CAPSULES.pdf
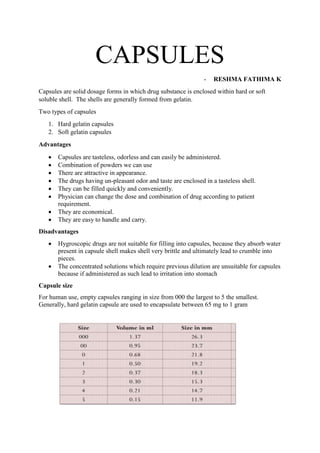
- 1. CAPSULES - RESHMA FATHIMA K Capsules are solid dosage forms in which drug substance is enclosed within hard or soft soluble shell. The shells are generally formed from gelatin. Two types of capsules 1. Hard gelatin capsules 2. Soft gelatin capsules Advantages Capsules are tasteless, odorless and can easily be administered. Combination of powders we can use There are attractive in appearance. The drugs having un-pleasant odor and taste are enclosed in a tasteless shell. They can be filled quickly and conveniently. Physician can change the dose and combination of drug according to patient requirement. They are economical. They are easy to handle and carry. Disadvantages Hygroscopic drugs are not suitable for filling into capsules, because they absorb water present in capsule shell makes shell very brittle and ultimately lead to crumble into pieces. The concentrated solutions which require previous dilution are unsuitable for capsules because if administered as such lead to irritation into stomach Capsule size For human use, empty capsules ranging in size from 000 the largest to 5 the smallest. Generally, hard gelatin capsule are used to encapsulate between 65 mg to 1 gram
- 2. Hard gelatin capsules They are less plasticized than SGC. HGC contains two parts. One is called a Cap, and the other is the Body. They are most widely used for the filling of powders, granules, and pellets. They are manufactured by the dipping method, which involves the following steps: Dipping, Rotation, Drying, Striping, Trimming, and joining. Gelatin Gelatin is heterogeneous product derived by hydrolytic extraction of animal's collagen. Formulation of Hard Gelatin Capsules: A. Gelatin: Gelatin is prepared by the hydrolysis of collagen obtained from animal connective tissue, and bone skin. on hydrolysis, low polypeptide chain yields 18 amino acids, the most prevalent of which are glycine and alanine. Gelatin can vary in its physical and chemical properties depending on the source of the collagen and the manner of extraction. There are two basic types of Gelatin. Type a. (Acid hydrolyzed gelatin), which is formed by acid hydrolysis, is produced mainly from pork skin. Type b. (Base hydrolyzed gelatin), formed by alkaline hydrolysis, is produced mainly from bones. The two types can be differentiated by their isoelectric point as the Gelatin A type has an isoelectric point near pH value 9 while Type gelatin B has an isoelectric point near pH value 4.7 B. Opacifing agents used in HGC: Titanium dioxide. Opaque capsules are occupied for either protection from light or to cover the contents. C. Preservatives: most common preservatives used in capsules are Methylparaben (Lipid soluble)-and propyl Parabens (aqueous soluble) D. lubricants: Lubrication is used to lubricate the granules or powder-filled in capsules quantity less than 2%. E. Moisture content: Finished Hard gelatin capsule normally contains stable moisture content, from 12 to 15%. It is determined by the toluene distillation method. This moisture content is critical for the physical properties of the shell as lower content. This causes gelatin film to
- 3. brittle or has a moisture content of less than 18 % causing softness in capsules. Capsules are kept on RH 40-60% and temperature 21°C – 24°C to avoid extreme temperature during handling and sorting of capsules. Preparation of Gelatin MANUFACTURING OF HARD GELATIN CAPSULES Steps involved in making empty gelatin capsules… Dipping Spinning Drying Stripping Trimming and Joining Polishing Dipping : Pairs of the stainless steel pins are dipped into the dipping solution to simultaneously form the caps and bodies. The dipping solution is maintained at a temperature of about 500 C in a heated, jacketed dipping pan. Spinning :
