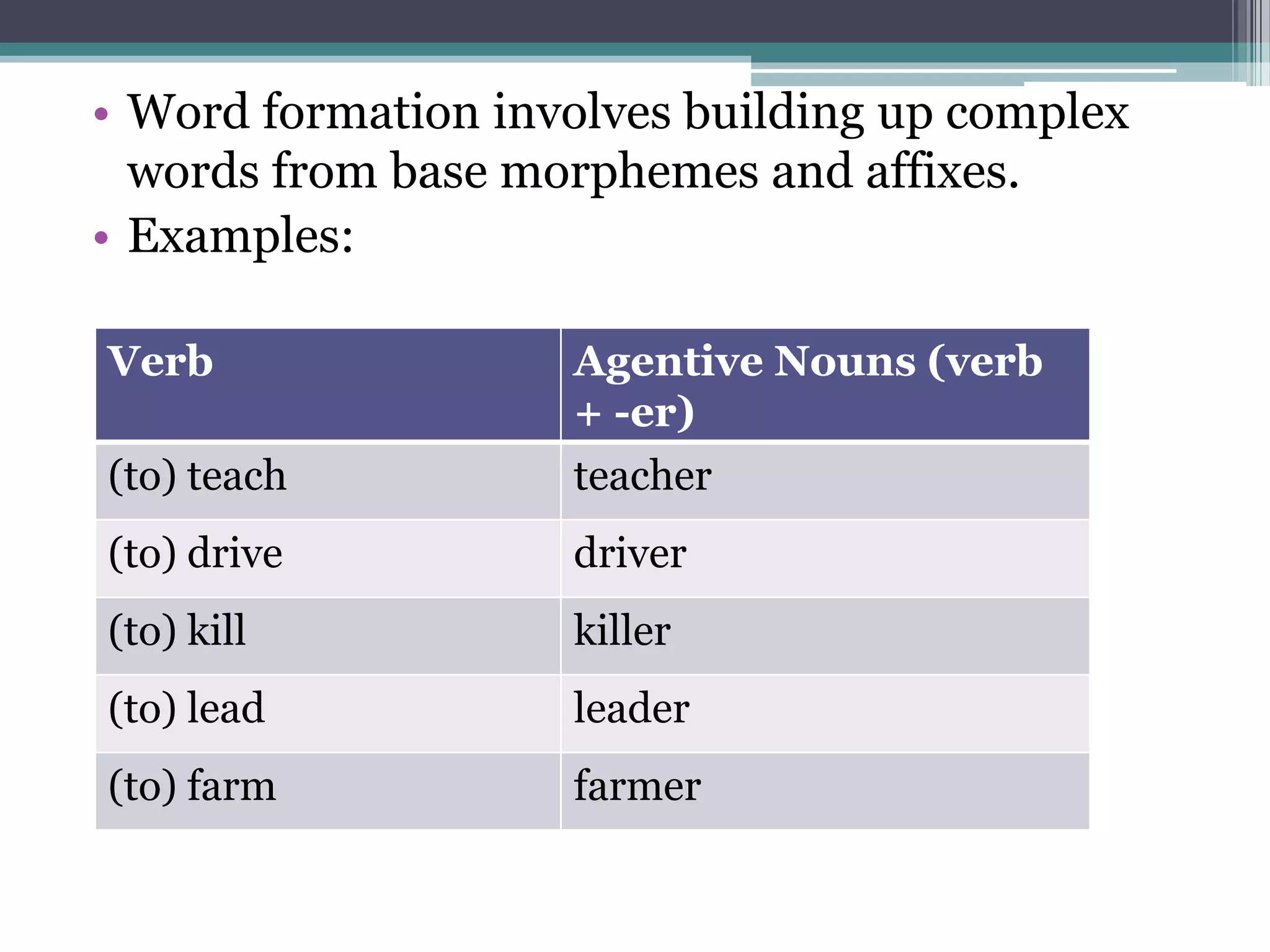
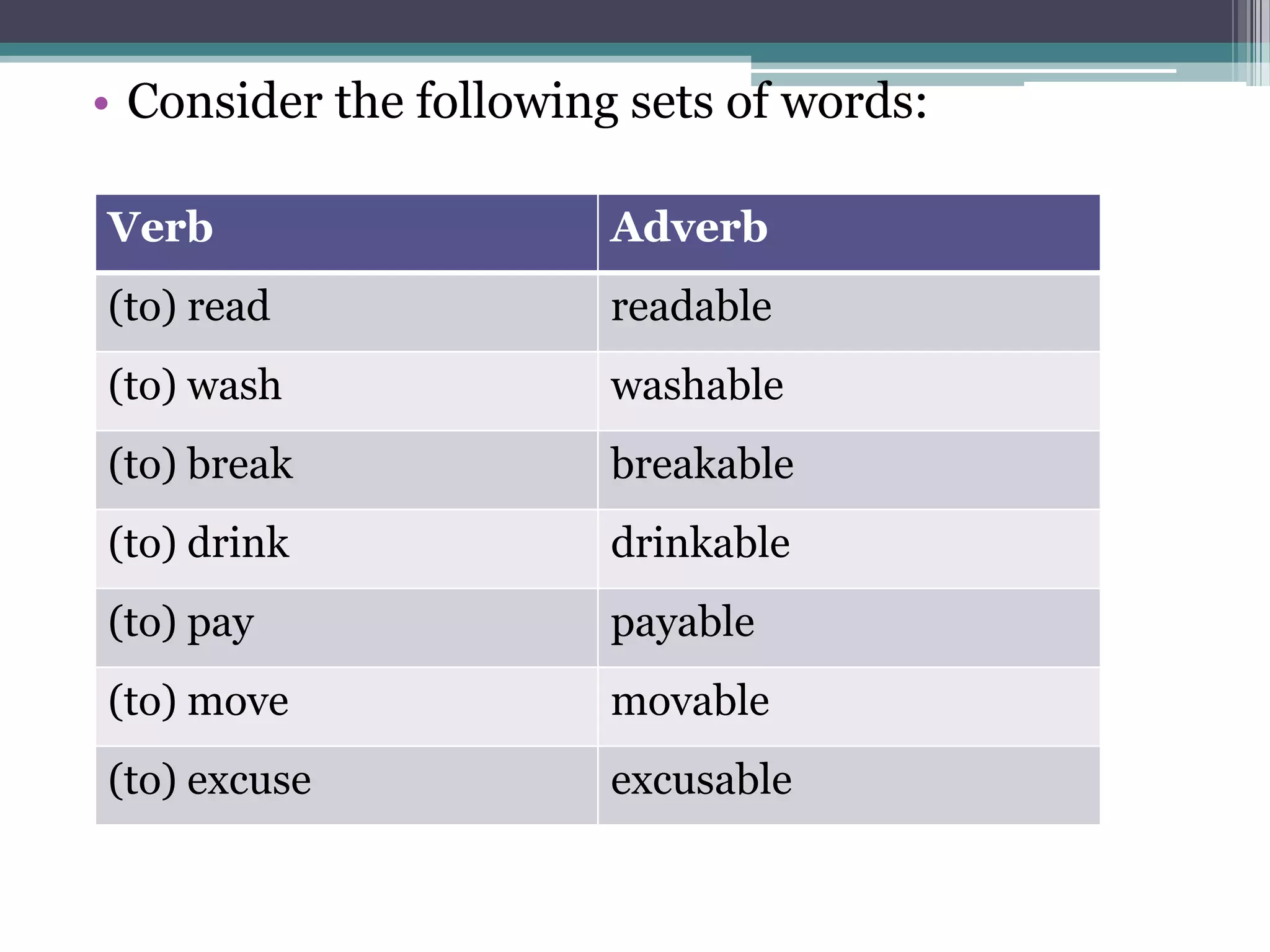
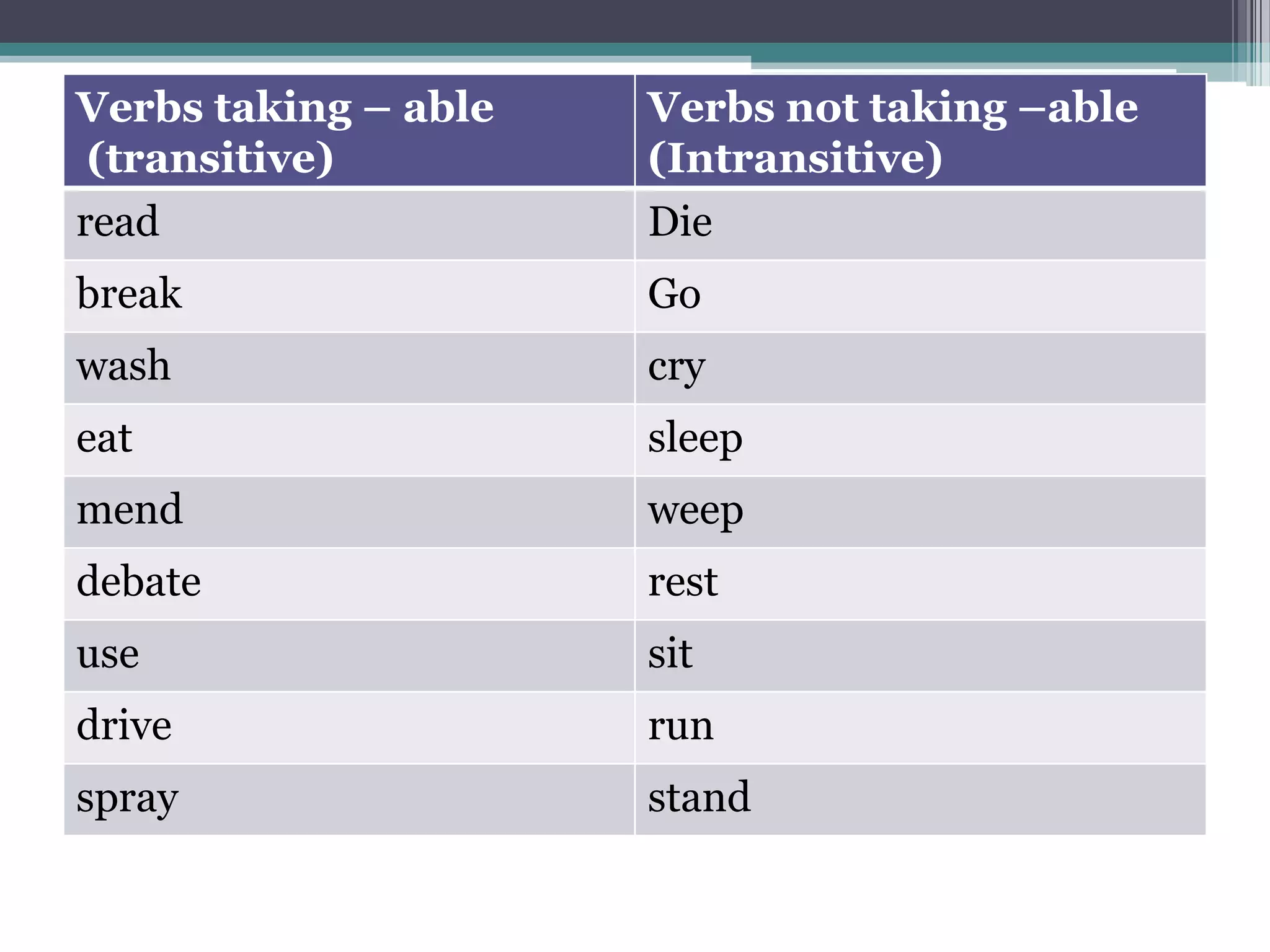
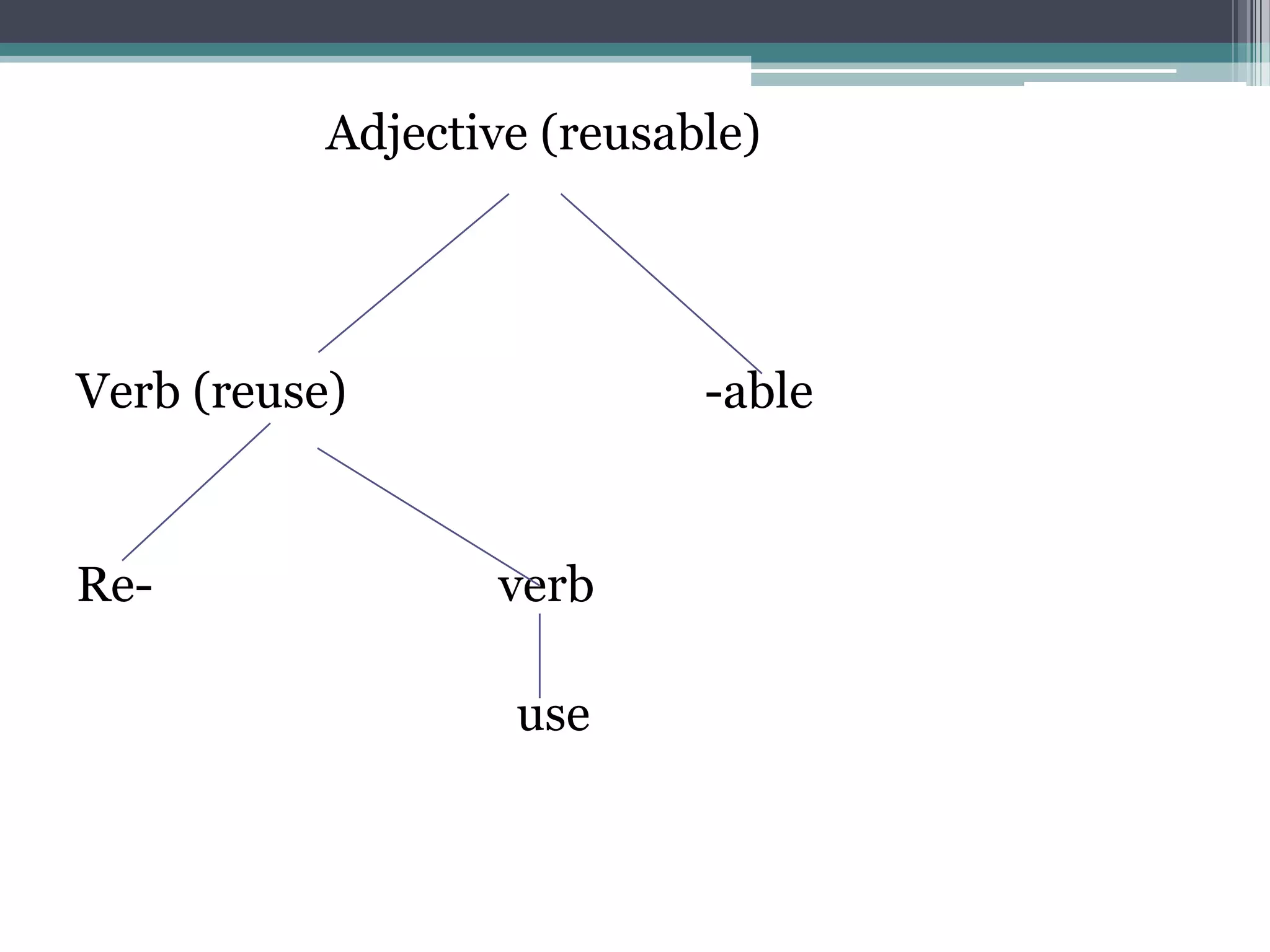
The document discusses word formation through the addition of affixes like suffixes. It provides examples of how verbs can form agentive nouns by adding "-er", and how verbs can form adjectives by adding "-able", following systematic morphological rules. These changes can involve phonological, part-of-speech, and semantic alterations. It notes some verbs can take the "-able" suffix while others cannot, and some nouns can also take "-able".