Smart Cities
- 1. Smart Cities
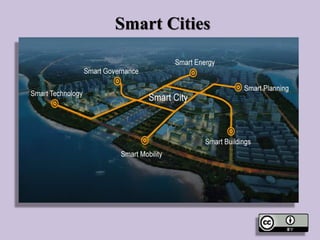
- 2. Smart City • “A developed urban area that creates sustainable economic development and high quality of life by excelling in multiple key areas; economy, mobility, environment, people, living, and government. Excelling in these key areas can be done so through strong human capital, social capital, and/or ICT infrastructure”.
- 3. Smart City
- 4. Smart City
- 5. What is a 'smart city'? • A city equipped with basic infrastructure to give a decent quality of life, a clean and sustainable environment through application of some smart solutions. (Public information, grievance redressal, electronic service delivery, citizens’ engagement, waste to energy & fuel, waste to compost, 100% treatment of waste water, smart meters & management, monitoring water quality, renewable source of energy, efficient energy and green building, smart parking, intelligent traffic management system.)
- 6. What is a 'smart city'?
- 7. What is a 'smart city'? • Smart City: A smart city is one that has digital technology embedded across all city functions. • Smart City Mean of (smarter city) A Smart City equipped with basic infrastructure to give a decent quality of life and clean and livable environment to live smarter.
- 8. 'smart city'
- 9. What is a 'smart city'? • Smarter City uses digital technology and information and communication technologies (ICT) to better quality and performance this engage more effectively and actively with its citizen. The Smart City includes government services, transport, traffic management, energy, health care, water and waste. • The smarter city applications are major goal of improving the management and transforming the urban areas. The major technological, economic and environmental changes have generated interest in smart cities.
- 10. 'smart city'
- 11. Smart City • The concept of smart cities must be seen in the Indian context and without the biases of techno-centrism and one- size-fit-all solutions.
- 12. Smart City • After analyzing the initiatives globally, certain common themes do emerge for formation of smarter cities and communities, namely:
- 13. Smart City • Integration: Energy, transport and information and communication technologies (ICT) seen as parallel and interdependent factors for smartness in urban areas.
- 14. Smart City • Smart Governance: This aspect is the backbone of smart solutions. Smarter governance is enabled through more informed decision making and participation of disparate opinions and agendas towards overall betterment of cities and communities.
- 15. Smart City • Innovation and Technologies: World over, technologies are enabling smarter solutions. Technology innovation is helping better collection, processing and analysis of data through conventional and crowd/social media methods.
- 16. Smart City • Interpreting 'Smart Cities' in the Indian context, following prima-facie impressions emerge:
- 17. Smart City • Energy: Although not within the urban local jurisdiction, energy is very much an urban concern. While fossil fuel fed mechanized transport remains the biggest head in energy consumption in cities. Increasing and inefficient electricity usage is also a cause of concern. Moreover, the fast growing cities of India also consume tremendous amounts of energy through real estate construction and infrastructure expansion activities.
- 18. Smart City
- 19. Smart City • Cities, globally, use more energy than the industrial and rural hinterlands, implying that energy efficiency is not just a regional but also an urban responsibility. Particularly in India we all suffer from scheduled and unscheduled power cuts.
- 20. Smart City
- 21. Smart City • Contributing to peaking of grid loads and fossil fuel needs is our erratic usage pattern where a few hours of use trumps the overall consumption across a day. This impacts the overall urban economy, having direct impacts on the revenues of any city and its potential for growth. • Better energy management can not only help with the national level Jawaharlal Nehru Solar Mission goals on efficiency, but can also contribute towards better management of distribution and as a result more plentiful availability of energy, across the 24 hours, for growth and development.
- 22. Smart City • Traffic and Transport: As discussed above, transport is a major concern from energy and carbon perspectives. Moreover, mobility is the basic need for any urban economy. Time lost due to traffic congestion has a direct impact on the overall efficiency of any city, including that of the businesses and economic activities. Congestion management is also critical for provision of essential and emergency services. Good quality public transport system not only helps curb the use of personal vehicles and the resulting pollution but also has benefits in terms of safety and accessibility.
