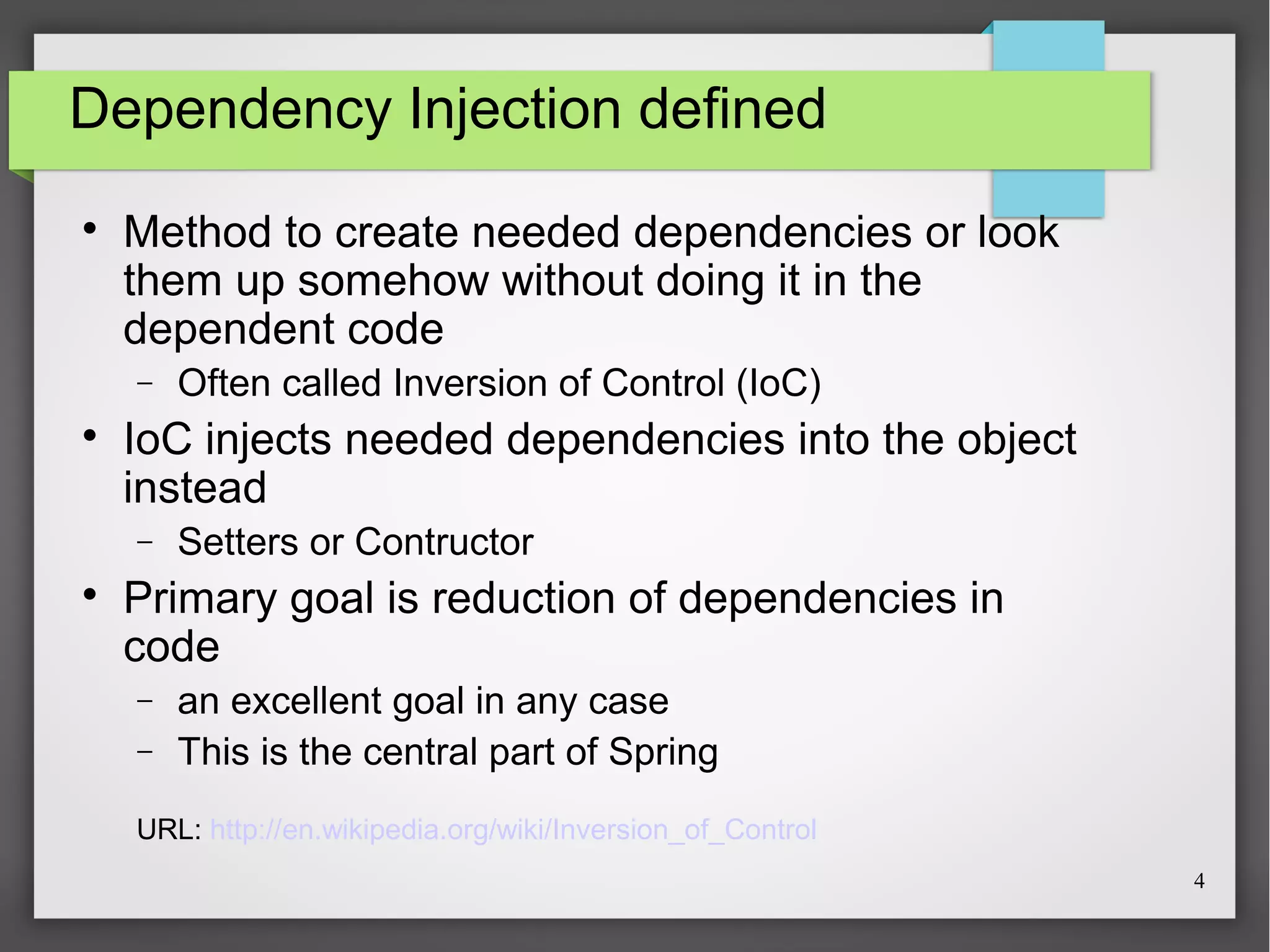
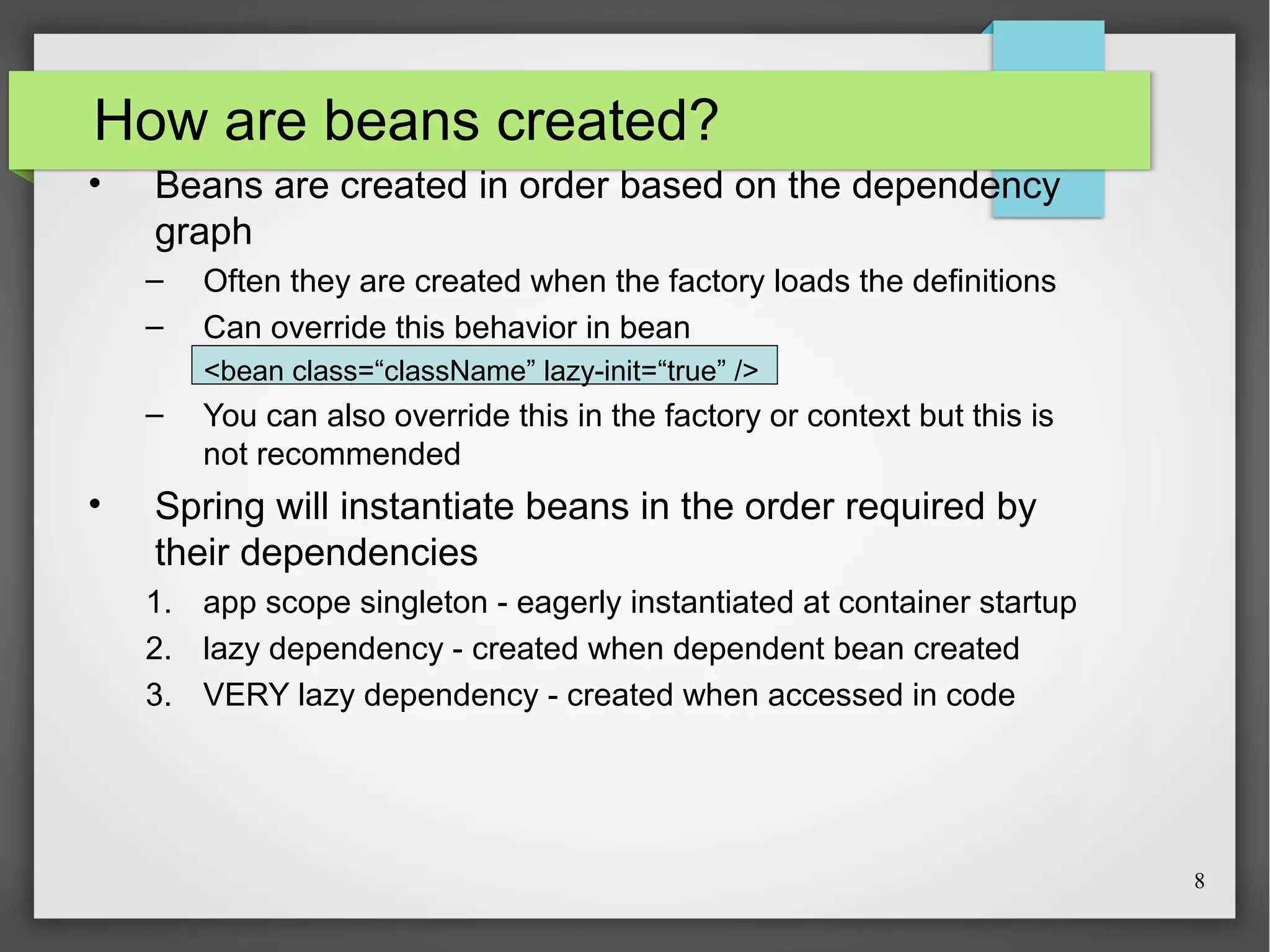
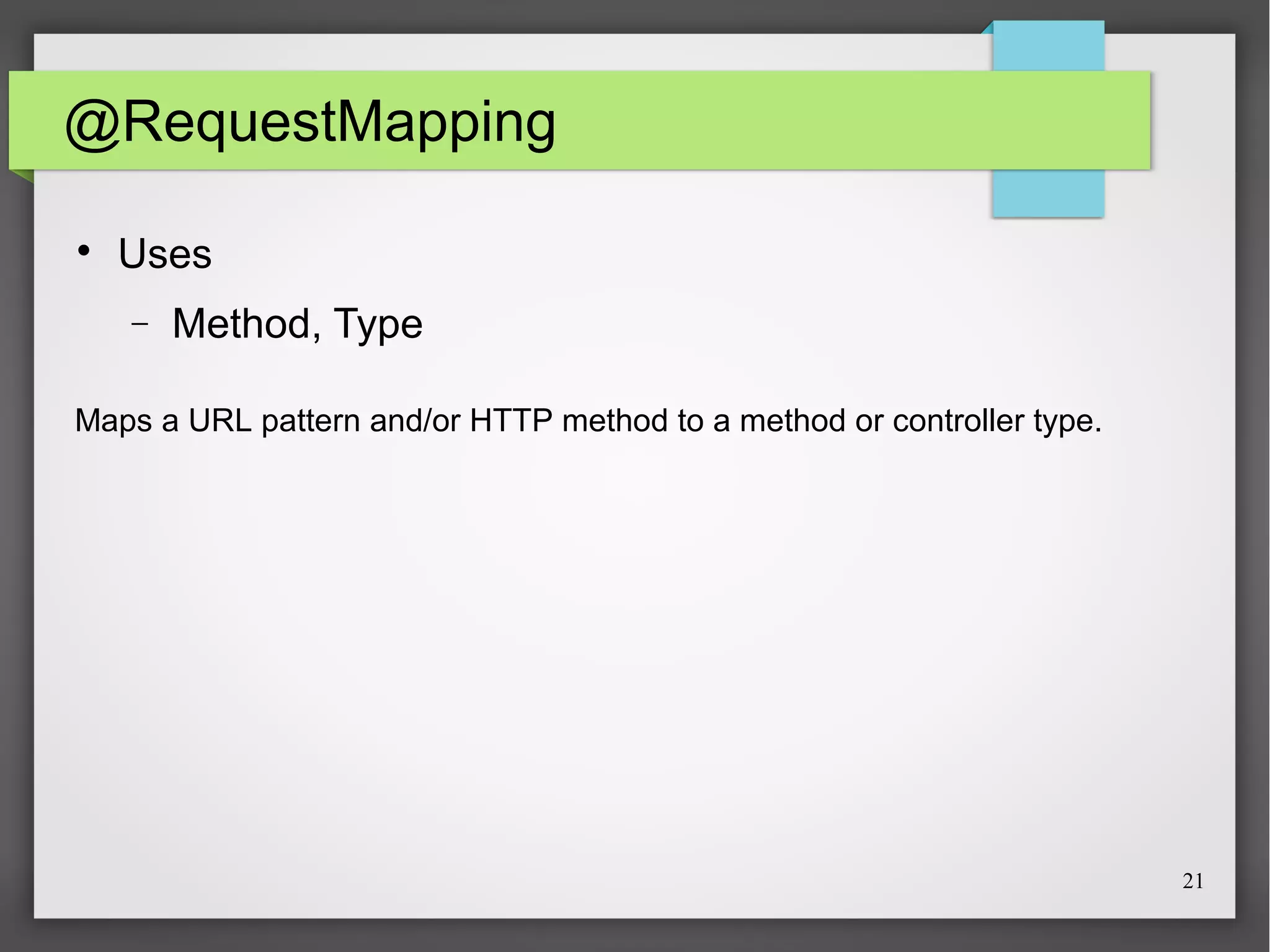
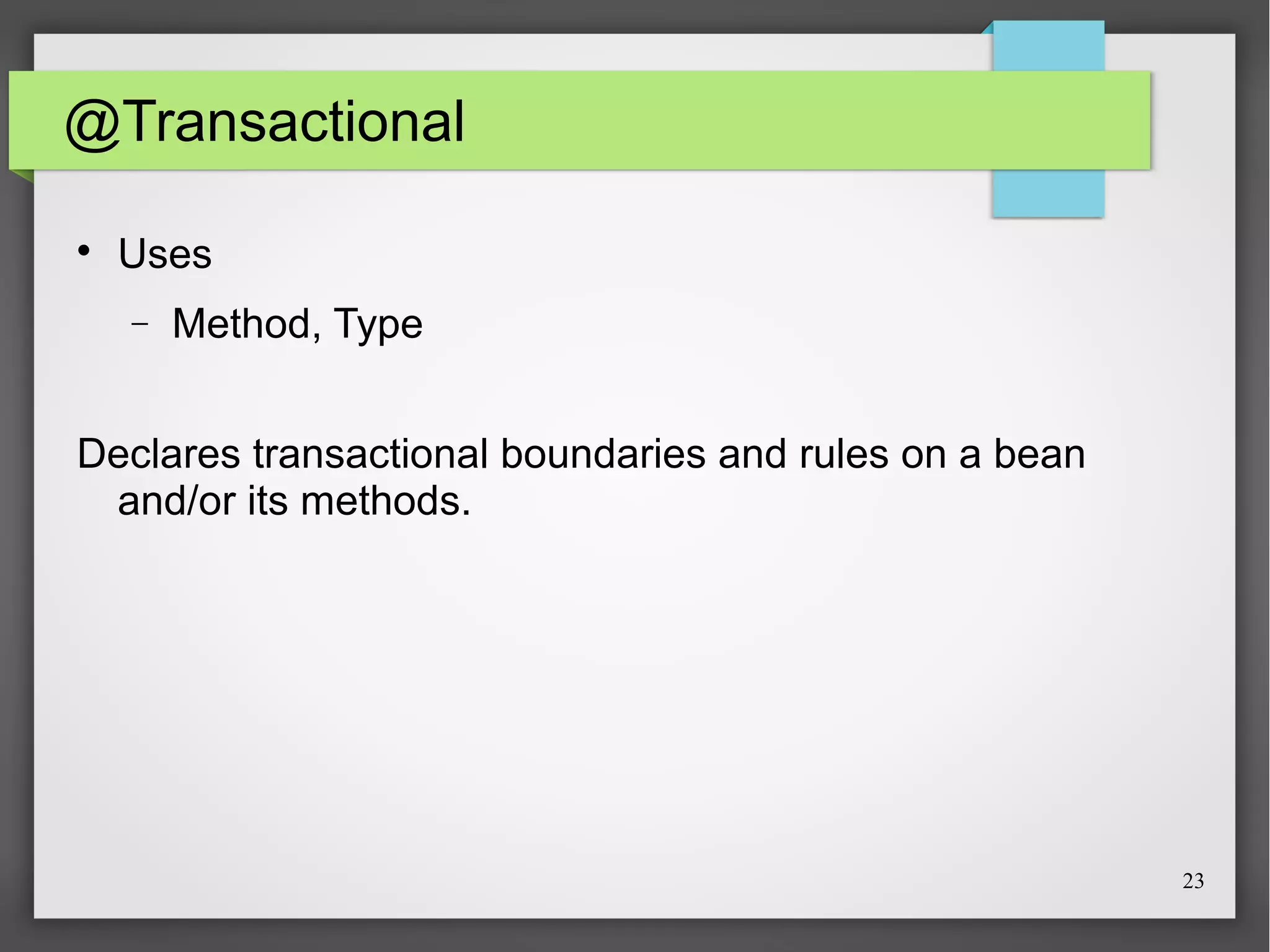
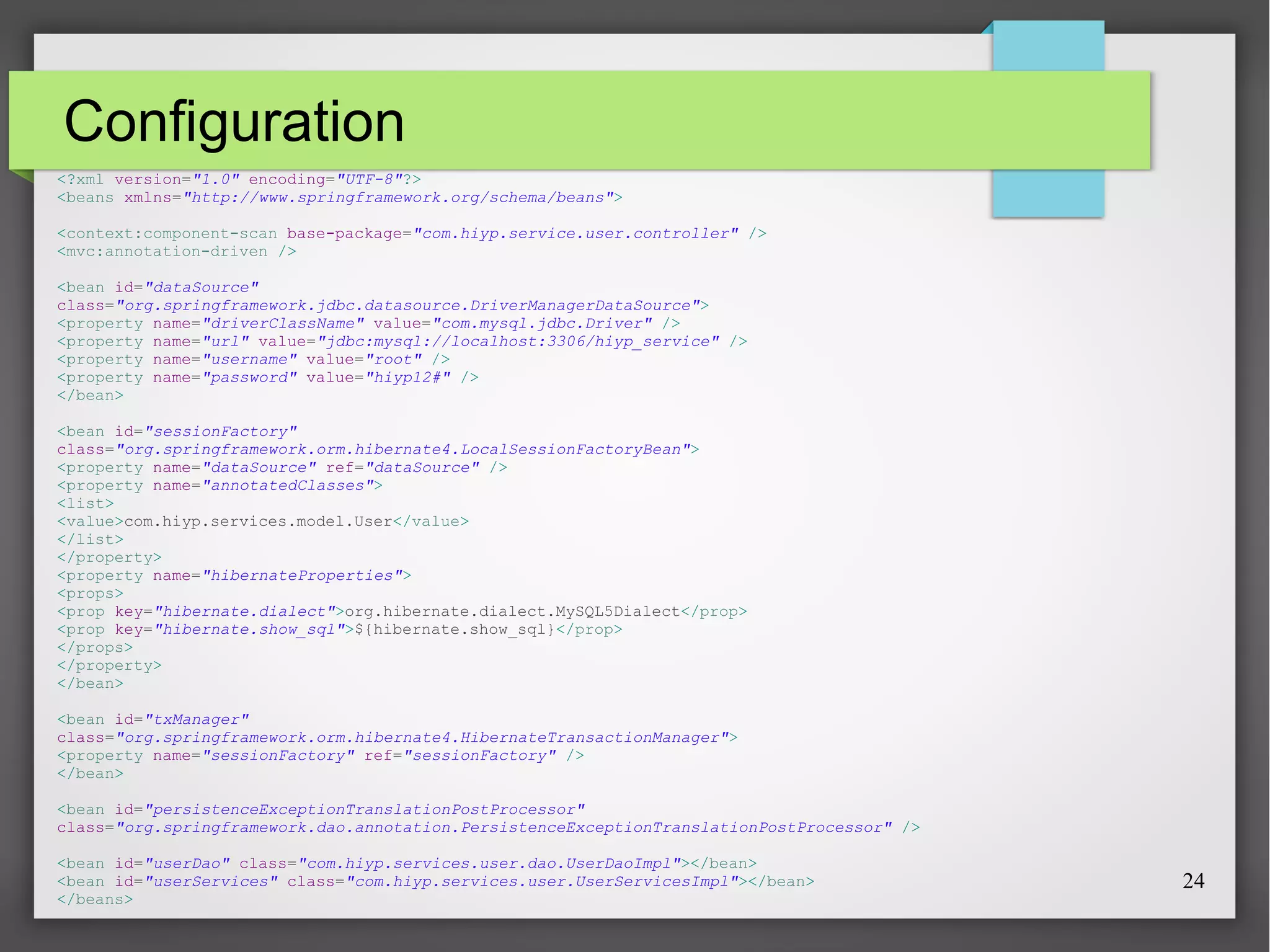