- 4. The pins are rotated to distribute the gelatin over the pins uniformly and to avoid the formation of a bead at the capsule ends. Drying : The gelatin is dried by a blast of cool air to form a hard shells. The pins are moved through a series of air drying kilns to remove water Stripping : A series of bronze jaws strip the cap and body portions of the capsules from the pins. Trimming and joining The stripped cap and body portions are trimmed to the required length by stationary knives. After trimming to the right length, the cap and body portion are joined and ejected from the machine. Polishing Pan Polishing: Acela-cota pan is used to dust and polish. Cloth Dusting: Capsule are rubbed with cloth. Brushing: Capsule are feed under soft rotating brush Types of excipients used in powder-filled capsules: Diluent — Diluents are the excipients that are usually present in the greatest concentration in a formulation, and they make up the necessary bulk when the quantity of the active ingredient is deficient in making up the required bulk, e.g., Lactose, maize starch, calcium sulfate, etc. Lubricants and Glidants — This reduces powder to metal adherence and promotes free flow properties, e.g., Magnesium stearate talc. Wetting agents — A wetting agent helps in the penetration of Water for less soluble drugs, e.g., Sodium lauryl sulfate. Disintegrates– Disintegrates help in splitting the powder mass. e.g., cross povidone and sodium starch glycolate. HARD GELATIN CAPSULES FILLING Hard gelatin capsule filling is done by the following process: Rectification: During Rectification empty capsules are oriented so that they can be laying in the same direction, i.e., laying the capsule Body end in downward direction. Moving forwards caps will separate from the Body as the upper plate slides towards the left, leaving the lower plate exposed to the filling, it leads to feeding coming from the hopper filling the capsule body.
- 5. the last step is the replacement of caps on the Body and the ejection of filled capsules from the die, parallelly de-dusting, polishing, and printing are done. Equipment for filling of Hard gelatin capsule: 1. Lilly Park devis 2. Rotofil 3. Hofliger 4. Macofar 5. MG2 6. Osaka 7. Zanasi 8. Perry/ Accofil In the case of farmatic, Rotofil, Macofar, MG2, and Zanasi equipment, the power must be sufficient cohesiveness to retain slug or pellet during the delivery to the capsules. Equipment for de-dusting of Hard gelatin capsule: 1. Rotosort: A mechanically shorting device that removes loose powder, and unfilled joined capsules. Filled or unfilled Bodies and loose caps. 2. Erweka KEA: For both de-dusting and polishing 3. Seidender machine: for visual inspection by using a belt. Advantages of Hard gelatin capsule: The Gelatin shell dissolves rapidly and ruptures, which results in the rapid release of a drug, although in capsule no compression force is required to manufacture as in tablets. So it gives more bioavailability rather than tablets. The solubilities limits of empty capsules are: (a) Water resistance: Fails to dissolve in 1-10 at 20-30° C in 15 minutes. (b) Acid solubility: Dissolve in less than 5 minutes in 0.5% aqueous HCI at 36-38° C. Disadvantages of Hard gelatin capsule: Disadvantages of Hard gelatin capsules including; Highly soluble salts like iodides, bromides, and chlorides generally should not be dispensed in HGC. It may cause gastric irritation due to Its rapid release and formation of high drug concentrations in localized areas. FILLING OF HARD GELATIN CAPSULES Hand operated capsule filling method Semi Automatic capsule devices Automatic filling machine Hand Operated Capsule Filling Machine is table top machine suitable for pilot & production batch requirements. Machine is having 300 holes with 25 x 12 combinations made in Stainless Steel constructions meeting GMP requirements. Machine can fill size 00 to size 5 capsules with
- 6. help of different machines and interchangeable parts. Assembly has been done in such a way that it can be easily dismantle for cleaning operations Synonyms: Hand Operated Capsule Filler, Manually Operated Capsule Filling Machine Application: Filling Capsules with powder, pellets, granules & tablets Usage: Pharmaceutical, Nutritional, Biotech, Health Supplement, Food Product & Cosmetics Suitability: Hard Gelatin, HPMC & Veg Capsules in 00, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 & 5 sizes Process Operation Place empty capsules onto the loading tray and place tray onto the machine. Check the front knob it should be turned to the right. Pull locking lever forward. Push down long handle which will lifts the caps off all the bodies. Set aside the tray containing all the caps. Push locking lever back, by which capsule bodies will drop down and become level with filling surface. Place powder tray on filler: keeps powder from spilling. Pour & spread the pre-measured powder. Move extra powder onto powder tray's shelf. Lower tamper and lock. Turn handle to compress powder: this allows you to fill more powder in each capsule. HAND OPERATED CAPSULE FILLING METHOD
