This document provides an overview of the Spring framework. Key points include:
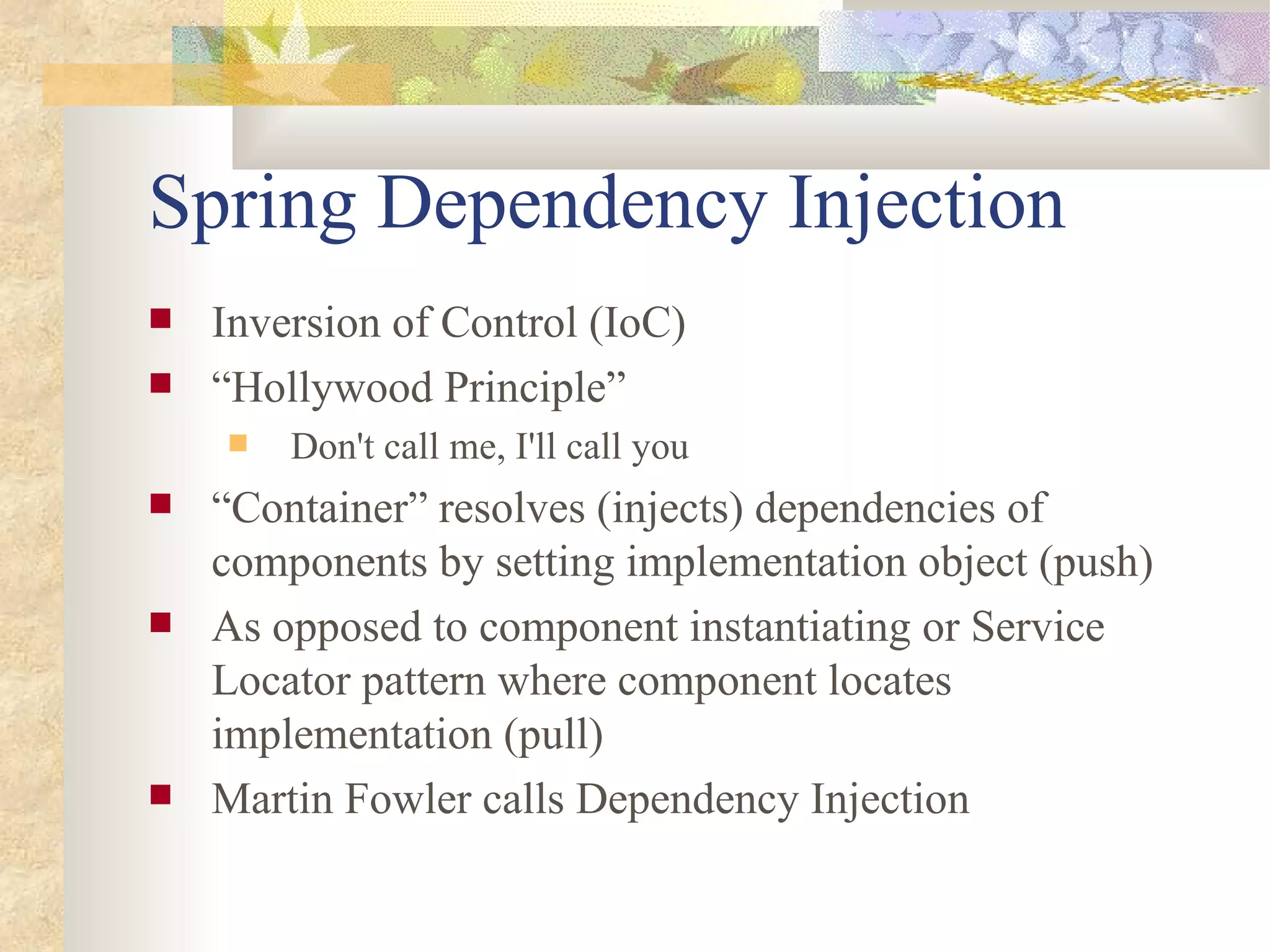
- Spring is a lightweight container that promotes loose coupling and separation of concerns through dependency injection.
- It simplifies programming without J2EE by providing declarative transaction management and abstraction from underlying technologies.
