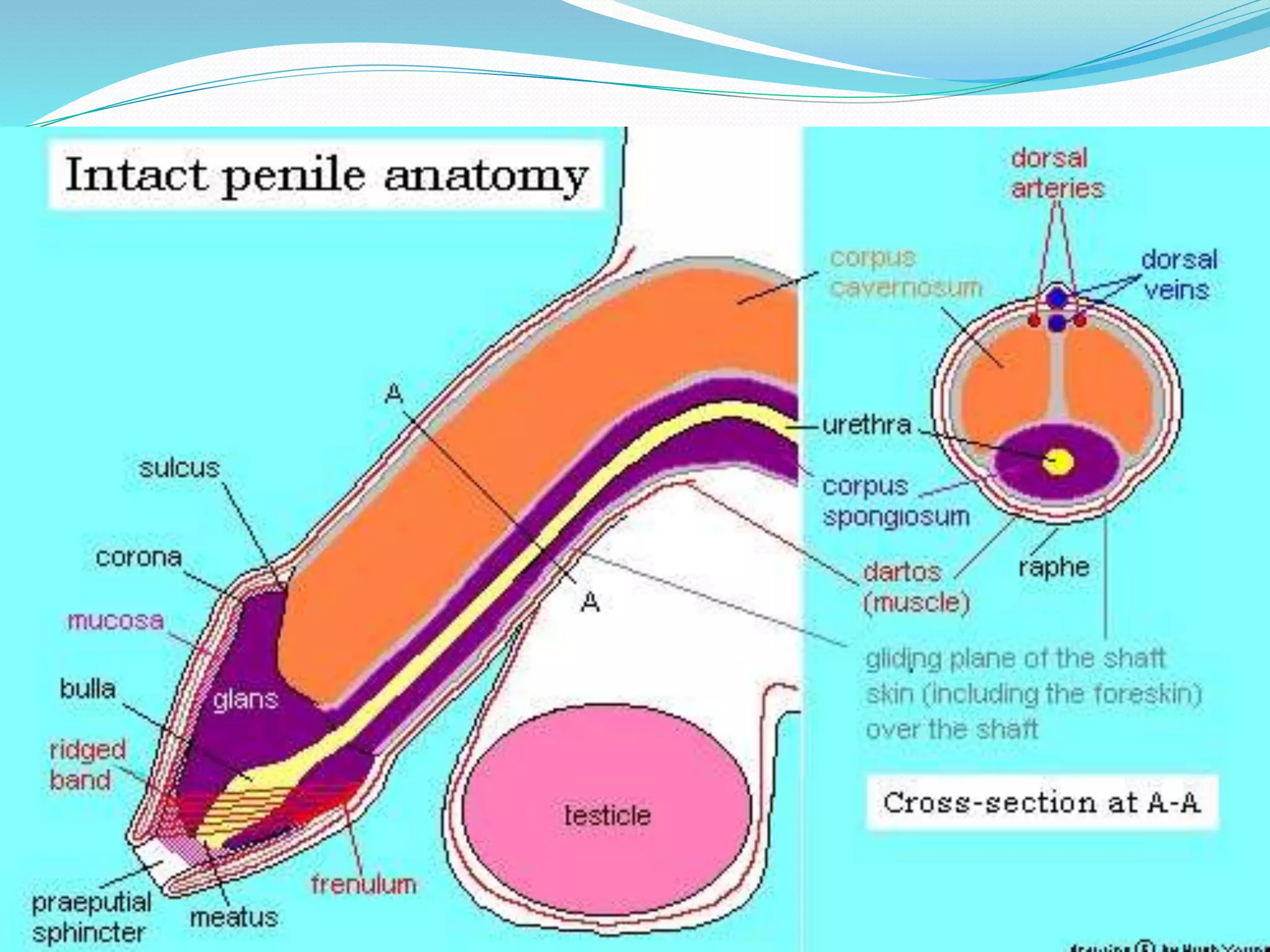
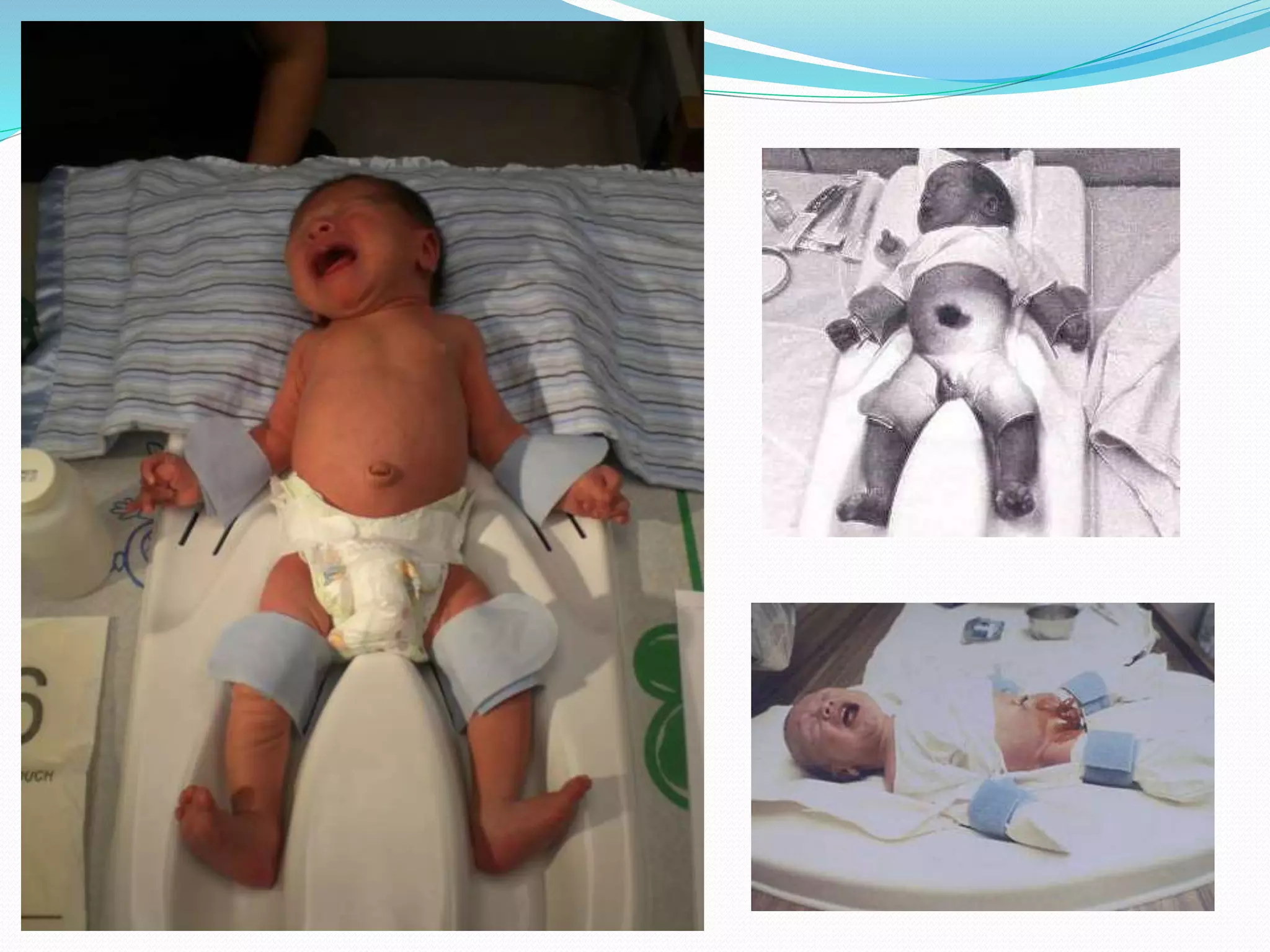
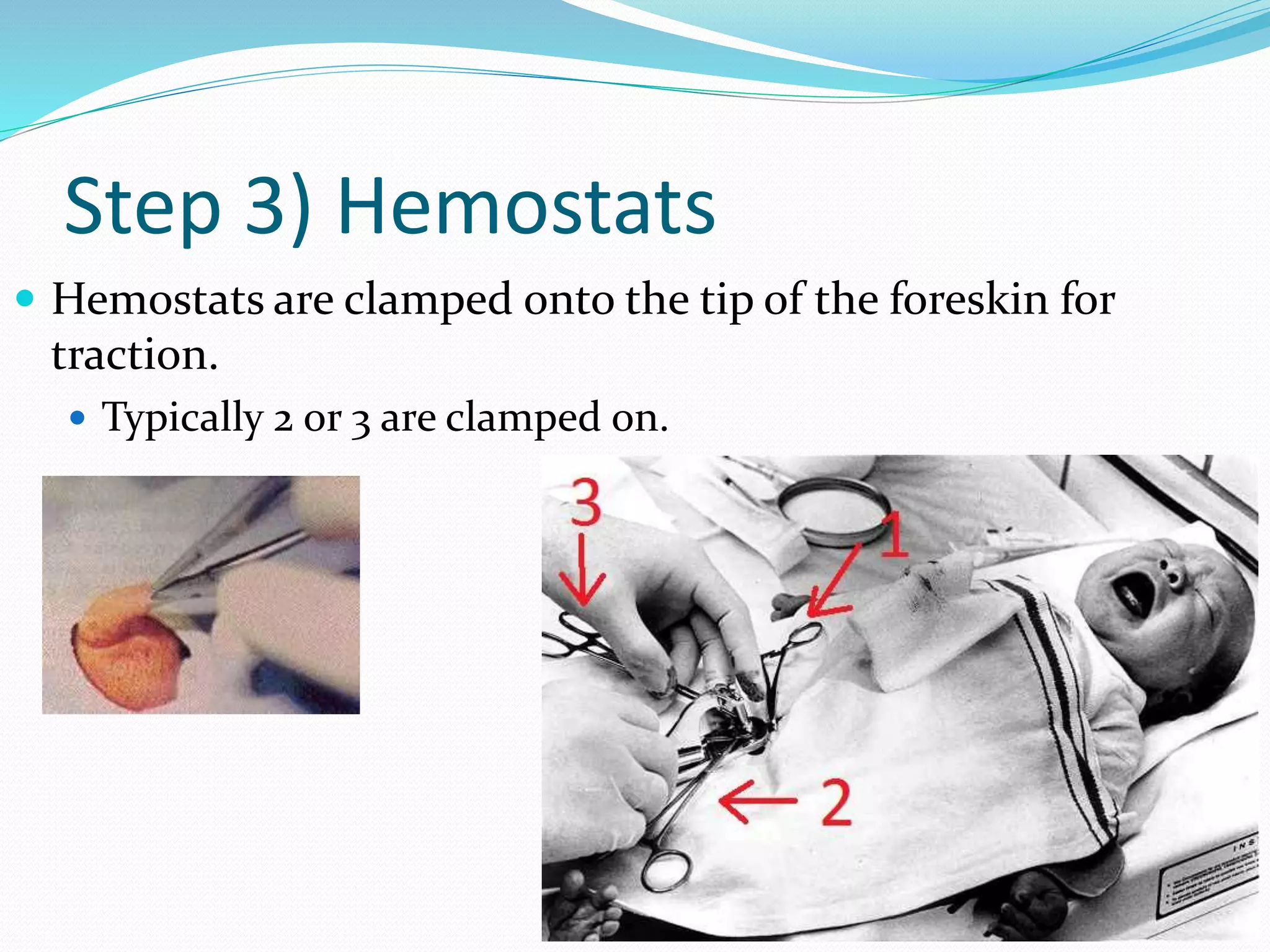