- 7. Raise tamper & spread extra powder from shelf into capsules: ensures uniform fill weights. Return the tray containing caps to filler. Turn front knob to the left and lower locking plate. Engage lock for locking plate. Hold tamper handle and push down on long handle. Bodies are pushed up into caps: all the capsules are now locked in one step. Disengage lock for locking plate. Lift locking plate and turn front knob to the right. Push down long handle and remove tray of completed capsules. Capsules are filled now. Turn tray and all the capsules will get out from the tray. Semi Automatic Capsule Filling Machine Semi Automatic Capsule Filling Machine is designed for precision manufacturing requirements of modern pharmaceutical procedures. Capsule Filling Machine is suitable to fill size 00 to 5 capsules with powder, granules or pellets, which provide production output ranging from 25000 capsules per hour to 45000 capsules per hour. Machine provides high Degree of automation with higher levels of filling weight accuracy. . Synonyms: Semi-automatic Capsule Filling Machine, Semi Automatic Capsule Filler Application: Filling Capsules with powder, pellets & granules Usage: Pharmaceutical, Nutritional, Biotech, Health Supplement, Food Product & Cosmetics Suitability: Hard Gelatin, HPMC & Veg Capsules in 00, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 & 5 sizes Working principle Empty capsules of suitable size are loaded in capsule hopper of filling machine. Powder then loaded into a separate hopper. This is a corkscrew driven hopper, which allows a constant fill throughout each capsule. The operator then uses the vacuum sucker to individually sort out and fill the capsules into the loading rings. Loading Rings can be made from 00 to 5 sizes as per requirements. The operator then uses the vacuum to separate the capsules.Once the capsules are separated, the loading rings are pulled apart to release just the bottom section. This bottom section is then placed into the filling part of the machine. Once the loading rings has been placed into this section of the machine, the operator can switch on the filling. This causes the filler to slide across onto the capsules, and the capsules to rotate beneath it. The corkscrew then evenly forces the powder down into the capsules. This ensures that each capsule is of the same
- 8. size and weight. The two loading rings are then placed back together and placed into the sealing section of the capsule filling machine. Once they are aligned, the operator closes the guard and uses air pressure to seal the capsules. The capsules are then released from the loading ring.Once the capsules have been produced, there is also a capsule polishing option for this machine. The capsule polishing has a set of corkscrew brush bristles inside and uses a dust extractor unit connect with this capsule polishing machine. This dust extractor system de-dust the capsules by the vacuum, to leave them with a high-quality and professional finish. Automatic capsule filling machine After starting up the machine, the empty capsules in hopper will be fed into the slot of magazine vertically. With each stroke of machine, the fingers of magazine will release one row of capsules into rectifier raceway. The horizontal fingers rectify the direction of capsules and vertical fingers push the capsules into hole of segment with all caps on the up position. The capsules in the holes are sent to each working station along with the intermittent rotation of the turn table. At the 1st & 2nd station, the vacuum system separates the capsules in position. At 3rd station, the lower segment with capsule body extends out ready for the filling. 4th station uses to fill pellets. At the 5th station, the tamping pins push the pressed powder slug into capsule body. 6th station to re-joint cap & body segments. At 7th station non-separated capsule get eject.