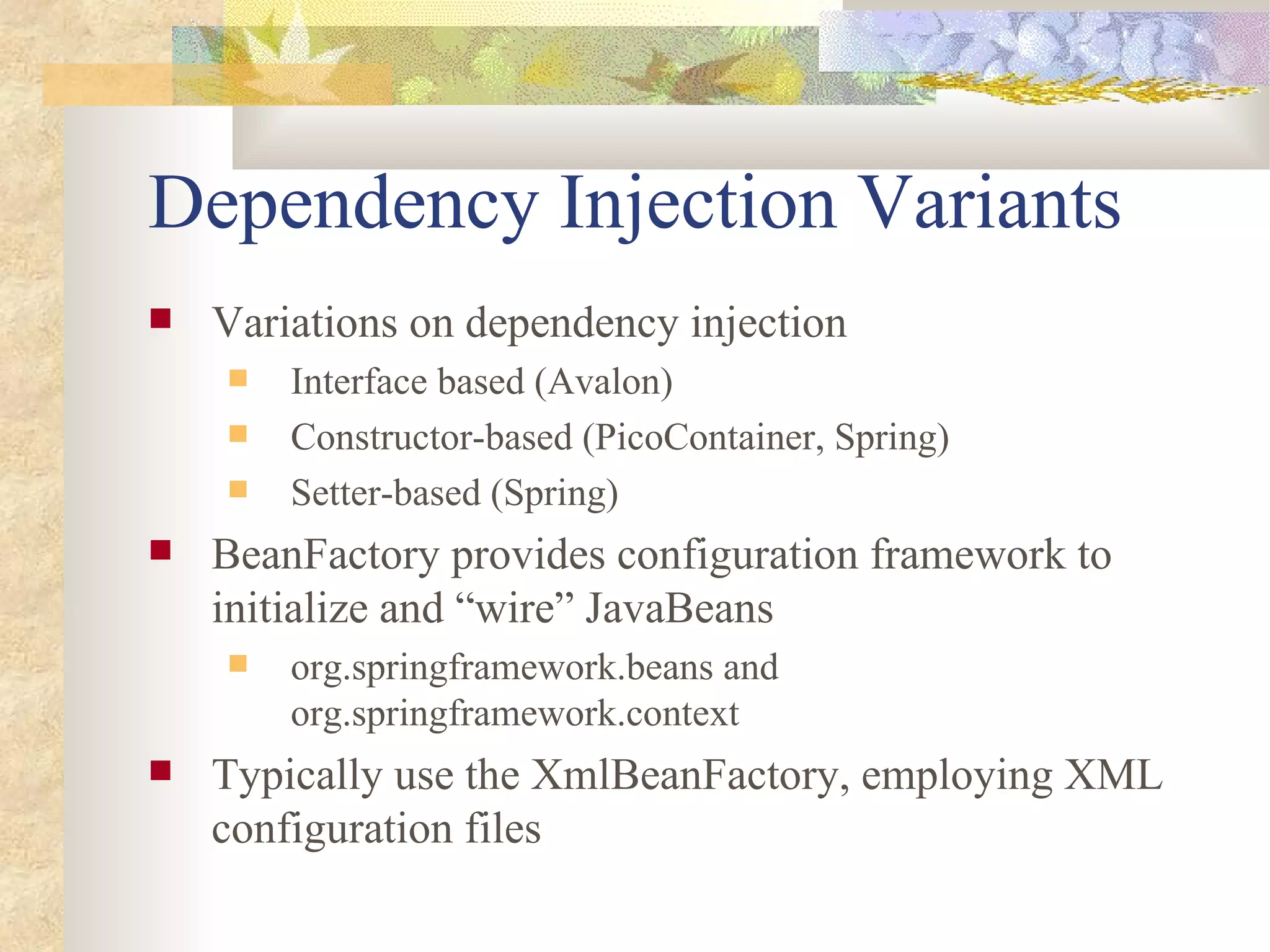
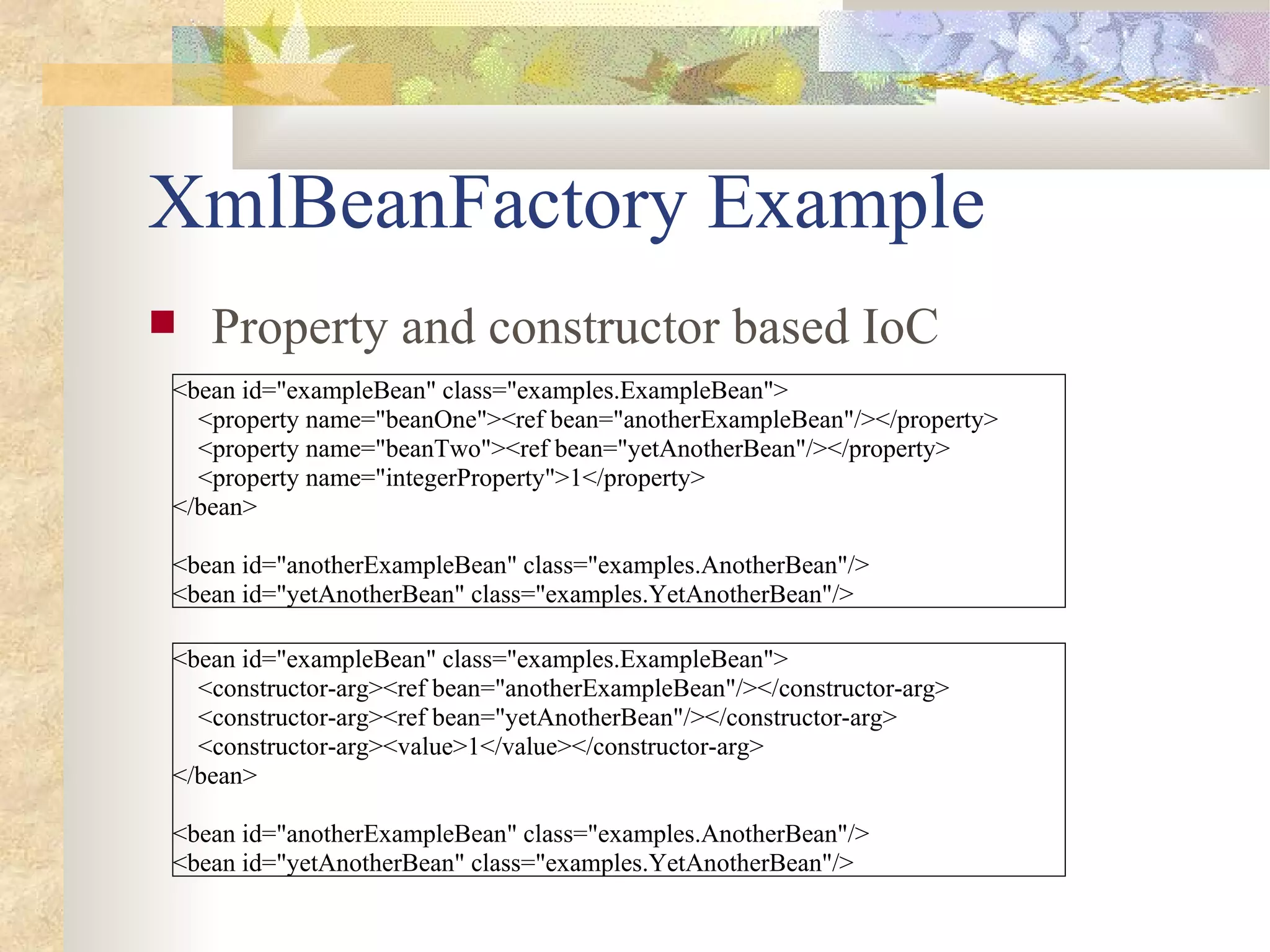
- Spring uses dependency injection and inversion of control to configure and wire together components. It supports setter, constructor, and autowiring of dependencies.
