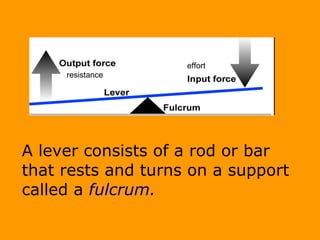
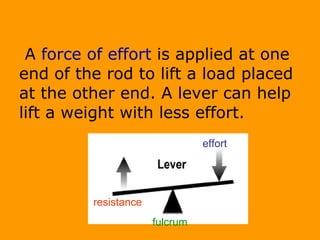
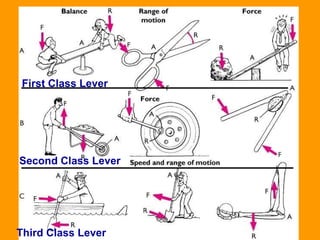
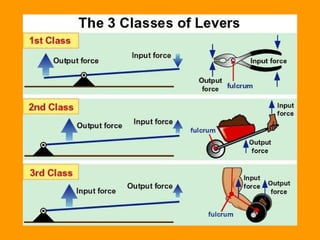
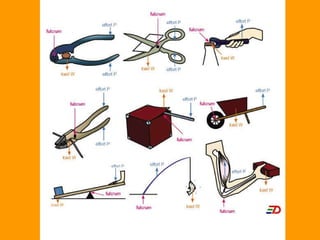
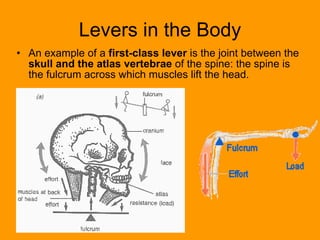
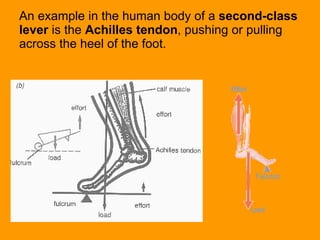
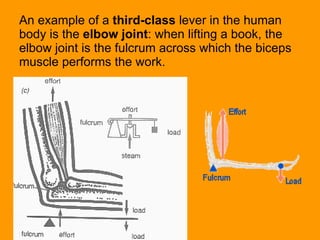
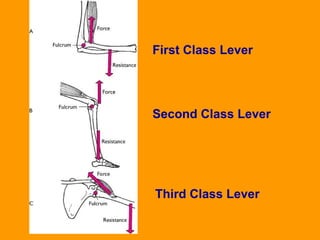
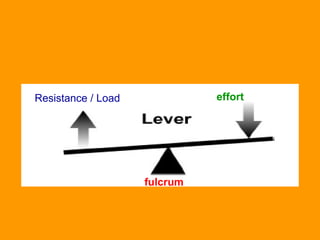
A lever is a simple machine that consists of a rod or bar that rests on and rotates around a fixed point called a fulcrum. Applying force at one end of the lever allows a load to be lifted at the other end with less effort. There are three classes of levers - first class has the fulcrum between the effort and load, second class has the load between the effort and fulcrum, and third class has the effort between the fulcrum and load. Levers are used in machines like catapults and are also found in the human body at joints.