- 9. At 8th station vertical pins pushing body of capsule into the cap for re-join and close the filled capsules. The 9th station is to eject the finished capsules. At the 10th station the holes of segments are cleaned by vacuum cleaner and compressed air. Then the segments are ready for next cycle of operation. The powder from a SS hopper entered to a chamber of dosing plate & temping pins for dosing, the height of the powder is controlled at chamber by a material level sensor. Tamping device is work by a 6 working station of intermittent mechanism, there are 6 groups of standard holes on dosing disc. The powder filled in holes was made of a slug that reaches the weight of dose after 5 tamped. At the 6th working station the slug pushed by tamping pin into capsule body. Adjusting the height of tamping pin holder can be changed the filling weight of powder. SOFT GELATIN CAPSULES Soft Gelatin capsules are one piece, hermetically sealed, soft gelatin shells containing a liquid, a suspension, or a semisolid. Soft gelatin is mainly composed of gelatin, plasticizers, preservative, colouring and opacifying agents, flavoring agents and sugars.
- 10. SHAPE OF CAPSULE The shape of soft gelatin capsule are round, oval, oblong, tube Composition of the shell The basic component of soft gelatin shell is gelatin; however, the shell has been plasticize The ratio of dry plasticizer to dry gelatin determines the “hardness” of the shell and can vary from 0.3-1.0 for very hard shell to 1.0-1.8 for very soft shell Up to 5% sugar may be included to give a “chewable” quality to the shell The residual shell moisture content of finished capsules will be in the range of 6-10% Formulation Formulation for soft gelatin capsules involves liquid, rather than powder technology. Materials are generally formulated to produce the smallest possible capsule consistent with maximum stability, therapeutic effectiveness and manufacture efficiency. The liquids are limited to those that do not have an adverse effect on gelatin walls. Emulsion cannot be filled because water will be released that will affect the shell The pH of the liquid can be between 2.5 and 7.5
- 11. MANUFACTURE OF SOFT GELATIN CAPSULES Is manufactured by four methods Plate process Rotary die process Reciprocating die Accogel machine Plate process Place the gelatin sheet over a die plate containing numerous die pockets. Application of vacuum to draw the sheet in to the die pockets. Fill the pockets with liquid or paste. Place another gelatin sheet over the filled pockets, and Sandwich under a die press where the capsules are formed and cut out Rotary die press In this machine the soft gelatin capsules are prepared & then filled immediately with liquid medicaments it is having two hoppers & two rotating dies Liquid mixture is placed in one hopper & the liquid medicament in other Hooper. The two rotating dies rotate in opposite directions when the fluid gelatin mixture enters the machine from the hopper it produces two continuous ribbons . These half shell of the capsule is formed. At this stage the measured quantity of the medicament is filled in to it with the stroke of a pump with the subsequent movement of the dies the other half capsule is formed. As the die rolls rotate, the convergence of the matching die pockets seals and cuts out the filled capsules
- 12. Accogel Capsule Machine Accogel Capsule Machine Or Stern machine, uses a system of rotary dies but is unique in that it is the only machine that can successfully fill dry powder into a soft gelatin capsule. vehicles used in soft gelatin capsules: Two main groups Water immiscible, volatile or more likely more volatile liquids such as vegetable oils, mineral oils, medium-chain triglycerides and acetylated glycerine. Water miscible, non-volatile liquids such as low molecular weight PEG have come in to use more recently because of their ability to mix with water readily and accelerate dissolution of dissolved or suspended drugs. All liquids used for filling must flow by gravity at a temperature of 350C or less. The sealing temperature of gelatin films is 37-400 C The Bloom strength: It is a measure of gel rigidity. It is determined by preparing a standard gel (6.66% w/v) and maturing it at 10°C. It is defined as the load in grams required to push a standard plunger 4 mm into the gel. The gelatin used in hard capsule manufacture is of a higher bloom strength (200-250 g) than that used for soft capsules (150 g) because a more rigid film is required for the manufacturing process Base Adsorption of Solids to be suspended in soft gelatin capsules ▸ Base adsorption is expressed as the number of grams of liquid base required to produce a capsulatable mixture when mixed with one gram of solids. ▸ The base adsorption of a solid is influenced by such factors The solids particle size and shape, Its physical state Its density Its moisture content, and Its lipophilic or hydrophilic nature
