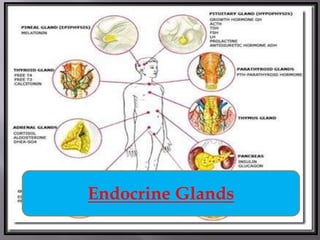
Glands
- 2. INTRODUCTION A gland is an organ in humans & animal's body that synthesizes a substance such as enzymes/hormones for release them into the bloodstream or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface. Types of glands… Exocrine gland ( Duct gland) Endocrine gland ( Ductless gland)
- 3. Differences Exocrine gland Endocrine gland Have ducts Ductless They secretes enzymes They secretes hormones. Hormones convey information via the bloodstream to target cells. They control short term activity They control long term activity Salivary gland, sweat gland Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland
- 4. The endocrine system made up of following glands: Pituitary Gland Structure and Function Pancreas Gland Structure and Function Thyroid Gland Structure and Function Adrenal Gland Structure and Function
- 5. Pituitary Gland The major endocrine gland, pea-sized body attached to the base of the brain that is important in controlling growth and development and the functioning of the other endocrine glands. Shape & Size- Pea shaped, 1cm diameter & about the size of a pea with the weight of 0.5 grams. Location – At the base of the brain in the cranial cavity and it is connected with the hypothalamus in the brain. It consist of two lobes anterior and posterior.
- 6. Cont…..
- 7. HORMONES HORMONES SECRETED BY PITUITARY GLAND The Anterior Lobe 1. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) 2. Growth Hormone (GH) 3. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) 4. Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) 5. Luteinizing Hormone (LH) 6. Prolactin (PRL) The Posterior Lobe 1. Antidiuretic Hormone 2. Oxytocin
- 12. Shape & Colour - Butterfly-shaped with weight of 30-60 grams and Brownish-red in colour. Location - On the front of the neck, below the prominence of thyroid cartilage sometimes called the Adam's apple a long the front of the windpipe. The thyroid has two lobes, connected by a bridge (Isthmus) in the middle. The thyroid secretes several hormones, collectively called thyroid hormones. The main hormone is thyroxine, also called T4.
- 13. It is typically larger in adult males, in whom it is usually clearly visible and palpable. In females, the bump is much less visible and is hardly perceived on the upper edge of the thyroid cartilage. Although both sexes have an Adam's apple, it is considered to be a characteristic feature of adult males, because its size tends to increase considerably during puberty. Its development is considered a secondary sexual characteristic of males that appears as a result of hormonal activity.
- 14. HORMONES The Follicular cells secrete the hormone iodine-containing thyroid hormones Thyroxine (T4) Triidothyronine (T3) Function - These hormones helps in regulating the metabolism of carbohydrate, protein and fats. Growth and development and during infancy and childhood, adequate thyroid hormone is crucial for brain development. Regulate body temperature. The Extrafollicular cells secrete the hormone Calcitonin Function - This hormones helps in regulating the blood calcium and phosphate level.
- 15. Functions It releases hormones that control metabolism—the way your body uses energy. The thyroid gland uses iodine from the foods you eat to make two main hormones. The thyroid's hormones regulate vital body functions, including: Breathing Heart rate Central and peripheral nervous systems Body weight Muscle strength Menstrual cycles
- 16. It is important that T3 and T4 levels are neither too high nor too low. Two glands in the brain—the hypothalamus and the pituitary communicate to maintain T3 and T4 balance. When T3 and T4 levels are low in the blood, the pituitary gland releases more TSH to tell the thyroid gland to produce more thyroid hormones. If T3 and T4 levels are high, the pituitary gland releases less TSH to the thyroid gland to slow production of these hormones.
- 17. STIMULUS: Rising blood Ca2+ level Thyroid gland releases calcitonin. Calcitonin Stimulates Ca2+ deposition in bones Reduces Ca2+ uptake in kidneys Blood Ca2+ level declines to set point Homoeostasis: Blood Ca2+ level (about 10 mg/100 mL) STIMULUS: Falling blood Ca2+ level Blood Ca2+ level rises to set point Stimulates Ca2+ release from bones PTH Parathyroid gland Stimulates Ca2+ uptake in kidneys Active vitamin D Increases Ca2+ uptake in intestines
- 18. Adrenal Gland
- 19. Adrenal Gland The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands. Location- Sit atop the kidneys; in humans. Sape and size- It is pyramidal in structure. The right suprarenal gland is triangular shaped, while the left suprarenal gland is semilunar shaped. Weights about 4 grams.
- 20. Parts Of Adrenal Gland Each adrenal gland has two distinct structures, the adrenal cortex and the medulla, both of which produce hormones. The cortex mainly produces cortisol, aldosterone and androgens. The medulla chiefly produces epinephrine and norepinephrine.
- 21. Functions These hormones control many important functions in the body, such as: 1. Maintaining metabolic processes, such as managing blood sugar levels and regulating inflammation 2. Regulating the balance of salt and water 3. Controlling the "fight or flight" response to stress 4. Maintaining pregnancy. 5. Initiating and controlling sexual maturation during childhood and puberty.