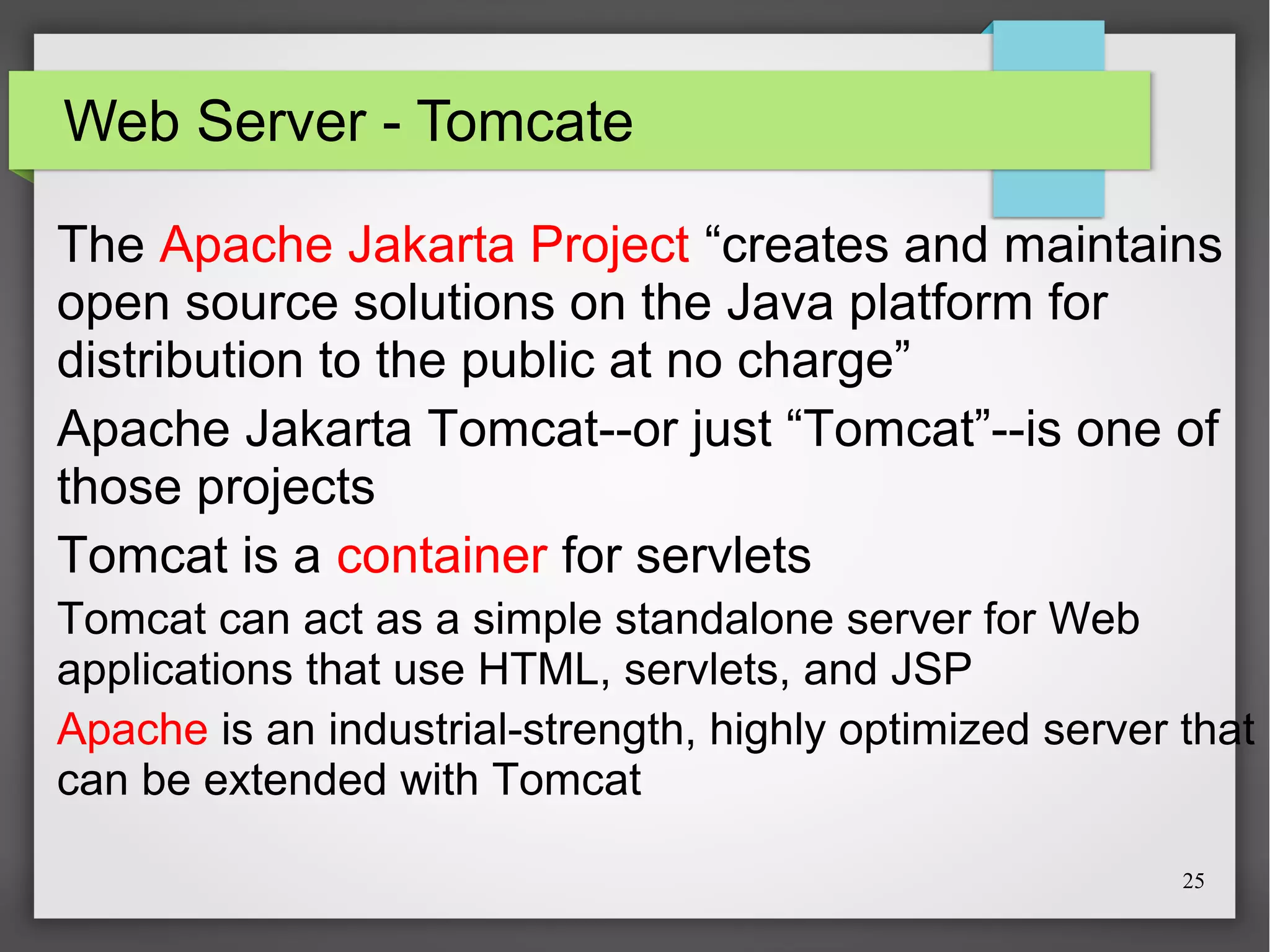
This document discusses Spring, a Java framework for building web applications. It describes key Spring concepts like dependency injection, inversion of control, and beans. It explains how Spring uses dependency injection to reduce coupling between objects. It also covers Spring annotations like @Component, @Controller, and @Repository that can be used to define beans. The document provides an example XML configuration file for configuring a Spring application context. It briefly mentions Tomcat as a web server that can run Spring web applications and the Eclipse IDE for developing Spring applications.



















![thAnks
Question can be sent sandesh.sharma [at]jabong.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springwebservicewebservereclipsebyaintroductionsandeshsharma-150831044433-lva1-app6891/75/Spring-web-service-web-server-eclipse-by-a-introduction-sandesh-sharma-30-2048.jpg)