- 13. The base adsorption is obtained by weight of the base/weight of the solid =Base Adsorption Determination of Base Adsorption Weight the definite amount (40g is convenient) of the solid substance into a 150ml tared beaker In a separate 150ml tared beaker place 100g of the solid base Add small amount of liquid base into the solid and stir it with spatula until consistent soft ointment is produced Continue to add liquid until the mixture flows steadily from the spatula blade when held at a 45 degree angle above the mixture Calculate the base adsorption using the above given formula Minim per gram" FACTOR (M/g) OF THE SOLID ▸ The base adsoorption is used to determine the "minim per gram" factor (M/g) of the solid(s). ▸ The minim per gram factor is the volume in minims that is occupied by one gram of the solid plus the weight of the liquid base(BA) required to make capsulatable mixture. ▸ The minim per gram factor is calculated by dividing the weight of the base plus the gram of solid base (BA+S) by the weight of the mixture (W) per cubic centimeter or 16.23 minims (V). (BA+S) x V/W = M/g Thus lower the base absorption of the solids and higher the density of the mixture, the smaller the capsule will be. Quality Control Tests for Capsule Drug Products In-process quality control tests for capsule drug products In-process quality control tests for capsule drug products are carried out at predefined intervals during the product manufacturing, by the manufacturing personnel, and their results recorded on the batch record. Adverse findings in these tests can be used as a guide to altering the manufacturing-process parameters. During the encapsulation of soft gelatin capsules, the following parameters are usually closely monitored and controlled: Gel ribbon thickness and uniformity across the ribbon Softgels seal thickness at the time of encapsulation Weight of the capsule fill and its variation from capsule-to-capsule
- 14. Weight of the capsule shell and its variation from capsule-to-capsule Moisture level of the capsule shell before and after drying Visual inspection, fill weight, and fill-weight uniformity are the key in-process tests used for hard gelatin capsules. Finished product quality control tests for capsule drug products Finished capsules are subjected to a number of tests in accordance with compendial standards and regulatory requirements for unit dose capsule products. These batteries of tests help identify whether the batch is acceptable for marketing or its intended usage. Finished capsules are evaluated by the following tests: a. Permeability and sealing Soft gelatin capsules are tested for physical integrity (absence of leakage) by visual inspection. Similarly, hard gelatin capsules are tested for any breach of physical integrity (breakage or opened cap and body). b. Potency and impurity content All capsules are tested for drug content (potency, as a per cent of label claim). In addition, most drug products are tested for related substances or impurities. These must meet predefined specifications for a batch to be acceptable. c. Weight variation test The uniformity of dosage units may be demonstrated by determining weight variation or content uniformity. The weight variation method is as follows. d. Weight variation test for hard gelatin capsules Ten hard gelatin capsules are usually weighed individually and the contents are removed. The emptied shells are individually weighed and the net weight of the contents is calculated by subtracting the weight of the shell from the respective gross weight. The content of active ingredient in each capsule may be determined by calculation based on the per cent drug content in the formulation.