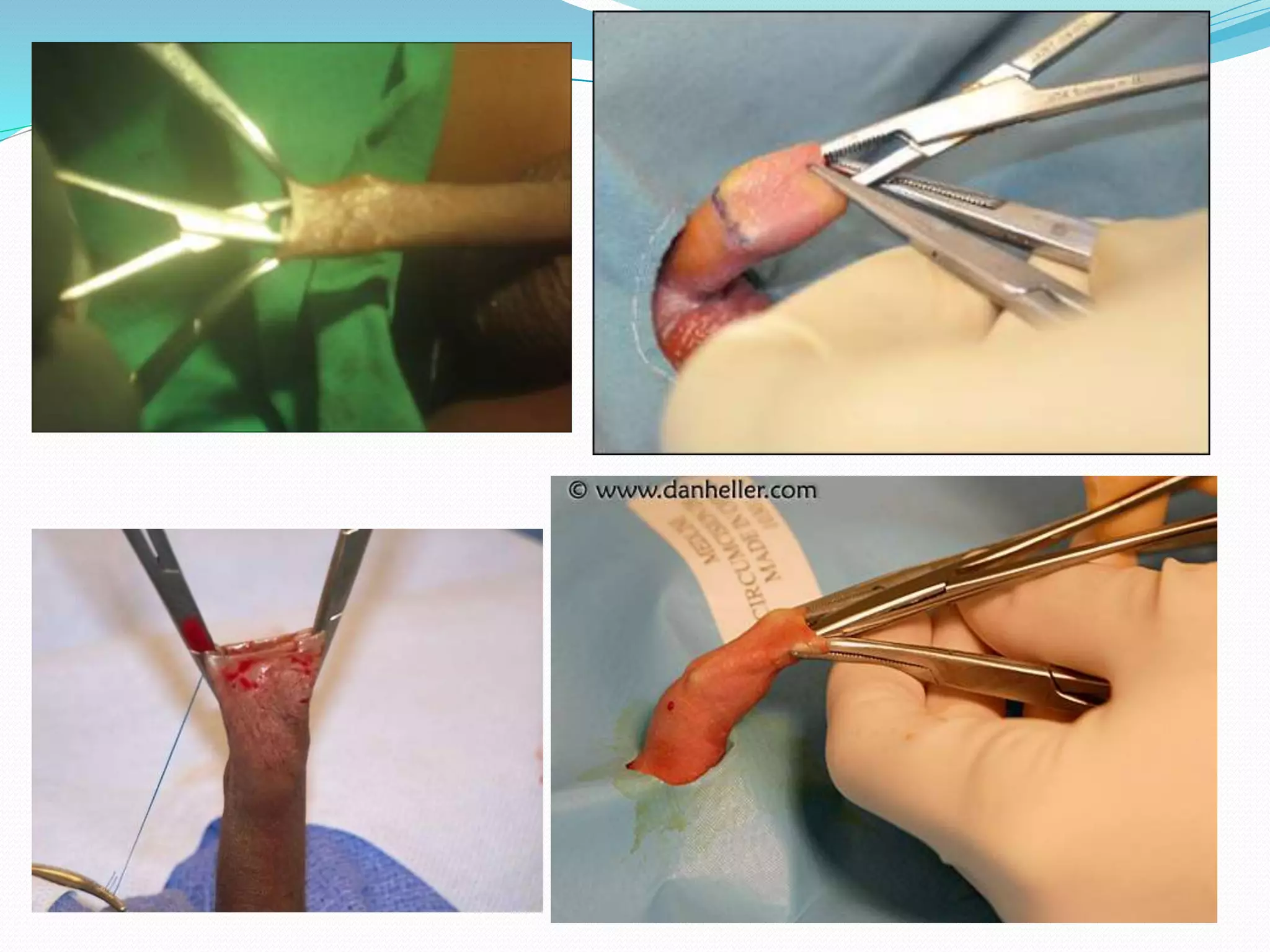
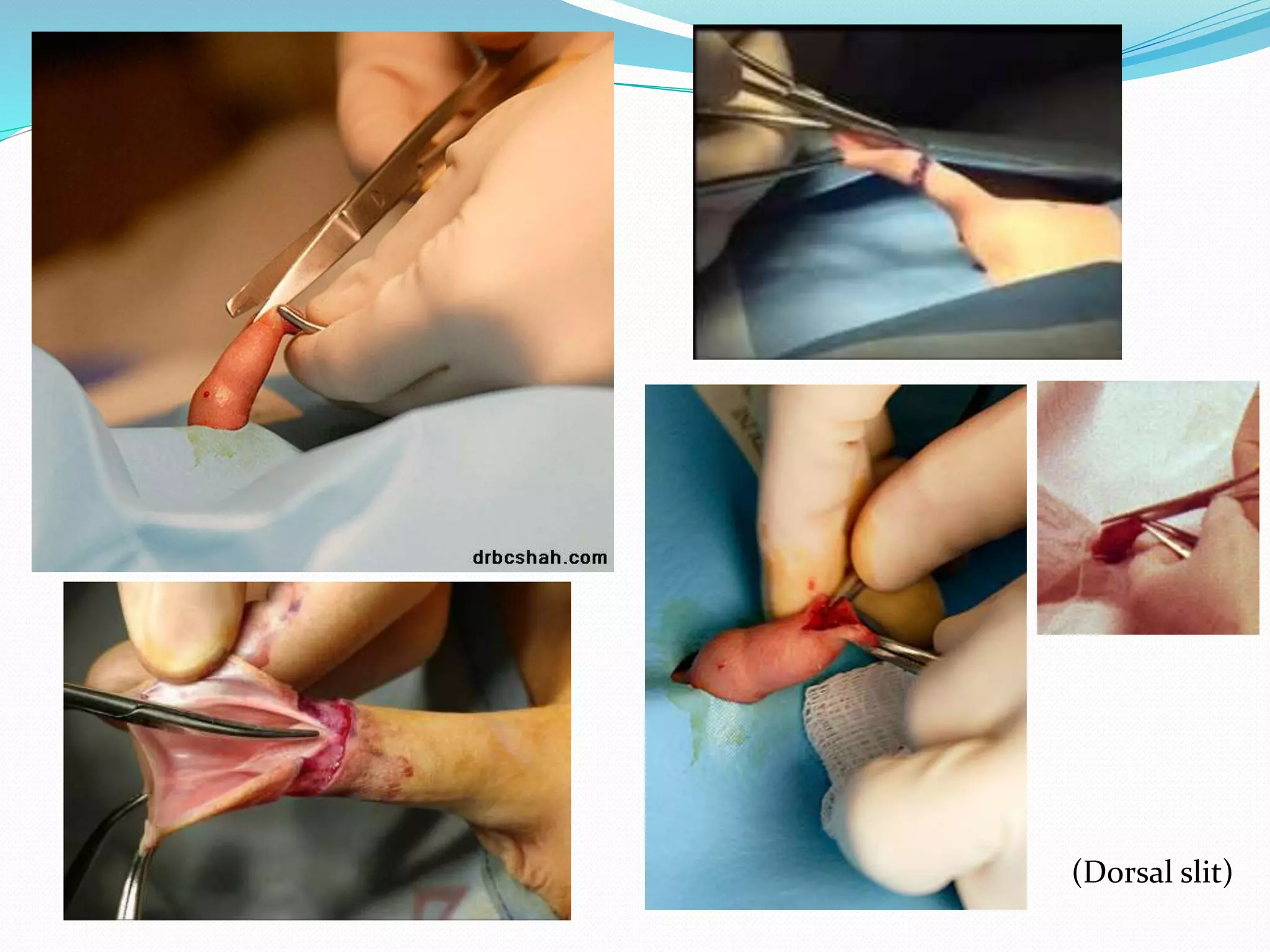
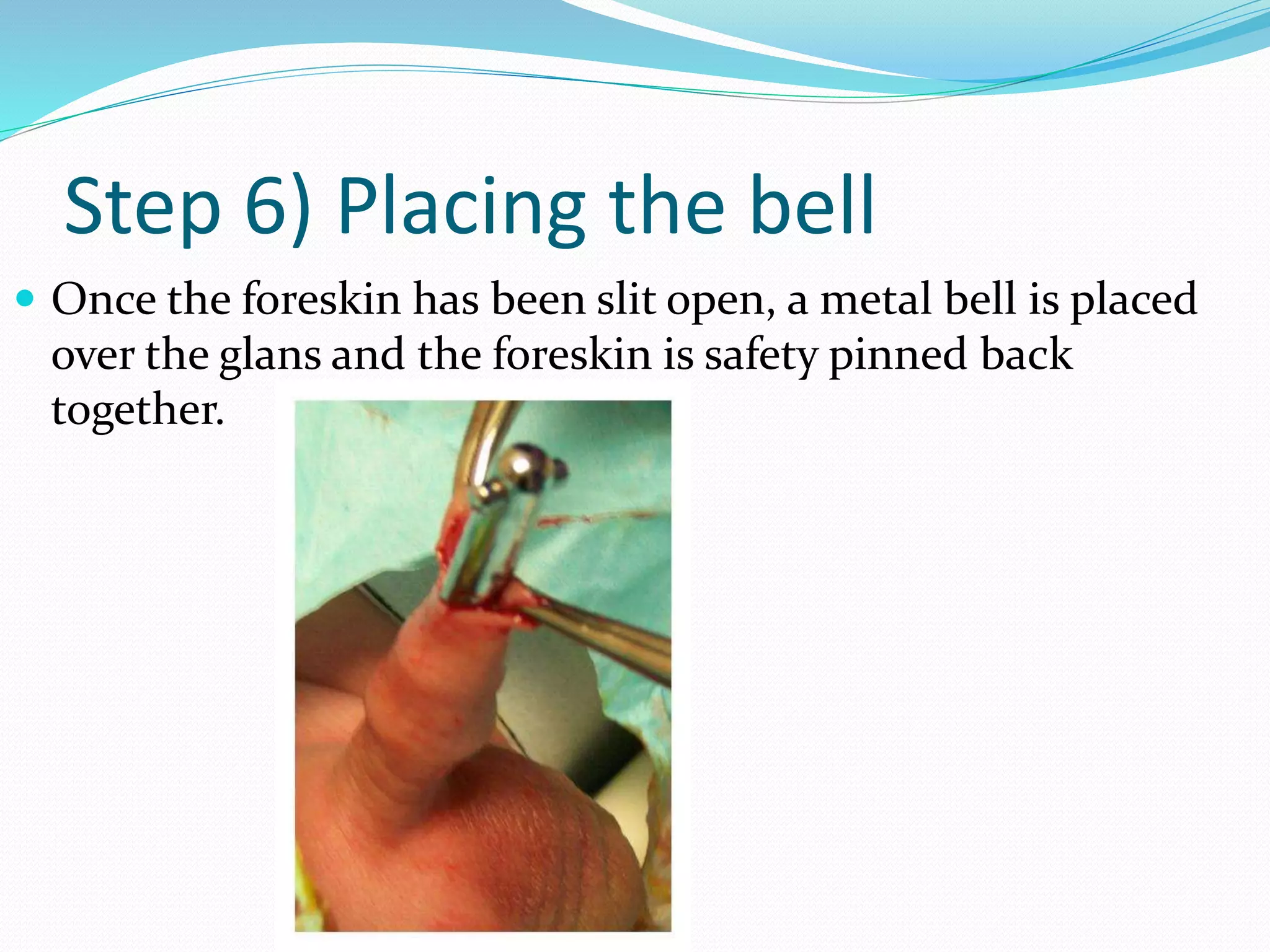
