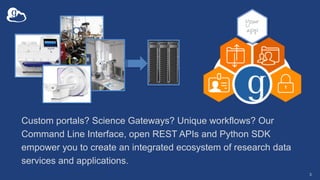
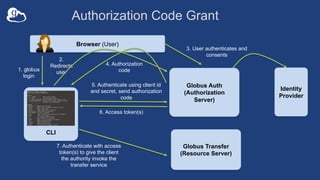
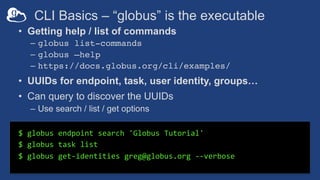
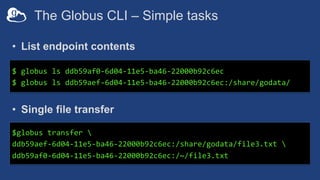
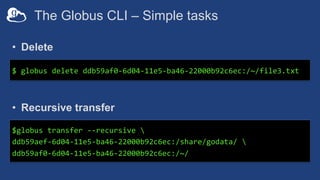
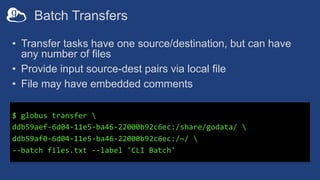
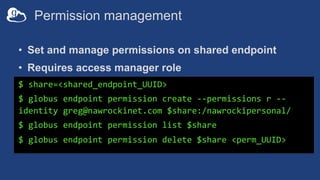
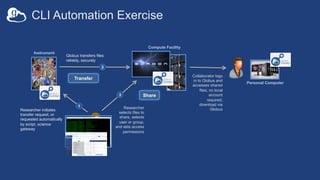
The document provides information about using the Globus Command Line Interface (CLI) to automate data transfers and sharing. It discusses installing the CLI and some basic commands like searching for endpoints, listing files, and doing transfers. It also covers more advanced topics like managing permissions, batch transfers, notifications, and examples of automation scripts that use the CLI to move data between endpoints and share it with other users based on permissions. The final section walks through an example of using a shell script to automate the process of moving data from an instrument to a shared guest collection and setting permissions for another user to access it.







![Parsing CLI output
$ globus endpoint search --filter-scope my-endpoints
$ globus endpoint search --filter-scope my-endpoints --format json
$ globus endpoint search --filter-scope my-endpoints --jmespath
'DATA[].[id, display_name]'
• Default output is text; for JSON output use --format
json
• Extract specific attributes using --jmespath
<expression>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/211013gwtouraps03globuscli-211014032022/85/Globus-Command-Line-Interface-APS-Workshop-14-320.jpg)







![What else could you do?
• Stage data in / out for a compute job
– Create a user specific subdirectory in the “inbound” directory
– Set read / write ACL on that subdirectory
o globus endpoint permission create --permissions rw
– When an inbound file appears, move it to be processed (could be moved with Globus)
– Create a user specific subdirectory in the “outbound” directory, set read ACL on that
subdirectory, move the processed file there for retrieval
o The example we previously ran
– Tear it all down after file is retrieved (or time expires)
o Remove ACL
o Delete files
o Remove subdirectories
• Notification
– Let a user know they have a place to put a file or that there is a file waiting for them for
retrieval
o globus endpoint permission create --notify-email --notify-message
– Need to find the email address for a user identity?
o globus get-identities --jmespath 'identities[0].[email]’ “identity_string_or_UUID" | tr -d '"[]n ‘
• Error Checking! 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/211013gwtouraps03globuscli-211014032022/85/Globus-Command-Line-Interface-APS-Workshop-24-320.jpg)
