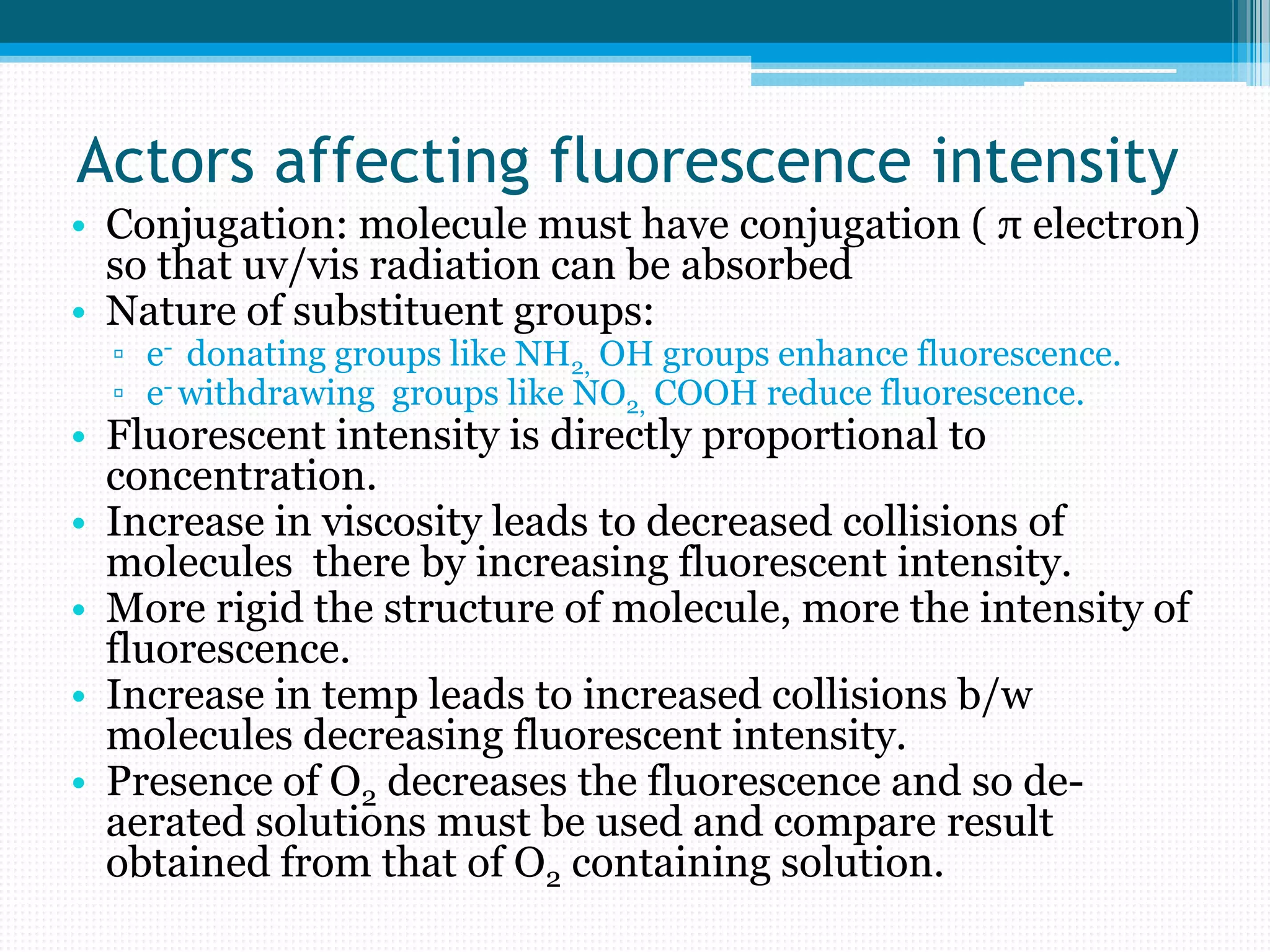
Spectrofluorimetry involves the absorption of UV or visible radiation by a molecule, exciting it to a higher energy state. The molecule then relaxes and emits light of a longer wavelength. It is a sensitive technique that can detect low concentrations of organic and inorganic substances. Factors like conjugation, substituents, temperature, and oxygen presence affect fluorescence intensity. Instrumentation includes a light source, filters, sample cell, and detector. Applications include analysis of foods, pharmaceuticals, clinical samples, and natural products.



![Understanding the terms……..
• Singlet ground state : state in which electrons in a
molecule are paired. [ ]
• Singlet excited state: state in which electrons are
unpaid but of opposite spins. [ ]
• Triplet state: state in which unpaired electrons of
same spin are present. [ ]
• Excitation process: absorption of energy or light
followed by conversion from ground state to excite
state.
• Relaxation process: process by which atom or
molecule losses energy & returns to ground state.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spectrofluorimetry-111104090937-phpapp02/75/Spectrofluorimetry-4-2048.jpg)