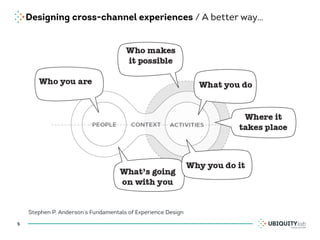
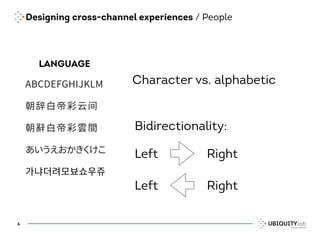
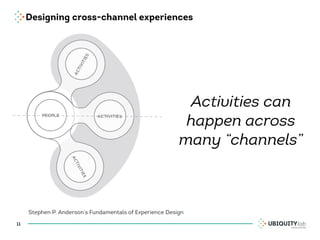
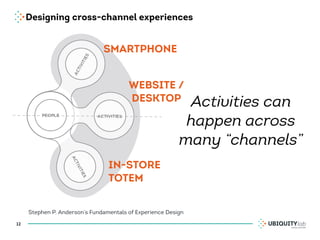
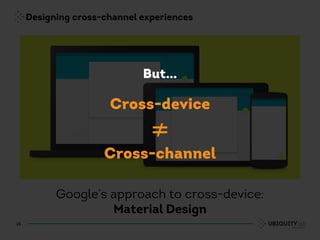
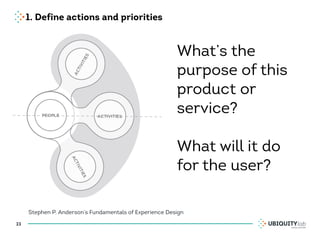
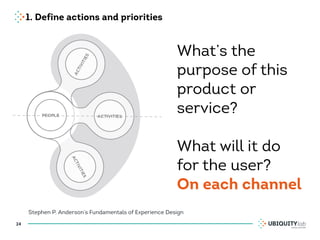
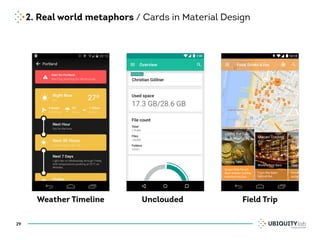
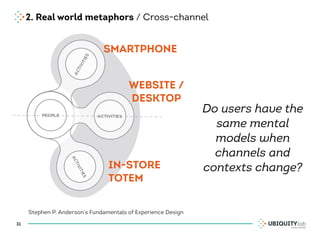
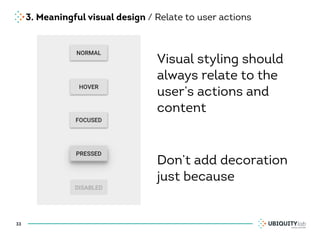
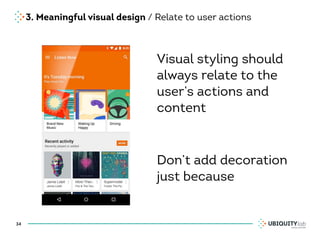
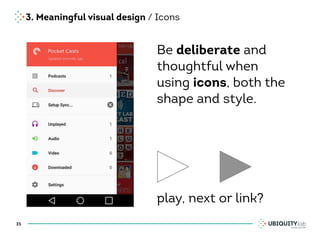
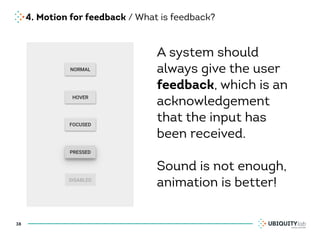
This document summarizes a presentation on cross-channel digital experiences and lessons learned from Material Design. It discusses defining user actions and priorities across channels, using real-world metaphors to help users understand digital experiences, employing meaningful visual design related to user actions, and using motion and animation for user feedback. The presentation concludes by recommending that for future Android projects, designers read Material Design documentation, create a personal pattern library, define priorities and activities upfront, and support cross-channel experiences.