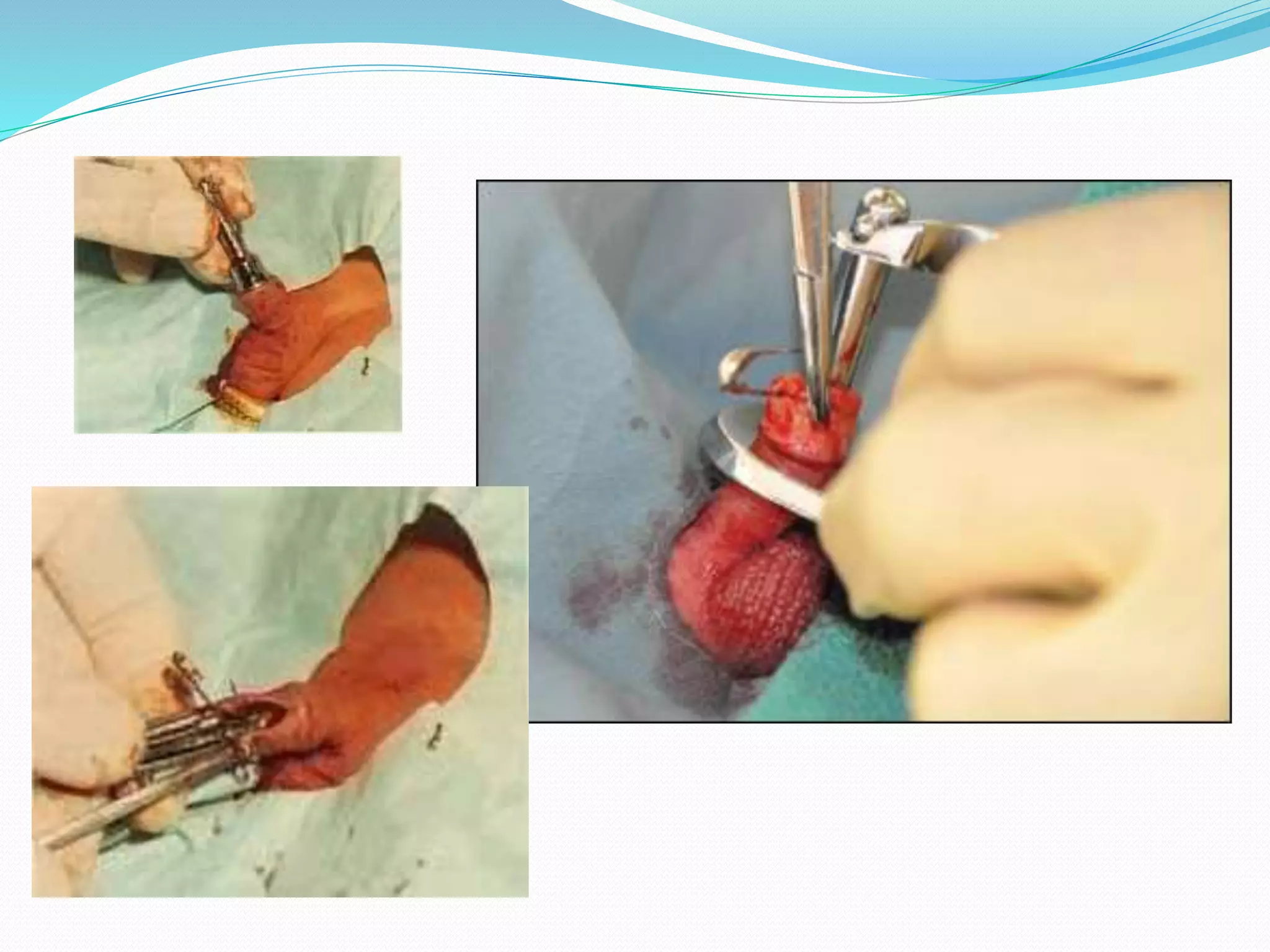
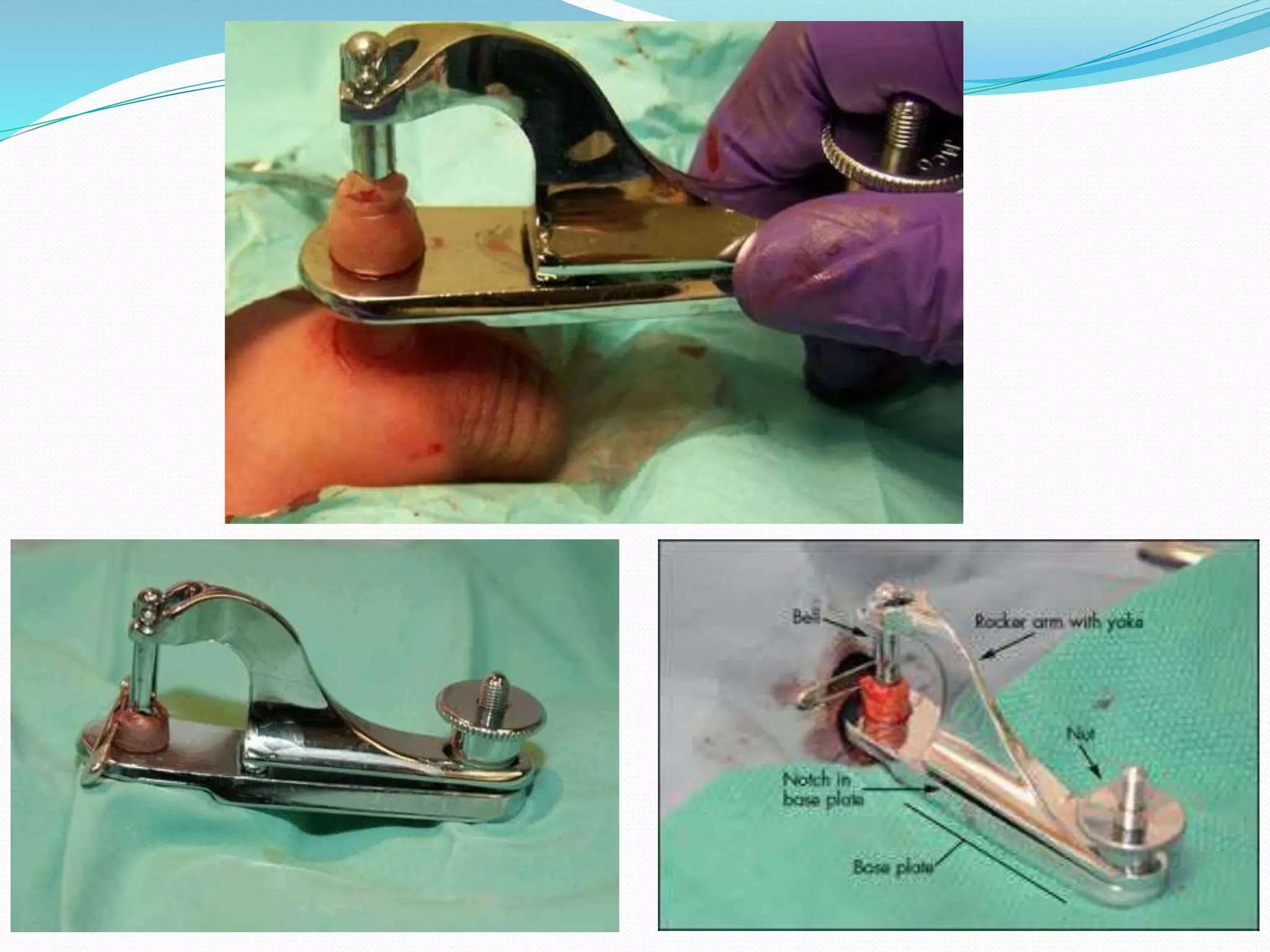