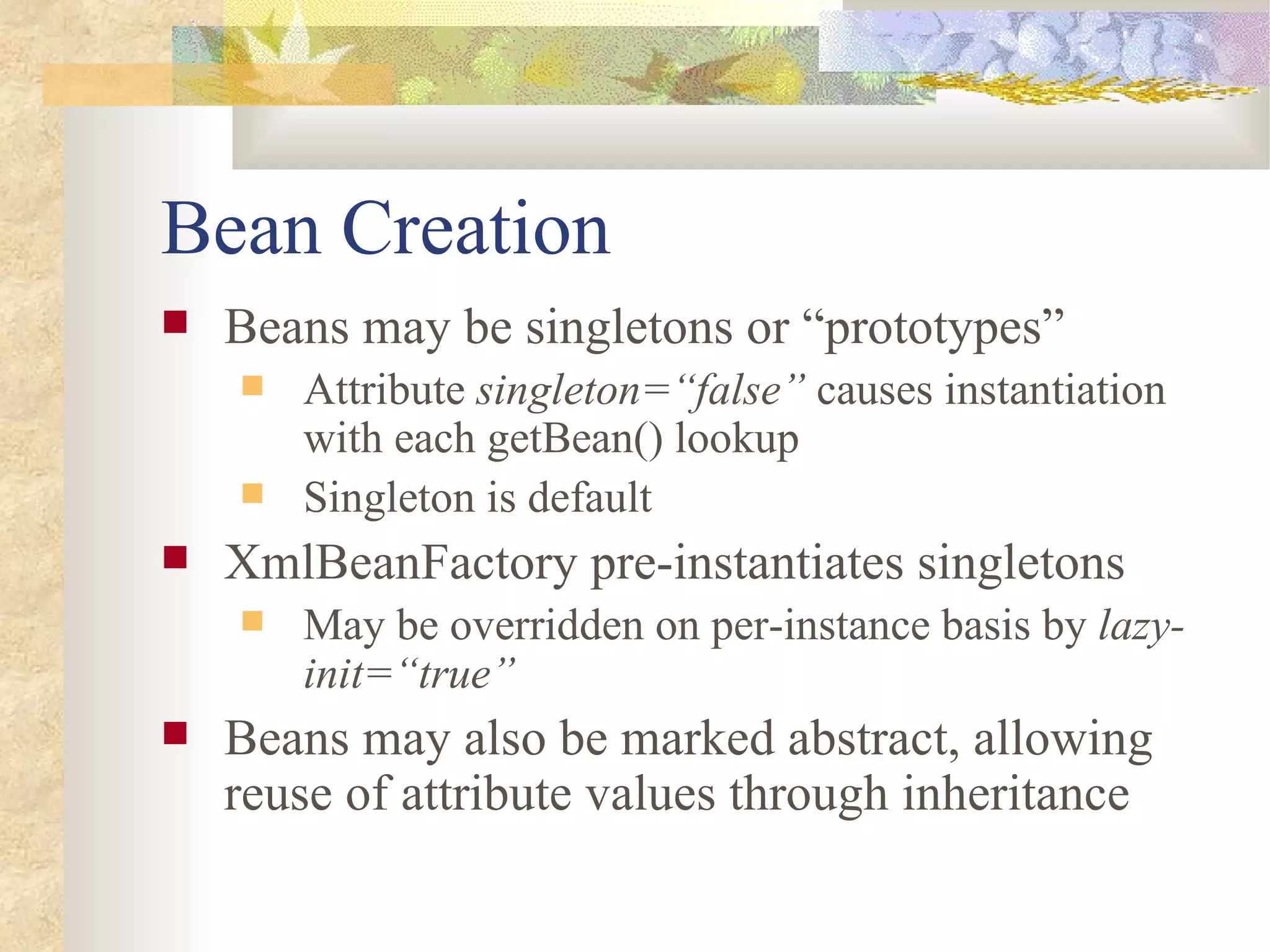
- The Spring container manages the lifecycle of beans through initialization and destruction callbacks.



















![Pointcuts (cont'd)
Pointcut may be statically or dynamically
evaluated based on isRuntime()
Abstract class StaticMethodMatcherPointcut
requires override of 1st method only
public interface MethodMatcher {
boolean matches(Method m, Class targetClass);
boolean isRuntime();
boolean matches(Method m, Class targetClass, Object[] args);
}
Only called if isRuntime() == true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springtalk111204-120325201547-phpapp02/75/Spring-talk111204-28-2048.jpg)

![Spring Advice
MethodBeforeAdvice
void before(Method m, Object[] args, Object target)
Cannot alter return type
ThrowsAdvice
Marker interface
Implementors define methods of form:
afterThrowing([Method], [args], [target], subclassOfThrowable)