- 15. e. Weight variation test for soft gelatin capsules For soft gelatin capsules, the gross weight of 10 gelatin capsules is determined individually. Then each capsule is cut open with a suitable clean, dry cutting instrument (e.g., scissors or a sharp open blade), and the contents are removed by washing with a suitable solvent (that dissolves the fill but not the shell). The solvent is allowed to evaporate at room temperature over a period of about 30 minutes, followed by weighing of the individual washed shells. The net contents are calculated by subtraction and the content of active ingredient in each of the capsules can be determined by calculation based on the per cent drug content in the formulation. Fill-weight variation of capsules is often a function of equipment setup and filling operation. An automated capsule sizing machine and/or weight checker is frequently used to discard over- or under filled capsules. f. Uniformity of content This test is performed only when the content is specified in the individual monographs and when capsules fail weight variation test. If the weight of capsules is completely filled no need of test. Unless otherwise stated in the monograph for an individual capsule, the amount of drug substance, determined by assay, is within the range of 85.0 % to 115.0 % of the label claim for nine (9) of ten (10) dosage units assayed, with no unit outside the range of 75.0 % to 125.0 % of the labelled drug content. Additional tests are prescribed when two or three dosage units are outside of the desired range but within the stated extremes. g. Disintegration time test for capsules Disintegration of hard and soft gelatin capsules is evaluated to ensure that the drug substance is fully available for dissolution and absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. The compendial disintegration test for hard and soft gelatin capsules follows the same procedure and uses the same apparatus described in the article “Quality Control Tests for Tablets”. The capsules are placed in the basket-rack assembly, which is repeatedly lowered 30 times per minute into a thermostatically controlled bath of fluid at 37 ± 2 ˚C and observed over the time described in the individual monograph. To fully satisfy the test, the capsules disintegrate completely into a soft mass with no firm core and only some fragments of the capsule shell.
- 16. h. Dissolution test for capsules Drug absorption and physiological availability depend on the drug substance being in the dissolved state at the site of drug absorption. The rate and extent of dissolution of the drug from the capsule dosage form is tested by a dissolution test. This test provides means of quality control in ensuring that different batches of the drug product have similar drug release characteristics and that a given batch has similar dissolution as the batch of capsules that was shown initially to be clinically effective The compendial dissolution test for capsules uses the same apparatus, dissolution medium, and test as that for uncoated and plain coated tablets. However, in instances in which the capsule shells interfere with the analysis, the contents of a specified number of capsules can be removed and the empty capsule shells dissolved in the dissolution medium before proceeding with the sampling and chemical analysis. If the capsule floats on the surface of the dissolution fluid, a small, loose piece of nonreactive material, such as a few turns of a wire helix, may be attached to the dosage form to force it to sink to the bottom of the vessel. i. Moisture content Water content of the entire capsule or the capsule contents are determined by Karl Fisher titrimetric to enable the correlation of water content with the degradation profile or drug-release characteristics of capsules. j. Moisture permeation test The USP requires determination of the moisture-permeation characteristics of single-unit and unit dose containers to assure their suitability for packaging capsules. The degree and rate of moisture penetration is determined by packaging the dosage unit together with a colour- revealing desiccant pellet, exposing the packaged unit to known relative humidity over a specified time, observing the desiccant pellet for colour change (indicating absorption of moisture) and comparing the pre-test and post-test weight of the packaged unit. k. Microbial content The capsules are tested to ensure lack of growth of bacteria and mould by microbiological tests. These tests are usually carried out by incubation of the capsule contents in a growth medium and counting the colonies formed after a predefined period of time. Selection of the growth
- 17. medium and duration of the test, as well as maintenance of aseptic conditions during the testing, are critical to successful assessment of microbial contamination by this method. Shelf-life test These tests are frequently carried out after defined periods of storage at predetermined conditions. They help to assign and verify the shelf life and usability of the drug product. Stability testing of capsules Stability testing of capsules is performed to determine the physicochemical stability of the drug substance in the finished drug product under specified package and recommended storage conditions intrinsic stability of the active drug molecule and the influence of environmental factors (e.g., temperature, humidity, light), on formulation components, and the container and closure system. The battery of stress-testing, long-term stability and accelerated stability tests help determine the appropriate storage conditions and the product’s anticipated shelf life.