- 23. Smart City
- 24. Smart City • Internet and Communication Technologies: ICTs help cities connect better to their citizens, enabling better feedback and cross fertilization of ideas. Technological solutions help model and analyze urban issues, incorporating multiple factors and generating solutions that have multiples co-benefits. However, pursuing technologies for the sake of technology introduction is never fruitful. Technology is merely the means towards the desired ends and not the other way round.
- 26. Need of Smart Cities What is a Smart City? • It’s a city outfitted with high-tech communication capabilities. It uses digital technology to enhance performance and well being, to reduce costs and resource consumption, and to engage more effectively and actively with its citizens.
- 27. Need of Smart Cities • The idea of smart city came into formulation owing to the need to accommodate rapid urbanization of the age. Interest in smart cities continues to grow, driven by a range of socioeconomic and technological developments across the globe. It is due to the increasing number of smart cities that established suppliers from energy, transport, buildings, and government sectors are moving into the smart city market, while startups are addressing a range of emerging opportunities in the same field.
- 28. What is the Scope of Smart Cities in India? • India is drawing on the development of smart cities at the global level. Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision ‘Digital India’, has a plan to build 100 smart cities across the country. Modi in his speech said, “Cities in the past were built on riverbanks. They are now built along highways. But in the future, they will be built based on availability of optical fiber networks and next-generation infrastructure.”
- 29. Need of Smart Cities Good infrastructure – The main aim of constructing a smart city is to provide good infrastructure to the residents, such as water and sanitation services, 24*7 electricity supply etc. The information will be collected through the detectors – gas, electricity and other government analytics, which will be carefully complied into small grids and then, will be fed into the computers. This process can focus on making the city efficient. Smart solutions – Smart cities are required as it would also provide smart solutions such as providing public data, electronic service delivery, 100% treatment of water waste, monitoring water quality etc.
- 31. Smart Solutions
- 32. Need of Smart Cities 3. Promotes development – Smart cities enhance the developmental activities of a region. A lot of developmental activities such as building schools, organizations, shopping malls can take place. These activities benefit everybody including citizens, businesses, government and environment. 4. Housing for All – The main aim of a smart city is “housing for all”. More than 70% of the Indian population would be living in cities by 2050. Due to the rising urbanization, a better standard of living is required. To support this rising shift, a sustainable model of housing should be developed. 5. Provides employment – A smart city is an economy of agglomeration. It provides various opportunities and advantages to its residents. India is expanding rapidly and the emergence of smart city can provide employment for many. The construction of a smart city requires a lot of manpower.
- 33. Need of Smart Cities
- 34. Components of Smart Cities
- 35. Components of Smart Cities • SMART CONNECTIONS is about being connected. A smart city is one that meets the needs of its citizens by providing the necessary connections: • Transportation --ensuring adequate access and means of transportation, whether it’s through well planned bus routes, installation of bicycle lanes or the provision and maintenance of bike trails • Online Access – understands the need for mobile technology and access to the internet through Wi-Fi or public computer space and the need to ensure broadband availability for local businesses to compete globally at affordable rates • Technology -- adapts to technology and the need for innovation for tomorrow • Community –ensures inclusion of all citizens by providing opportunities to get involve, become part of the very fabric of the community
- 36. Components of Smart Cities
- 37. Components of Smart Cities • Being connected allows the citizens and businesses to: • Move throughout our community effortlessly; ship and receive goods easily • Research, access information and take online education courses/watch “how to” videos; reach a broader consumer market • Instantly connect with loved ones, friends, customers or business partners • Shop online worldwide; reach new markets • Share files online instantly increasing faster responses to meet customer demands
- 38. Components of Smart Cities • SMART ECONOMY provides high quality high paying jobs while supporting local business to compete globally by: • Promoting innovation • Supporting the very foundation of entrepreneurship and fostering leadership • Providing an environment in which businesses are productive, efficient and can remain competitive • Collaborating and working together to reach success
- 39. SMART ECONOMY
- 40. Components of Smart Cities • SMART PEOPLE are really the foundation of what makes a smart city. Having access to a knowledgeable workforce that: • Meets the needs of employers tomorrow • Has access to information and technology • Embraces creativity and innovation • Explores new ways of doing things • Are supported by community leaders, mentors, services and programs that encourage development and forward thinking
