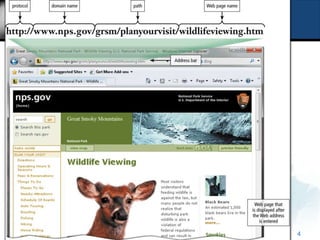
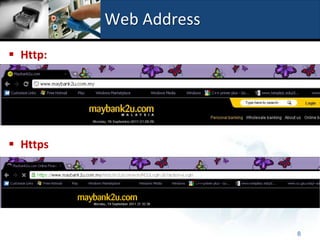
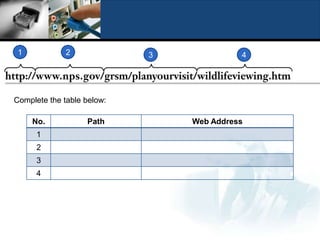
A web address, also called a URL, uniquely identifies a web page and consists of a protocol, domain name, and path to a specific page or location. Common protocols for web addresses include HTTP and HTTPS, with HTTP representing the standard protocol and HTTPS using SSL for added security. Key components of a web address are explained and examples are provided to illustrate the structure and differences between HTTP and HTTPS addresses.