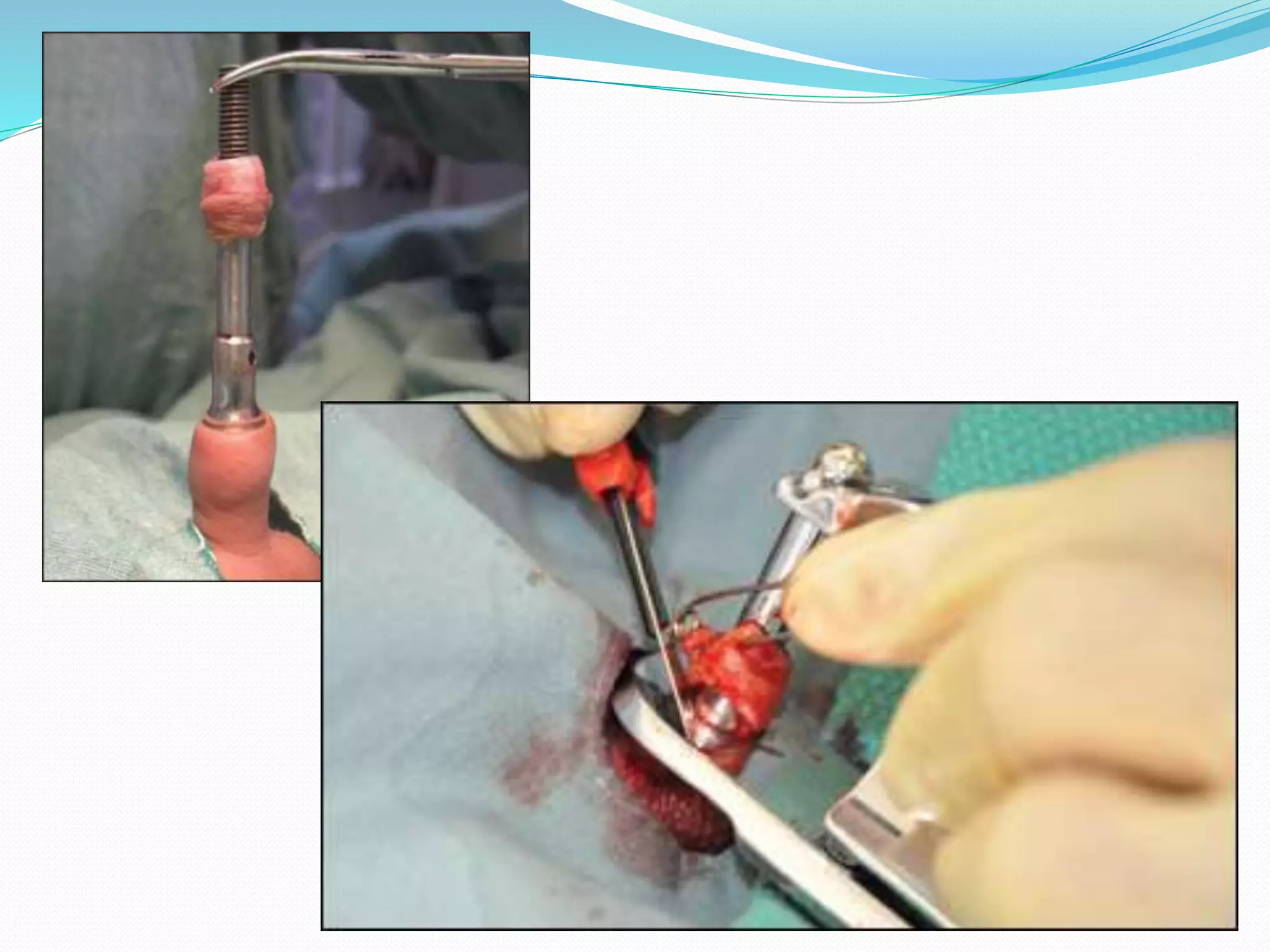
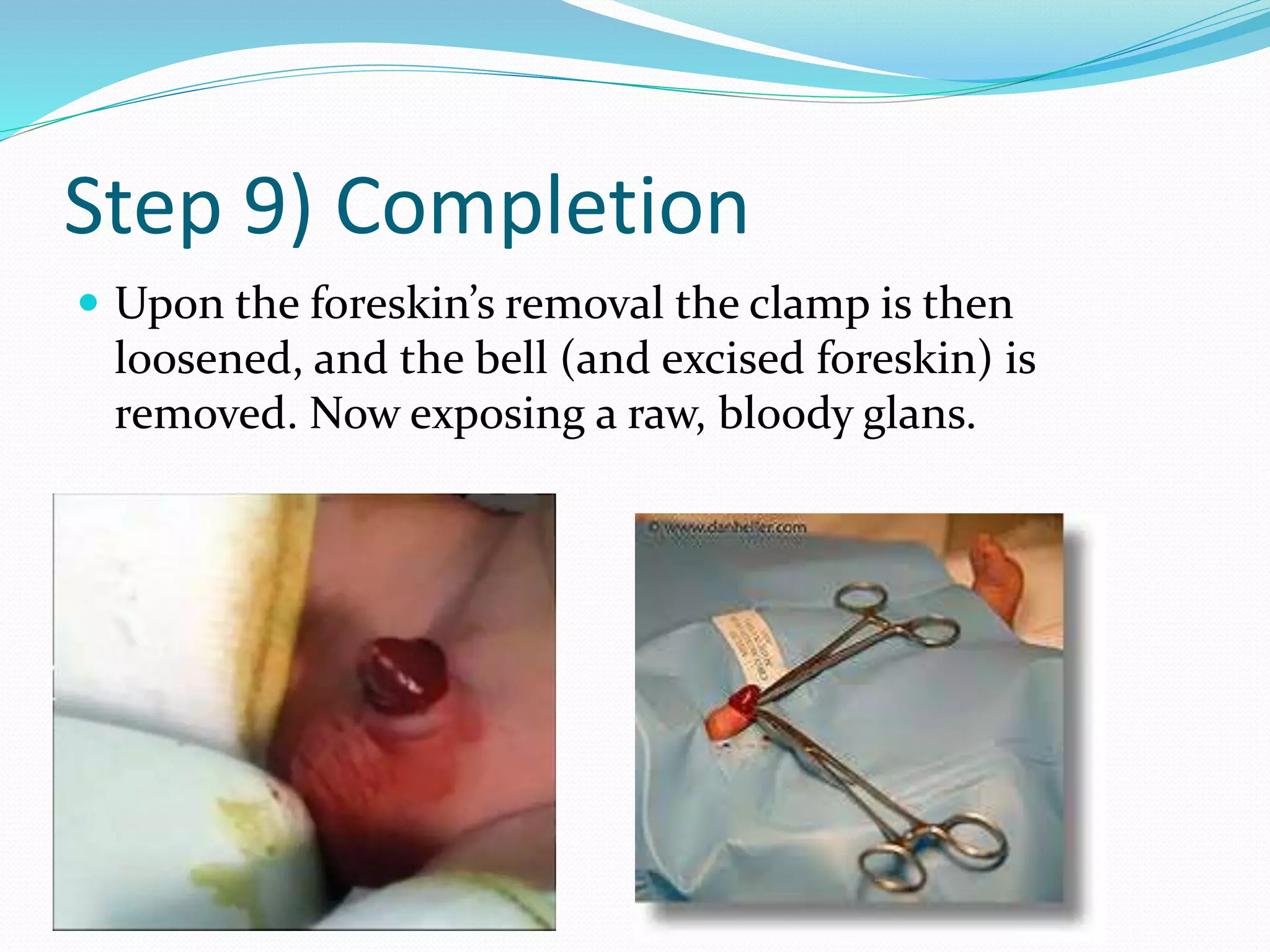
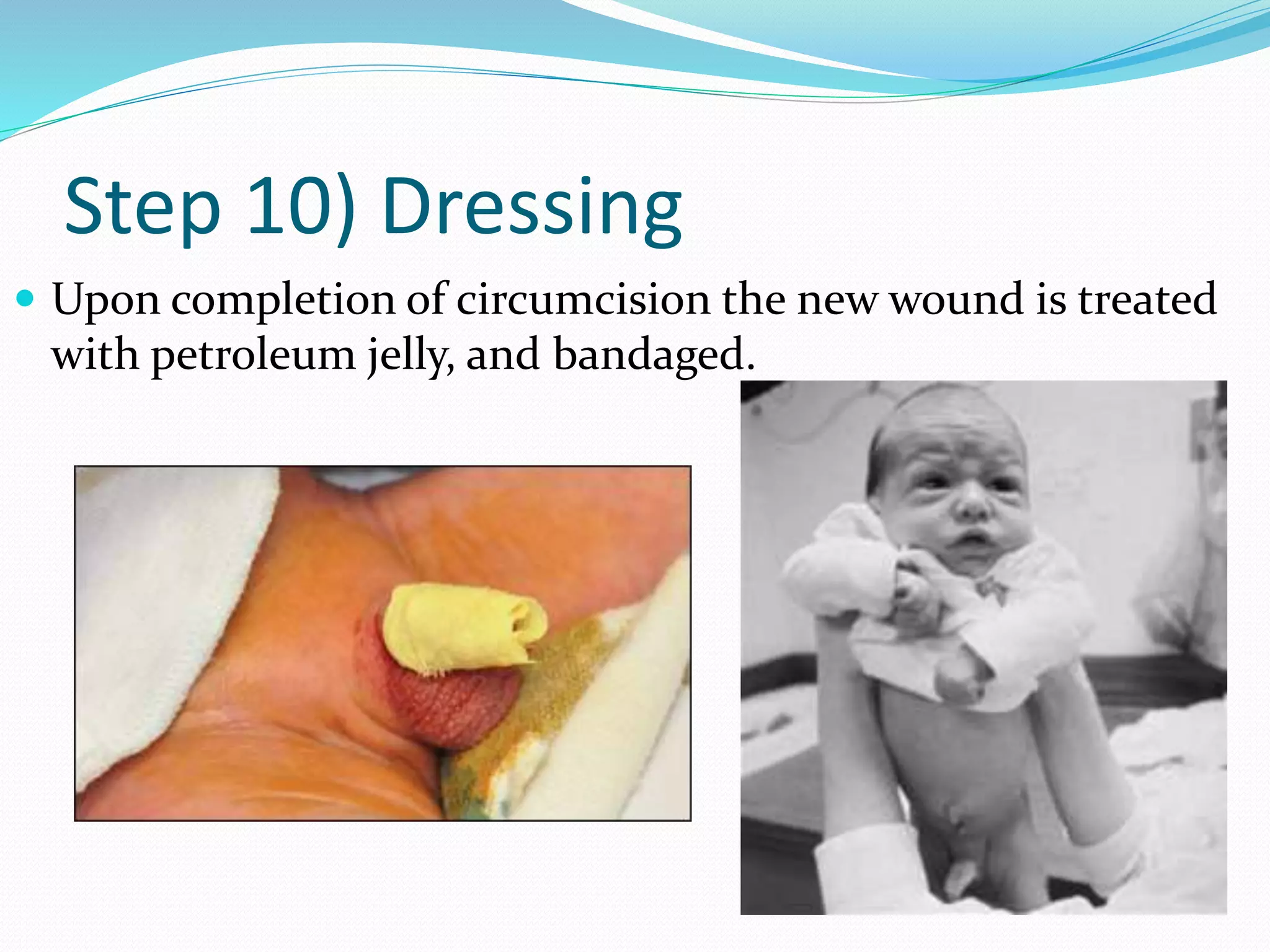