- 41. SMART PEOPLE
- 42. Components of Smart Cities • Creating a knowledgeable workforce means developing partnerships between education, employers and citizens that provides for: • Access to quality, trained employees • Training based on needs of employers • Increased career guidance and employment information • Job shadowing and mentoring opportunities • Access to diverse range of education/training opportunities locally or online
- 43. Components of Smart Cities • SMART GOVERNANCE ensures that what we have as a city we use well and effectively. It’s about planning for and delivering services while maximizing resources whether it is: • Making sure information and services are available and accessible to everyone • Planning and maintaining infrastructure such as roads and bridges or underground systems • Providing safe drinking water and waste management • Ensuring it remains open, transparent • Valuing the input of its citizens and encourages engagement • Embracing technology to provide information to you when and where you want it
- 44. SMART GOVERNANCE
- 45. Components of Smart Cities • SMART ENVIRONMENT is one that is built on providing a balance between planning for growth and protecting resources. A smart city is diligent in: • Protecting our natural environment while planning for the future • Harmonizes living and workspace • Balances energy supply and energy use
- 47. Components of Smart Cities • The City of Brantford enjoys a well-balanced community, one that provides: • Open spaces • Parks and Trail • Balances residential growth with business growth • Recognizes the need to protect our water and local environment • Commitment to redeveloping brownfield sites • Community involvement in creating green spaces
- 48. Components of Smart Cities • SMART LIVING is about providing opportunities for a healthy lifestyle for all citizens including quality healthcare, education and safety.
- 49. Components of Smart Cities • A smart city is one that: • Features environments, services and opportunities for everyone • Recognizes the need for affordable housing • Plans for and supports an aging population • Is culturally vibrant • Supports sports for all ages • Promotes diversity • Recognizes its heritage, its current and past leaders • Reaches out to everyone to ensure inclusion • Is positive and takes pride in its community
- 50. Benefits of Smart Cities • A Smart City is at heart, a city; the reason for a city to exist is to provide a place for people to live, work, and play with others who want to do the same. A Smart City helps people to live, work, and play while requiring fewer resources. • A Smart City is therefore an extension of a sustainable city: creating the most benefit for the most people while minimizing the impacts.
- 51. Benefits of Smart Cities
- 52. Benefits of Smart Cities • In simple terms, a Smart City offers these benefits by making life easier for members of the community. That ease is provided by operating the community’s systems efficiently, including physical systems (such as transport and power) as well as administration (such as applications for assistance).
- 53. Benefits of Smart Cities
- 54. Benefits of Smart Cities • The benefits accrue to the entire community by reducing energy consumption, reducing costs, and simplifying the time and energy an individual needs to expend to live, work, and play. Cost savings are also realized by community services being able to increase the pace by which they adapt to changing condition; the more one department learns how to better serve the community, the faster all departments can learn the same lesson
- 55. Benefits of Smart Cities
- 56. Benefits of Smart Cities • Reducing the cost (in terms of dollars, time, and energy), offers two additional beneficial spinoffs: individuals with more time and money have more time and money to spend on their individual pursuits. More freedom for personal choice of time and money offer an improved quality of life. At the same time, reduced time and money also spur economic growth, with businesses requiring fewer resources to be financially successful. • Smart Cities also offer the members of the community more venues to participate in their community. By providing connections, Smart Cities allow people to provide input on the direction of their community; learn about goods, services, or volunteer activities; and connect to other people with similar interests, all on their own time and in manners that encourage connection. • The primary benefit of Smart Cities, therefore, is to create a more connected community
- 57. Barriers in Development of Smart Cities • Most smart initiatives involve the use of new and disruptive technologies that allow things to be done that weren’t possible before. • As a result, smart technologies require the creation of new markets with new ways of working and new financial and governance models. • These markets also need the right conditions to emerge: a new innovation and entrepreneurial ecosystem where stakeholders interact effectively and where new business models and ways of working can be created so that new technologies can be adapted. Without this ecosystem, the smart technologies industry is unlikely to grow and mature.