- 22. The Liver
- 23. The largest internal body organ The liver is the body's largest internal organ. Largest organ apart from skin The liver is reddish-brown in colour and feels rubbery to the touch. Weighs about 1.5kg Found in the upper abdominal cavity: extends from right upper quadrant to left upper quadrant of the abdomen. The liver has two large sections, called the right and the left lobes. Attached to diaphragm by falciform and coronary ligaments
- 24. Functions The liver performs multiple critical functions to keep the body pure of toxins and harmful substances.: 1. It produces bile, a substance needed to digest fats. Bile’s salts break up fat into smaller pieces so it can be absorbed more easily in the small intestine. 2. Detoxifies the blood to rid it of harmful substances such as alcohol and drugs 3. Stores some vitamins and iron 4. Stores the sugar glucose 5. Converts stored sugar to functional sugar when the body’s sugar (glucose) levels fall below normal 6. Breaks down haemoglobin as well as insulin and other hormones 7. Converts ammonia to urea, which is vital in metabolism 8. Destroys old red blood cells (called RBC’s)
- 25. Hepatocytes (Hepar=Liver + Cyte=cell) are responsible for making many of the proteins (protein synthesis) in the body that are required for many functions, including blood clotting factors, and albumin, required to maintain fluid within the circulation system. The liver is also responsible for manufacturing cholesterol and triglycerides. Carbohydrates are also produced in the liver and the organ is responsible for turning glucose into glycogen that can be stored both in the liver and in the muscle cells. The liver also makes bile that helps with food digestion. The liver plays an important role in detoxifying the body by converting ammonia, a byproduct of metabolism in the body, into urea that is excreted in the urine by the kidneys. The liver also breaks down medications and drugs.
- 26. The liver is also stores vitamins and chemicals that the body requires as building blocks. These includes: Vitamin B12- It is an especially important vitamin for maintaining healthy nerve cells, and it helps in the production of DNA and RNA, the body's genetic material. Vitamin B12 works closely with vitamin B9, also called folate or folic acid, Folic acid B9- iron required to make red blood cells, Folic acid is also needed to make DNA and other genetic material. Vitamin A for vision, Vitamin D for calcium absorption- It is commonly known as ergocalciferol (Vitamin D2) and cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3). Vitamin D2 and D3 are broken down to their active form, calcitriol, in the body. Vitamin K to help blood to clot properly.
- 27. The Pancreas
- 28. Pancreas Gland The pancreas is an organ located in the abdomen. It plays an essential role in converting the food we eat into fuel for the body's cells. The pancreas has two main functions: an exocrine function that helps in digestion and an endocrine function that regulates blood sugar. Location- The pancreas is located behind the stomach in the upper left abdomen. It is surrounded by other organs including the small intestine, liver, and spleen. Sape and size- It is spongy, about 15-20cm long, 2.5 – 3.8cm broad, 1.2 – 1.8cm thick, Weighs 80g, and is shaped like a fish extended horizontally across the abdomen.
- 29. Parts of Pancreatic Gland the pancreas is divided into the head of pancreas, the neck, body of pancreas, and the tail of pancreas.
- 30. Endocrine function of the pancreas - Between exocrine cells are cluster of cells called the Islets of Langerhans that contain actually 4 types of cells: 1) Alpha cells – produce glucagon (hormone); 25% total cells 2) Beta cells – site of insulin synthesis and secretion; 60% 3) Delta cells –produce somatostatin (inhibits GH);10% 4) PP cells – least common; secretes pancreatic polypeptide;<5%
- 31. Hormones These hormones control many important functions in the body, such as: 1. Insulin- Purpose: Regulate blood glucose (sugar) in the normal range Action: Forces many cells of the body to absorb and use glucose thereby decreasing blood sugar levels Secreted in response to: High blood glucose Secretion inhibited by: Low blood glucose Disease due to deficient action: Diabetes . Disease due to excess action: Hypoglycaemia
- 32. Glucagon Purpose: Assist insulin in regulating blood glucose (sugar) in the normal range Action: Forces many cells of the body to release glucose (increasing blood sugar) Secreted in response to: Low blood glucose Secretion inhibited by: High blood glucose Disease due to deficient action: Some times nothing, sometimes hypoglycemia Disease due to excess action: Hyperglycemia
- 33. Somatostatin Purpose: Regulate the production and excretion of other endocrine tumors Action: Slows down production of insulin, glucagon, gastrin, and other endocrine tumors Secreted in response to: High levels of other endocrine hormones Secretion inhibited by: Low levels of other endocrine hormones
- 34. Gastrin Purpose: Assist in digestion within the stomach Action: Induce acid producing cells of the stomach to produce acid Secreted in response to: Food in the stomach and intestines Secretion inhibited by: Absence of food in stomach and intestines Disease due to deficient action: Poorly defined, some times no symptoms at all Disease due to excess action: Stomach ulcers due to excess stomach acid
- 35. References Difference Between Exocrine and Endocrine | Difference Between http://www.differencebetween.net/sci ence/health/difference-between-exocrine-and- endocrine/#ixzz4uc0lPkT3
- 36. Thank you have a nice day