AfterReturningAdvice
void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method, m,
Object[] args, Object target)
Cannot modify return value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springtalk111204-120325201547-phpapp02/75/Spring-talk111204-31-2048.jpg)











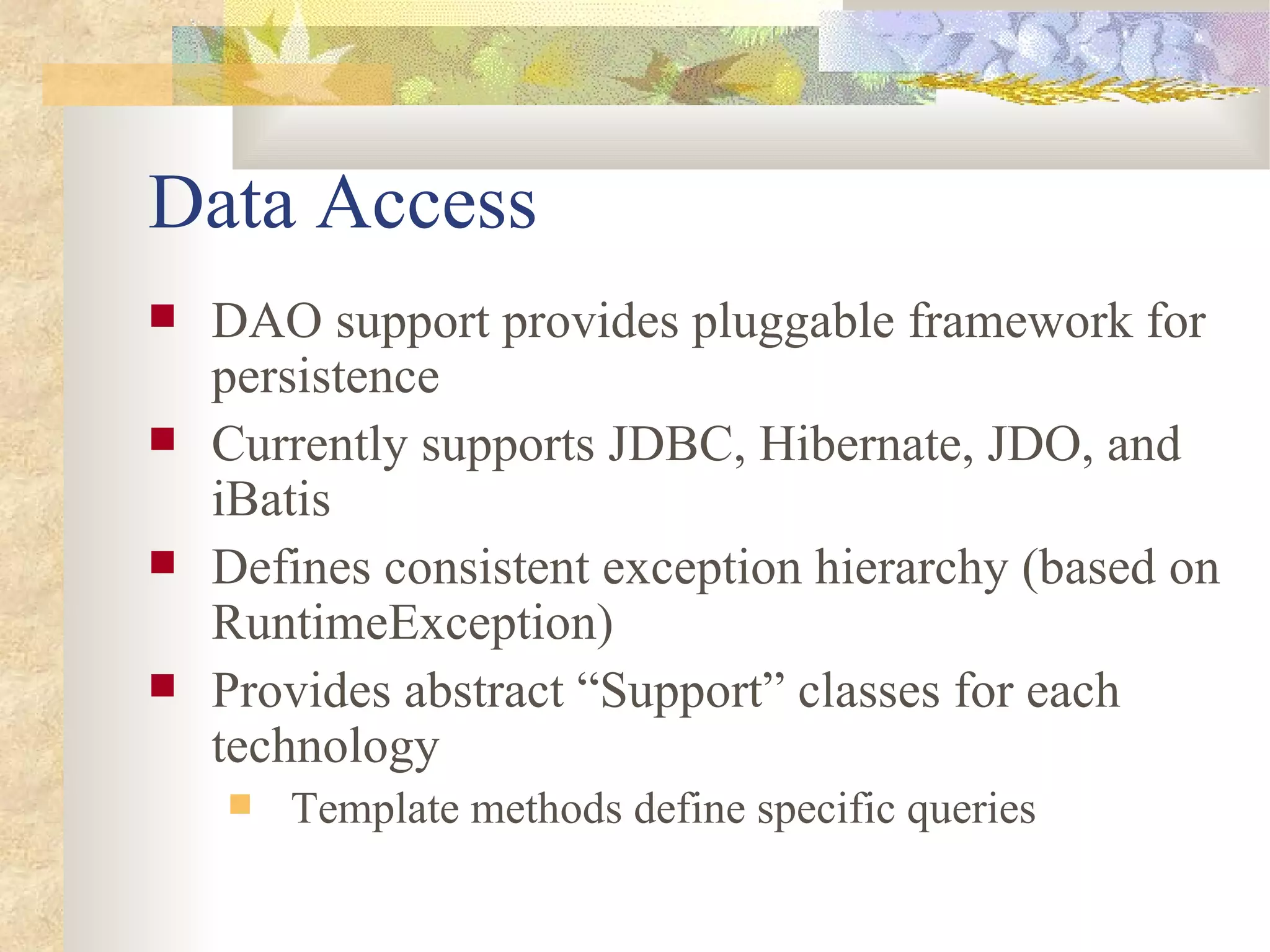

![Hibernate DAO (cont’d)
public Reservation[] findReservations(Room room) {
List list = getHibernateTemplate().find(
"from Reservation reservation “ +
“ where reservation.resource =? “ +
“ order by reservation.start",
instrument);
return (Reservation[]) list.toArray(new Reservation[list.size()]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springtalk111204-120325201547-phpapp02/75/Spring-talk111204-47-2048.jpg)
![Hibernate DAO (cont’d)
public Reservation[] findReservations(final DateRange range) {
final HibernateTemplate template = getHibernateTemplate();