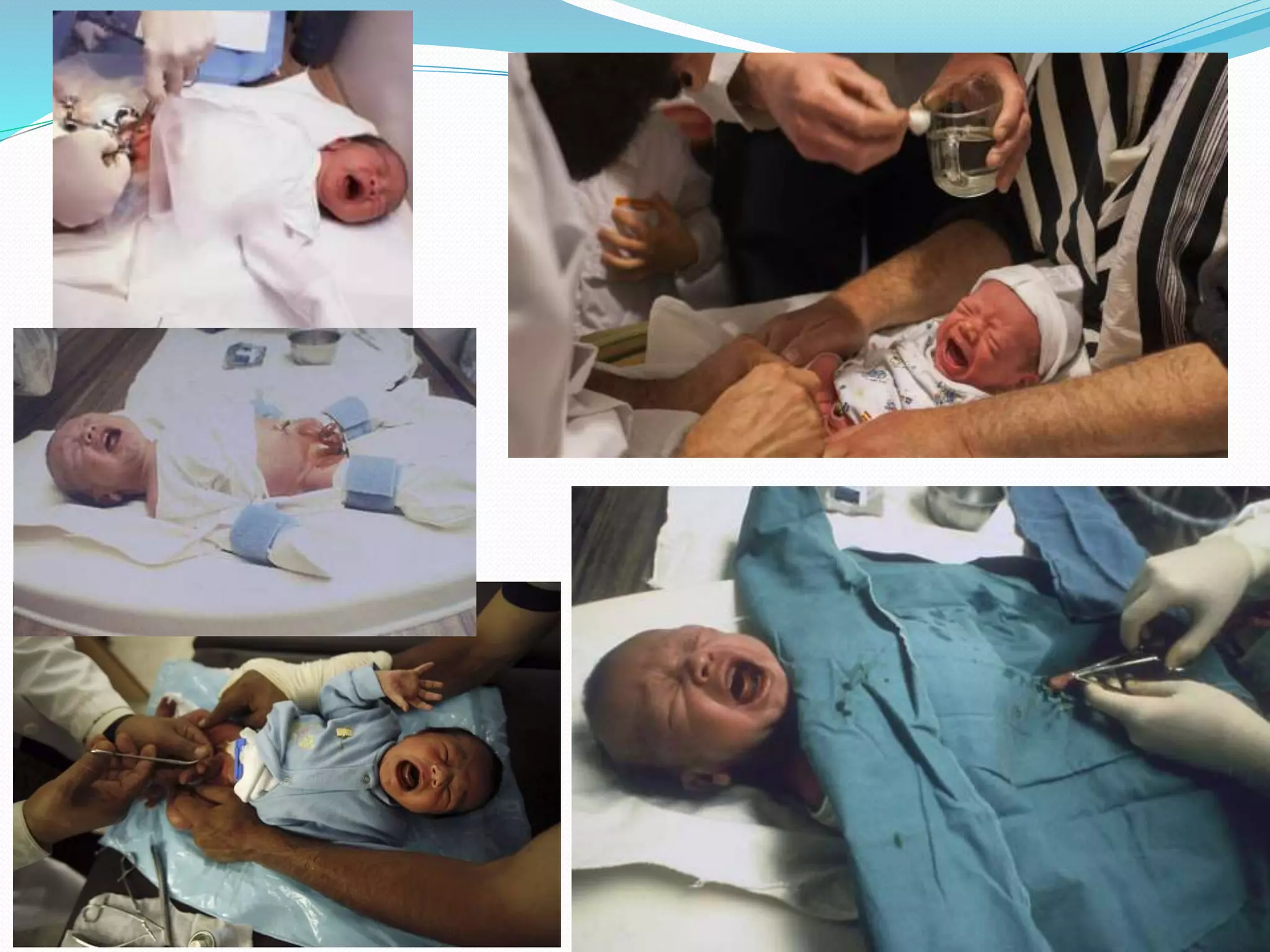
Circumcision is the surgical removal of the foreskin from the penis. The foreskin is a sensitive structure containing nerves, blood vessels, and immune cells. Circumcisions in infants are commonly performed using the Gomco clamp method. This involves forcibly retracting the foreskin, crushing it within a bell-shaped clamp to cut off blood flow, and then excising it with a scalpel, leaving the glans exposed and bloody.