- 58. Barriers in Development of Smart Cities
- 59. Barriers in Development of Smart Cities • Constrained demand from cities for smart initiatives. • Recent cuts to budgets are forcing most cities to concentrate on providing statutory services rather than ‘thinking outside the box’ and testing high-risk smart initiatives, even if these might actually save money
- 60. Barriers in Development of Smart Cities • Business models for rolling out smart technologies are still underdeveloped. • Even if money was available for investment, most of the smart technologies are still in their pre-commercial stage of development and the risk-sharing mechanisms and business models needed to take them forward are yet to be tested and developed. • These mechanisms need to be available before smart technologies can be publicly procured, mainly because they represent a higher- risk investment for the cash-strapped public sector. The lack of business models also restricts the availability of private sector financing, since the uncertain financial returns and long payback periods of many smart initiatives makes capital markets and traditional commercial financing rather inaccessible.
- 61. Barriers in Development of Smart Cities
- 62. Barriers in Development of Smart Cities • Cities lack technology-related skills and capacity. • Cities need to understand which technologies are available and how they might benefit their places in order to be effective co-designers, commissioners and clients of smart city projects. This requires specific ICT and technology- related skills and expertise which are often scarce within cities
- 63. Barriers in Development of Smart Cities • Cities find it difficult to work across departments and boundaries. • Many of the smart cities initiatives include integrating different policies and information systems such as linking cycling with carbon reduction or integrating data relating to unemployed individuals from different departments onto a single platform. This requires breaking down silos and joint working between departments and across boundaries. • At present, budgets and strategies are seldom coordinated across departments and data is rarely shared. • For example, funding for roads, rail, and sustainable transport is set separately
- 64. Barriers in Development of Smart Cities • Concerns about data privacy, security and value. • Data needed for initiatives such as open data platforms and the integration of health services is not always accessible. This is mainly due to privacy and security issues or other difficulties such as the lack of technical knowledge to generate or manipulate data. For example, the launch of care. data, a database which integrates data gathered from GPs with hospital medical files was postponed due to concerns over data privacy and possible breaches. • Moreover, the techniques to analyze data, communicate it and use it are yet to be fully developed and its monetary value is yet to be understood. • As a result, councils, businesses and other involved parties do not fully understand the value and benefits that data can generate, which makes the business case for releasing it hard to establish.
- 65. Barriers in Development of Smart Cities • Increasing citizen take up and participation is difficult. Currently, cities and the private sector are finding it difficult to increase citizen participation in the smart agenda beyond the committed few. This is due to some people having limited access to broadband or not having the skills and confidence to use the internet – especially in low income communities and among older people. • With e-services and online consultations becoming more popular, this creates the risk of social and political exclusion among these groups. Moreover, people might not have enough information on how the technology (such as smart meters) can be used or see it as irrelevant to their daily lives. • Issues around what kind of data citizens value, whether they understand the privacy and security implications of sharing their data and how smart technologies can benefit them are yet to be fully explored and understood.
- 66. "Smart cities are those who manage their resources efficiently. Traffic, public services and ... increase performance." - Eduardo Paes
- 67. References • http://www.smartcitieschallenge.in/ • http://smartcitiescouncil.com/ • http://smartcitiesofindia.in/
- 68. Thanks..