List list = (List) template.execute(new HibernateCallback() {
public Object doInHibernate(Session session) {
Query query = session.createQuery(
"from Reservation r “ +
“ where r.start > :rangeStart and r.start < :rangeEnd “);
query.setDate("rangeStart", range.getStartDate()
query.setDate("rangeEnd", range.getEndDate())
return query.list();
}
});
return (Reservation[]) list.toArray(new Reservation[list.size()]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springtalk111204-120325201547-phpapp02/75/Spring-talk111204-48-2048.jpg)

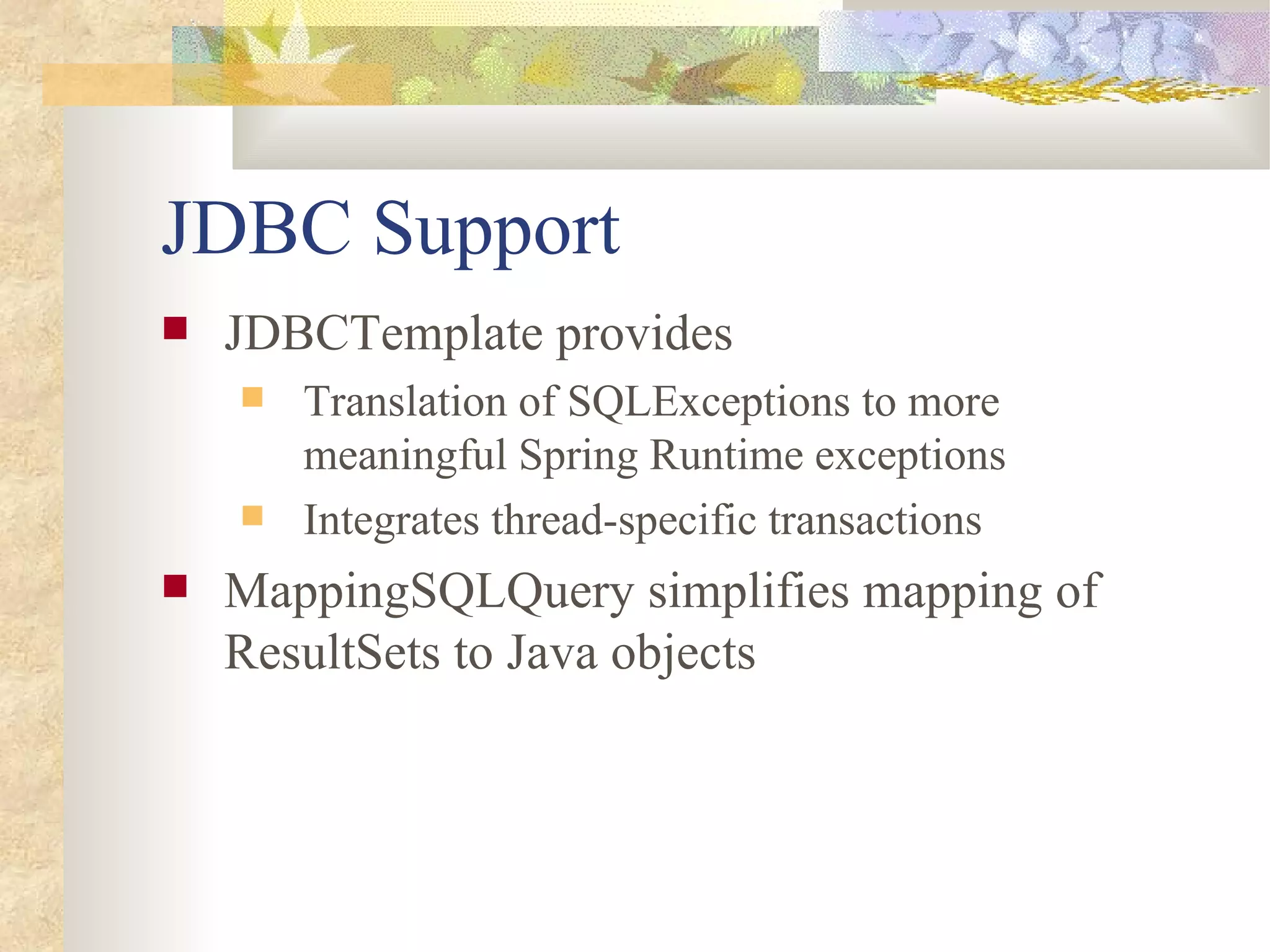

![DispatcherServlet
The DispatcherServlet is the Spring Front
Controller
Initializes WebApplicationContext
Uses /WEB-INF/[servlet-name]-servlet.xml by
default
WebApplicationContext is bound into
ServletContext](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springtalk111204-120325201547-phpapp02/75/Spring-talk111204-52-2048.jpg)